24 Oct 2025
// PRESS RELEASE
25 Jun 2025
// PRESS RELEASE
25 Jun 2025
// PRESS RELEASE
 KEY PRODUCTS
KEY PRODUCTS KEY SERVICES
KEY SERVICES
European CDMO and Gx manufacturer with 75 years of experience in delivering premium APIs to pharmaceutical partners worldwide.
About
Industry Trade Show
The Benjamin Royal Sonesta
23-26 March, 2026
Industry Trade Show
Attending
21-23 April, 2026
Industry Trade Show
Attending
16-18 May, 2026
CONTACT DETAILS




Events
Webinars & Exhibitions
Industry Trade Show
The Benjamin Royal Sonesta
23-26 March, 2026
Industry Trade Show
Attending
21-23 April, 2026
Industry Trade Show
Attending
16-18 May, 2026
https://www.pharmacompass.com/speak-pharma/polpharma-has-invested-over-35mln-euros-in-a-completely-new-facility-to-handle-hpapis
VLOG #PharmaReel
CORPORATE CONTENT #SupplierSpotlight
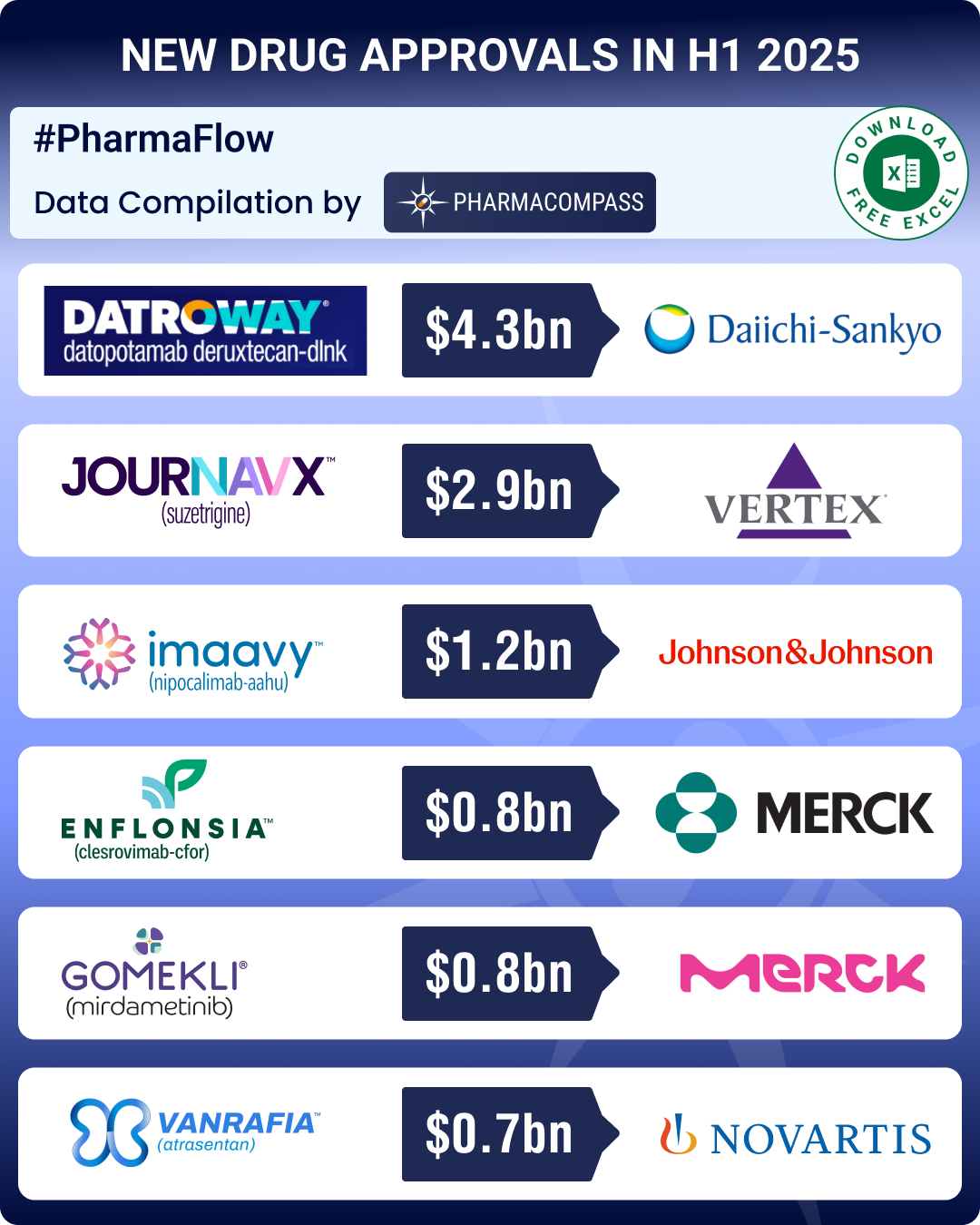
https://www.pharmacompass.com/radio-compass-blog/fda-approvals-drop-24-in-h1-2025-gsk-s-uti-med-vertex-s-non-opioid-painkiller-lead-pack-of-first-in-class-meds
https://www.pharmacompass.com/radio-compass-blog/cdmo-activity-tracker-veranova-carbogen-lead-adc-investments-axplora-polfa-tarchomin-famar-expand-european-footprint
https://www.pharmacompass.com/radio-compass-blog/cdmo-activity-tracker-bora-polpharma-make-acquisitions-evonik-euroapi-porton-announce-technological-expansions
https://www.pharmacompass.com/radio-compass-blog/fda-approves-record-eight-biosimilars-in-h1-2024-okays-first-interchangeable-biosimilars-for-eylea

24 Oct 2025
// PRESS RELEASE
https://polpharma.pl/en/polpharma-group-announces-leadership-transition-sebastian-szymanek-appointed-as-its-new-president/#:~:text=At%20the%20same%20time%2C%20Polpharma,Farmaceutyczne%20Polpharma%20S.A.%20in%20Poland.

25 Jun 2025
// PRESS RELEASE
https://www.api.polpharma.com/articles/rising-to-the-solubility-challenge-collaborative-solutions-in-api-development

25 Jun 2025
// PRESS RELEASE
https://www.api.polpharma.com/articles/rising-to-the-solubility-challenge-collaborative-solutions-in-api-development

14 May 2025
// PRESS RELEASE
https://polpharma.pl/en/polpharma-group-joins-the-call-to-action-to-finalize-pharmaceutical-reform-and-secure-early-and-sustainable-healthcare-for-european-patients/

01 Jan 2025
// PRESS RELEASE
https://www.api.polpharma.com/articles/antibody-drug-conjugates-adcs-revolutionizing-cancer-treatment

10 Oct 2024
// PRESS RELEASE
https://www.api.polpharma.com/articles/an-overview-of-breast-cancer-understanding-risks-treatments-and-market-trends
Services
API Manufacturing
API & Drug Product Development
Inspections and registrations
Country : Poland
City/Region : Sieradz
Audit Date : 2025-10-14
Audit Type : On-Site
Country : Poland
City/Region : Starogard Gdański
Audit Date : 2023-09-19
Audit Type : On-Site
 FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]
FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]ABOUT THIS PAGE
Polpharma is a supplier offers 76 products (APIs, Excipients or Intermediates).
Find a price of Acetazolamide bulk with DMF, CEP, JDMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Alendronate Sodium bulk with DMF, CEP, JDMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Hydrochlorothiazide bulk with DMF, CEP, JDMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Ibandronate Sodium bulk with DMF, CEP, JDMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Lamotrigine bulk with DMF, CEP, JDMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Risedronate Sodium bulk with DMF, CEP, JDMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Sildenafil Citrate bulk with DMF, CEP, JDMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Tadalafil bulk with DMF, CEP, JDMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Vardenafil Hydrochloride bulk with DMF, CEP, JDMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Zoledronic Acid bulk with DMF, CEP, JDMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Baclofen bulk with DMF, JDMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Carbamazepine bulk with DMF, CEP offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Dapagliflozin bulk with DMF, JDMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Etodolac bulk with DMF, JDMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Pentoxifylline bulk with DMF, CEP offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Rivaroxaban bulk with DMF, CEP offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Sodium Salicylate bulk with DMF, JDMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Abemaciclib bulk with DMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Apixaban bulk with DMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Apremilast bulk with DMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Aripiprazole bulk with DMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Baricitinib bulk with DMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Brexpiprazole bulk with DMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Carbamazepine bulk with CEP offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Carvedilol bulk with DMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Carvedilol Phosphate bulk with DMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Dapagliflozin Propanediol Monohydrate bulk with DMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Empagliflozin bulk with DMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Enzalutamide bulk with DMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Ibandronate Sodium bulk with CEP offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Isavuconazonium Sulfate bulk with DMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Lamotrigine bulk with JDMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Molsidomine bulk with CEP offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Palbociclib bulk with DMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Pimavanserin Tartrate bulk with DMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Piracetam bulk with CEP offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Sacubitril-Valsartan bulk with DMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Safinamide Methanesulfonate bulk with DMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Sildenafil Citrate bulk with CEP offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Sitagliptin Hydrochloride bulk with DMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Ticagrelor bulk with DMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Tolterodine Tartrate bulk with CEP offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Topiramate bulk with DMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Trametinib bulk with DMF offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Xylometazoline Hydrochloride bulk with CEP offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Acenocoumarol bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Alendronate Sodium bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Aniracetam bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Antazoline HCl bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Antazoline Mesylate bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Antazoline Sulfate bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Apixaban bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Aripiprazole bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Baclofen bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Carbamazepine bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Carvedilol bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Carvedilol Phosphate bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of CAS 66376-36-1 bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Clemastine bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Clopamide bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Denotivir bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Etodolac bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Hydrochlorothiazide bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Nefopam Hydrochloride bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Opipramol Dihydrochloride bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Pentoxifylline bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Phenyl Salicylate bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Risdiplam bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Risedronate Sodium bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Rivaroxaban bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Salicylamide bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Sulfiram bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Talazoparib bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Ticagrelor bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Topiramate bulk offered by Polpharma
Find a price of Vismodegib bulk offered by Polpharma


 Polpharma
Polpharma