Acquisitions and spin-offs dominated headlines in 2019 and the tone was set very early with Bristol-Myers Squibb acquiring
New Jersey-based cancer drug company Celgene in a US$ 74 billion deal announced on
January 3, 2019. After factoring
in debt, the deal value ballooned to about US$ 95 billion, which according
to data compiled by Refinitiv, made it the largest healthcare deal on
record.
In the summer, AbbVie Inc,
which sells the world’s best-selling drug Humira, announced its acquisition of Allergan Plc, known for Botox and other cosmetic
treatments, for US$ 63 billion. While the companies are still awaiting
regulatory approval for their deal, with US$ 49 billion in combined 2019
revenues, the merged entity would rank amongst the biggest in the industry.
View Our Interactive Dashboard on Top drugs by sales in 2019 (Free Excel Available)
The big five by pharmaceutical sales — Pfizer,
Roche, J&J, Novartis and Merck
Pfizer
continued
to lead companies by pharmaceutical sales by reporting annual 2019 revenues of
US$ 51.8 billion, a decrease of US$ 1.9 billion, or 4 percent, compared to
2018. The decline was primarily attributed to the loss of exclusivity of Lyrica in 2019,
which witnessed its sales drop from US$ 5 billion in 2018 to US$ 3.3 billion in
2019.
In 2018, Pfizer’s then incoming CEO Albert Bourla had mentioned that the company did not see the need for any large-scale M&A activity as Pfizer had “the best pipeline” in its history, which needed the company to focus on deploying its capital to keep its pipeline flowing and execute on its drug launches.
Bourla stayed true to his word and barring the acquisition of Array Biopharma for US$ 11.4 billion and a spin-off to merge Upjohn, Pfizer’s off-patent branded and generic established medicines business with
Mylan, there weren’t any other big ticket deals which were announced.
The
Upjohn-Mylan merged entity will be called Viatris and is expected to have 2020
revenues between US$ 19 and US$ 20 billion
and could outpace Teva to
become the largest generic company in the world, in term of revenues.
Novartis, which had
followed Pfizer with the second largest revenues in the pharmaceutical industry
in 2018, reported its first full year earnings after spinning off its Alcon eye
care devices business division that
had US$ 7.15 billion in 2018 sales.
In 2019,
Novartis slipped two spots in the ranking after reporting total sales of US$
47.4 billion and its CEO Vas Narasimhan continued his deal-making spree by buying New
Jersey-headquartered The Medicines Company (MedCo) for US$ 9.7
billion to acquire a late-stage cholesterol-lowering
therapy named inclisiran.
As Takeda Pharmaceutical Co was
busy in 2019 on working to reduce its debt burden incurred due to its US$ 62
billion purchase of Shire Plc, which was announced in 2018, Novartis also purchased
the eye-disease medicine, Xiidra, from the Japanese drugmaker for US$ 5.3 billion.
Novartis’ management also spent a considerable part of 2019 dealing with data-integrity concerns which emerged from its 2018 buyout of AveXis, the
gene-therapy maker Novartis had acquired for US$ 8.7 billion.
The deal gave Novartis rights to Zolgensma,
a novel treatment intended for children less than two years of age with the
most severe form of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). Priced at US$ 2.1 million,
Zolgensma is currently the world’s most expensive drug.
However,
in a shocking announcement, a month after approving the drug, the US Food and
Drug Administration (FDA) issued a press release on
data accuracy issues as the agency was informed by AveXis that
its personnel had manipulated data which
the FDA used to evaluate product comparability and nonclinical (animal)
pharmacology as part of the biologics license application (BLA), which was
submitted and reviewed by the FDA.
With US$
50.0 billion (CHF 48.5 billion) in annual pharmaceutical sales, Swiss drugmaker
Roche came in at number two position in 2019
as its sales grew 11 percent driven by
its multiple sclerosis medicine Ocrevus, haemophilia drug Hemlibra and cancer medicines Tecentriq and Perjeta.
Roche’s newly introduced medicines generated US$ 5.53 billion (CHF 5.4 billion) in growth, helping offset the impact of the competition from biosimilars for its three best-selling drugs MabThera/Rituxan, Herceptin and Avastin.
In late 2019, after months of increased
antitrust scrutiny, Roche completed
its US$ 5.1 billion acquisition of Spark Therapeutics to strengthen its presence in
gene therapy.
Last year, J&J reported almost flat worldwide sales of US$ 82.1 billion. J&J’s pharmaceutical division generated US$ 42.20 billion and its medical devices and consumer health divisions brought in US$ 25.96 billion and US$ 13.89 billion respectively.
Since J&J’s consumer health division sells analgesics, digestive health along with beauty and oral care products, the US$ 5.43 billion in consumer health sales from over-the-counter drugs and women’s health products was only used in our assessment of J&J’s total pharmaceutical revenues. With combined pharmaceutical sales of US$ 47.63 billion, J&J made it to number three on our list.
While the sales of products like Stelara, Darzalex, Imbruvica, Invega Sustenna drove J&J’s pharmaceutical business to grow by 4 percent over 2018, the firm had to contend with generic competition against key revenue contributors Remicade and Zytiga.
US-headquartered Merck, which is known as
MSD (short for Merck Sharp & Dohme) outside the United States and
Canada, is set to significantly move up the rankings next year fueled by its
cancer drug Keytruda, which witnessed a 55
percent increase in sales to US$ 11.1 billion.
Merck reported total revenues of US$ 41.75 billion and also
announced it will spin off its women’s health drugs,
biosimilar drugs and older products to create a new pharmaceutical
company with US$ 6.5 billion in annual revenues.
The firm had anticipated 2020 sales between US$ 48.8 billion and US$ 50.3 billion however this week it announced that the coronavirus pandemic will reduce 2020 sales by more than $2 billion.
View Our Interactive Dashboard on Top drugs by sales in 2019 (Free Excel Available)
Humira holds on to remain world’s best-selling drug
AbbVie’s acquisition of Allergan comes as the firm faces the expiration of patent protection for Humira, which brought in a staggering US$ 19.2 billion in sales last year for
the company. AbbVie has failed to successfully acquire or develop a major new
product to replace the sales generated by its flagship drug.
In 2019, Humira’s US revenues increased 8.6 percent to US$ 14.86 billion while internationally, due
to biosimilar competition, the sales dropped 31.1 percent to US$ 4.30 billion.
Bristol Myers Squibb’s Eliquis, which is also marketed by Pfizer, maintained its number two position
and posted total sales of US$ 12.1 billion, a 23 percent increase over 2018.
While Bristol Myers Squibb’s immunotherapy treatment Opdivo, sold in partnership with Ono in Japan, saw sales increase from US$ 7.57 billion to US$ 8.0 billion, the growth paled in comparison to the US$ 3.9
billion revenue increase of Opdivo’s key immunotherapy competitor Merck’s Keytruda.
Keytruda took the number three spot in drug sales that
previously belonged to Celgene’s Revlimid, which witnessed a sales decline from US$ 9.69 billion to US$ 9.4 billion.
Cancer treatment Imbruvica, which is marketed
by J&J and AbbVie, witnessed a 30 percent increase in sales. With US$ 8.1
billion in 2019 revenues, it took the number five position.
View Our Interactive Dashboard on Top drugs by sales in 2019 (Free Excel Available)
Vaccines – Covid-19 turns competitors into partners
This year has been dominated by the single biggest health emergency in years — the novel coronavirus (Covid-19) pandemic. As drugs continue to fail to meet expectations, vaccine development has received a lot of attention.
GSK reported the highest vaccine sales of all drugmakers with
total sales of US$ 8.4 billion (GBP 7.16 billion), a significant portion of its
total sales of US$ 41.8 billion (GBP 33.754 billion).
US-based Merck’s vaccine division also reported a significant increase in sales to US$ 8.0 billion and in 2019 received FDA and EU approval to market its Ebola vaccine Ervebo.
This is the first FDA-authorized vaccine against the deadly virus which causes
hemorrhagic fever and spreads from person to person through direct contact with
body fluids.
Pfizer and Sanofi also reported an increase in their vaccine sales to US$ 6.4
billion and US$ 6.2 billion respectively and the Covid-19 pandemic has recently
pushed drugmakers to move faster than ever before and has also converted
competitors into partners.
In a rare move, drug behemoths — Sanofi and GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) —joined hands to develop a vaccine for the novel coronavirus.
The two companies plan to start human trials
in the second half of this year, and if things go right, they will file
for potential approvals by the second half of 2021.
View Our Interactive Dashboard on Top drugs by sales in 2019 (Free Excel Available)
Our view
Covid-19 has brought the world economy to a grinding halt and shifted the global attention to the pharmaceutical industry’s capability to deliver solutions to address this pandemic.
Our compilation shows that vaccines and drugs
for infectious diseases currently form a tiny fraction of the total sales of
pharmaceutical companies and few drugs against infectious diseases rank high on
the sales list.
This could well explain the limited range of
options currently available to fight Covid-19. With the pandemic currently infecting
over 3 million people spread across more than 200 countries, we can safely
conclude that the scenario in 2020 will change substantially. And so should our
compilation of top drugs for the year.
View Our Interactive Dashboard on Top drugs by sales in 2019 (Free Excel Available)
Impressions: 54752
Now that it has been
established that the novel coronavirus is going to globally impact the drug
supply chain, it becomes imperative to analyze the extent of the impact.
Since the outbreak of
the novel coronavirus — COVID-19 — in December, PharmaCompass has been constantly reaching out to
manufacturers around the world to assess the current state of the drug supply
chain. This week, we share our preliminary analysis based on the feedback we
have received from drug manufacturers around the world.
Drug shortages are
for real
Last week, the US
Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced the first human drug shortage
as a result of the coronavirus outbreak. In addition, the FDA announced it was
tracking 20 drugs that could face shortages. Some generic drugmakers are predicting shortages
as early as in June or July, due to the novel coronavirus.
The FDA did not disclose the name of the drug in shortage or the 20 drugs it is tracking, as this is considered ‘confidential commercial information’.
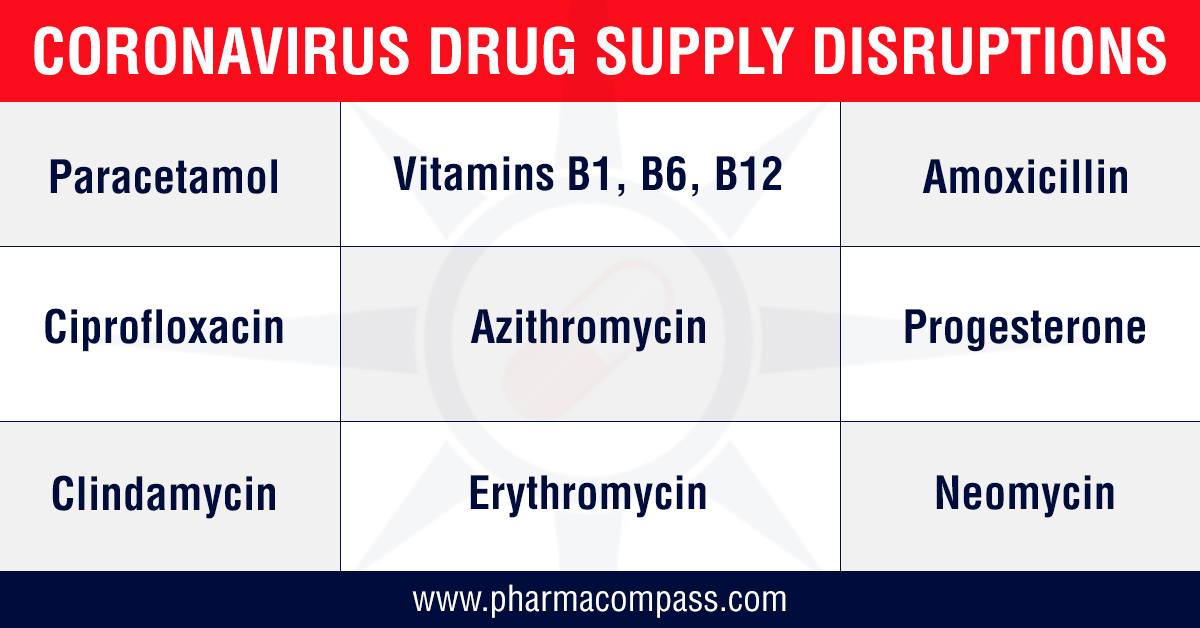
In India, a committee constituted by the country’s Department of Pharmaceuticals started monitoring the availability of 58 active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) to take preventive measures
against illegal hoarding and black-marketing in the country.
According to a report published in The Economic Times, after
reviewing the list of drugs, 34 were found to have no alternatives which
include critical and essential drugs like potassium clavulanate, ceftriaxone sodium sterile, piperacillin tazobactam, meropenem, vancomycin, gentamycin and ciprofloxacin.
This was immediately
followed by the Indian government restricting the exports of 13
APIs along with some of their finished formulations. The list includes paracetamol, tinidazole, metronidazole, acyclovir, vitamin B1, vitamin B6, vitamin B12, progesterone, chloramphenicol and neomycin. For most
of the products on this list, India is a net importer, as there is little
domestic manufacturing of these APIs.
COVID-19 is also
likely to impact bottomlines. Leading generic drugmaker Mylan said it expects the coronavirus outbreak to impact its financial results
while some of the largest drugmakers — including AstraZeneca, Merck and Pfizer — have said that the coronavirus outbreak could affect their supplies or sales.
Paracetamol
affected; prices double in less regulated markets
The decline in industrial activity in China is certainly taking its toll, as drugs which are on the World Health Organization’s Model list of Essential Medicines are beginning to face significant price increases in the wake of disruption of key starting raw materials for bulk drugs.
The export
restriction out of India on commonly used analgesic, Paracetamol — sold under the brand names such as Tylenol (in the US), Panadol (in the UK), Dafalgan (France) and Crocin
(India) — is not surprising as the API has witnessed almost doubling of prices in less regulated markets because exports of its key building block para-amino phenol (PAP) have dramatically reduced from China.
While there are only
a few manufacturers who produce paracetamol without being dependent on Chinese
PAP, a few major manufacturers in India depend almost completely on Chinese PAP
for their paracetamol production and usually only keep three to four months of
inventory.
By the end of
February, their inventory stockpiles had halved and in the event of a continued
supply disruption, their entire inventory pipeline is likely to dry out. In
addition, Chinese paracetamol manufacturers, who export a significant amount of
their bulk ingredient production globally, including to India, are also
currently unable to export. This is beginning to create the potential of panic
among sourcing executives across the world.
Several
antibiotics also in danger of acute shortages
While paracetamol was listed on the API watch list circulated by India’s Department of Pharmaceuticals, our survey has revealed that other products on the list like ciprofloxacin, amoxicillin and azithromycin are also facing severe raw material
shortages. As a result, the prices of these bulk drugs have also increased
sharply.
In a statement to The Economic Times, leading Indian generic manufacturer Mankind Pharma’s chairman and managing director said
amoxicillin is the most commonly used API to manufacture antibiotics and the
company has invested Rs 1 billion (US$ 14 million) in placing irregular orders
with vendors to try and address the potential shortage that is expected. He
went on to say that if the situation continues until April, there will be an
acute shortage.
In a statement to the US House of Representatives last October, Janet Woodcock, the FDA’s Director of Center of Drug Evaluation and Research, said the FDA has determined that there are three WHO Essential Medicines whose API manufacturers are based only in China. The three medicines are: capreomycin, streptomycin (both indicated to treat Mycobacterium
tuberculosis) and sulfadiazine (used to treat chancroid and trachoma).
Streptomycin is also on the watch list published by India’s Department of Pharmaceuticals along with commonly used anti-hypertensives like losartan, valsartan, telmisartan and olmesartan and diabetes treatment metformin.
Intermediates
becoming a problem for generic drugmakers
PharmaCompass’ discussions have also revealed that in many cases while API manufacturing factories in China have returned to work, there are disruptions in the availability of raw materials and/or logistics at sea ports and airports which have led to unavailability of supplies.
While the FDA has a
list of the number of API facilities in China which are in a position to supply
to the United States, Woodcock said in her statement that the FDA “cannot determine with any precision the volume of API that China is actually producing, or the volume of APIs manufactured in China that is entering the US market.”
This visibility
reduces drastically when one has to assess the dependence of each API
manufacturer around the world on China for intermediates. Our discussions have
revealed that it is these intermediates which are becoming a problem for most
API manufacturers, even those based in India.
It was worth
highlighting that a manufacturing process change at an intermediate stage of
commonly used blood pressure medicine valsartan resulted in the recall of
millions of pills as it was found to contain a cancer causing impurity above
acceptable levels. Similarly, in 2008, the adulteration of heparin in China,
which killed 81 people and left 785 severely injured, was an outcome of the
subcontracting of precursor chemicals of Heparin.
Our view
The over-dependence
on China for key starting materials has been the subject of discussion ever
since we launched PharmaCompass. Rosemary Gibson explored this subject
in detail in her book China Rx: Exposing the Risks of America’s Dependence on
China for Medicine.
The restrictions imposed on industrial activity and transportation in China in the first two months of this year has resulted in NASA’s satellite images showing a decline in pollution levels over China.
While China works
towards getting its industrial and transportation engine up and running to 2019
levels, the outbreak has spread to other countries which will further increase
the demand for drugs to fight the virus.
This is a time when
the pharmaceutical industry needs to act responsibly and make decisions which
are in the best interests of patients globally.
Sharing information is one such step — it will allow for drug stockpiles and inventories that exist to be re-distributed to areas which need them most. For, in the event of an urgent need, drugs will become available to those who are most in need.
Impressions: 8184
This week, PharmaCompass
reviews the recently released data on prescription drugs paid for under the
Medicare Part D Prescription Drug Program in the United States in calendar year
2016.
But first, let’s understand what is Medicare.
Medicare is the federal health insurance program in the US. In 2017, it covered 58.4 million people — 49.5 million aged 65 and older, and 8.9 million disabled.
Prescription drug coverage under this
program was started in 2006, and is known as Medicare Part D.
As part of this
coverage, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) contracts insurance
companies and other private companies, known as plan sponsors, that offer
prescription drug plans to their beneficiaries with varying drug coverage and
cost-sharing requirements.
In
2017, the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) had estimated that spending on
Medicare Part D would reach US$ 94 billion, or about 16 percent of all Medicare
expenditures for the year.
Click here to access the compilation of Medicare Part D
Prescriber Summary Report
According
to the CBO, Medicare Part D is the most significant expansion of the Medicare
program since it was created by Congress in 1965.
With
more than 1.48 billion claims from beneficiaries enrolled under the Part D
prescription drug benefit program under its umbrella, our analysis of Medicare
Part D provides valuable insights into how elderly Americans use prescription
drugs.
Top 10 drugs by
cost: The ones that bore the highest cost burden for Medicare
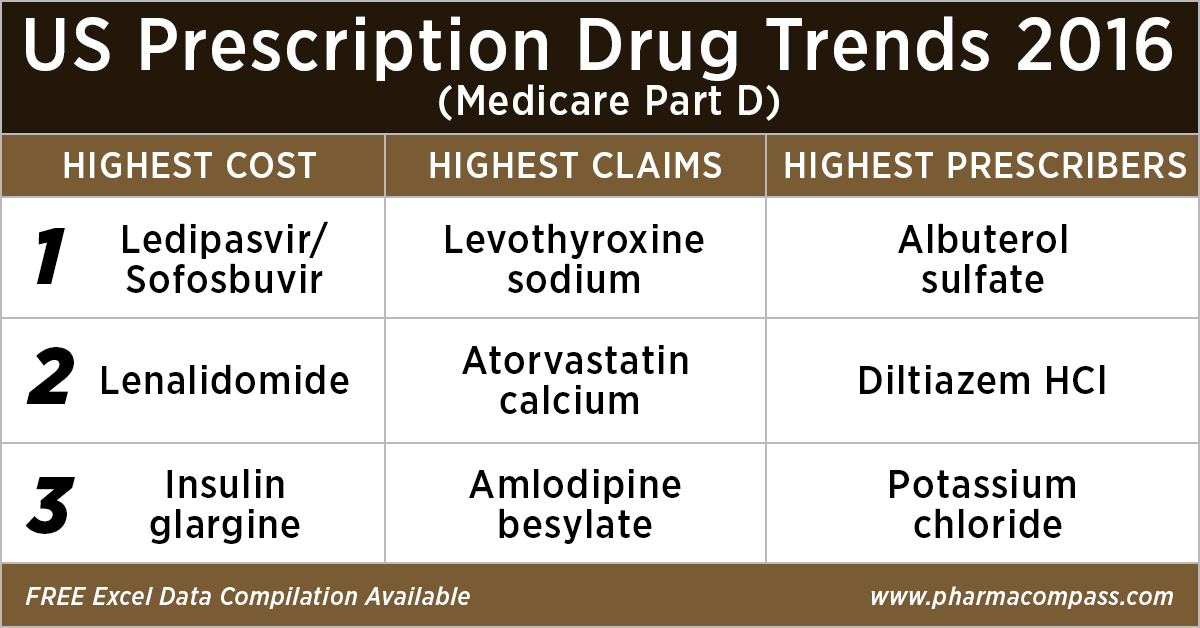
As in 2015, in 2016
too Gilead’s Hepatitis C treatment — Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir (Harvoni) — remained the single drug highest payout under the Medicare Part D Prescription Drug Program with a total cost of US$ 4.4 billion.
As Gilead continued
to face competition from AbbVie and Merck in the Hepatitis C space, the spending on Harvoni was down
37 percent from US$ 7.03 billion in 2015.
Click here to access the compilation of Medicare Part D
Prescriber Summary Report
Celgene’s cancer treatment, Lenalidomide (Revlimid), Sanofi and Merck’s diabetes treatments and AstraZeneca’s Crestor (Rosuvastatin Calcium) for
cholesterol followed Harvoni. All together, they cost the Medicare program over US$ 10 billion.
Generic Name
Number of Medicare Part D Claims
Number of Medicare Beneficiaries
Number of Prescribers
Aggregate Cost Paid for Part D
Claims (In USD)
LEDIPASVIR/ SOFOSBUVIR (HARVONI)
141,665
52,782
12,097
4,398,534,465
LENALIDOMIDE
239,049
35,368
10,382
2,661,106,127
LANTUS SOLOSTAR (INSULIN
GLARGINE, HUM.REC.ANLOG )
5,028,485
1,075,248
245,447
2,526,048,766
SITAGLIPTIN PHOSPHATE
4,742,505
864,442
206,223
2,440,013,513
ROSUVASTATIN CALCIUM
6,012,444
1,560,050
249,981
2,322,724,007
FLUTICASONE/SALMETEROL
5,194,391
1,196,007
275,442
2,319,808,482
PREGABALIN
4,940,115
852,497
267,532
2,098,953,250
RIVAROXABAN
4,403,332
807,820
252,141
1,954,748,890
APIXABAN
4,455,782
826,969
231,631
1,926,107,484
TIOTROPIUM BROMIDE
4,153,162
903,494
235,564
1,818,857,361
Click here to access the compilation of Medicare Part D
Prescriber Summary Report
Top 10 drugs by claims: The most commonly
used drugs of 2016
With 46.6 million claims, the thyroid hormone deficiency treatment — Levothyroxine Sodium — retained its position of being the most claimed product under Medicare’s Part D Prescription Drug Program in 2016.
The number of
Medicare Part D claims includes original prescriptions and refills.
Following Levothyroxine Sodium was the lipid-lowering agent — Atorvastatin Calcium — which had 44.5 million Medicare Part D claims that
were filed by almost 9.4 million beneficiaries.
Generic
Name
Number
of Prescribers
Number
of Medicare Part D Claims
Number
of Medicare Beneficiaries
LEVOTHYROXINE SODIUM
669,999
46,617,109
8,091,785
ATORVASTATIN CALCIUM
494,973
44,595,686
9,435,633
AMLODIPINE BESYLATE
497,017
39,913,468
7,802,905
LISINOPRIL
490,452
39,469,840
8,009,954
OMEPRAZOLE
492,951
32,909,236
7,001,160
METFORMIN HCL
611,700
31,007,932
6,394,014
SIMVASTATIN
380,560
29,687,947
6,201,911
HYDROCODONE/ACETAMINOPHEN
660,617
28,595,150
7,265,882
FUROSEMIDE
488,352
27,878,243
5,421,598
GABAPENTIN
555,997
27,627,466
5,363,382
Click here
to access the compilation of Medicare Part D Prescriber Summary Report
Top 10 drugs by prescribers: Medicines that were most popular with
doctors
Among the prescribers, albuterol sulfate (salbutamol) and Diltiazem had
over 900,000 unique providers (or
doctors) prescribing the drug.
Albuterol (salbutamol) is
used to provide quick relief from wheezing and shortness
of breath while Diltiazem is used to prevent chest
pain (angina).
Also
on the list of popular drugs with prescribers is Hydrocodone-Acetaminophen.
With more doctors prescribing Hydrocodone-Acetaminophen (an
opioid) than commonly used antibiotics, such as Cephalexin, Ciprofloxacin and Amoxicillin, the
series of new FDA initiatives to combat the epidemic of opioid misuse and abuse
should change the position of opioids in the top 10 drugs by prescribers in the
coming years.
Click here to access the compilation of Medicare Part D
Prescriber Summary Report
Generic
Name
Number of
Prescribers
Number of
Medicare Part D Claims
Number of
Medicare Beneficiaries
ALBUTEROL SULFATE
985,427
13,100,354
5,417,718
DILTIAZEM HCL
931,159
8,142,004
1,982,550
POTASSIUM CHLORIDE
879,491
18,945,969
4,278,000
PEN NEEDLE, DIABETIC
677,210
5,281,778
1,795,046
LEVOTHYROXINE SODIUM
669,999
46,617,109
8,091,785
HYDROCODONE/ACETAMINOPHEN
660,617
28,595,150
7,265,882
METFORMIN HCL
611,700
31,007,932
6,394,014
CEPHALEXIN
597,647
5,603,879
3,933,373
CIPROFLOXACIN HCL
594,129
7,000,081
4,851,657
AZITHROMYCIN
591,028
7,958,625
5,734,122
What does the
future hold?
Although the Part D Prescriber PUF (public use file) has a wealth of information on payment and utilization for Medicare Part D prescriptions, the dataset has a number of limitations. Of particular importance is the fact that the data may not be representative of a physician’s entire practice or all of Medicare as it only includes information on beneficiaries enrolled in the Medicare Part D prescription drug program (i.e., approximately two-thirds of all Medicare beneficiaries).
Click here to access the compilation of Medicare Part D
Prescriber Summary Report
Last
month, the Office of the Inspector General (OIG)
reviewed
the Part D claims data for the years 2011 to 2015 for brand-name drugs.
The OIG’s report found that the total reimbursement for all brand-name drugs in Part D increased 77 percent from 2011 to 2015, despite a 17-percent decrease in the number of prescriptions for these drugs.
With soaring drug prices being an issue for
regular debate in the Unites States and President Trump announcing that his
team will use strategies to strengthen the negotiating powers under
Medicare Part D and Part B, it remains to be seen how the data on prescription drugs paid for under
the Medicare Part D Prescription Drug Program will change in the coming years.
Click here to access the compilation of Medicare Part D
Prescriber Summary Report
Impressions: 2500
This week in Phispers, we bring you news on J&J’s Invokana, a drug that reduces heart risk while increasing the risk of amputation of toes. There is news from Google, which is tying up with India’s Aravind Eye Care System for its artificial intelligence eye doctor initiative. And WHO takes a step towards reducing antibiotic resistance by grouping antibiotics into ‘Access’, ‘Watch’ and ‘Reserve’.
Manufacturing errors trigger drug recalls by Lupin and Dr. Reddy’s in the US
Earlier this month,
we carried an article on the end of India’s pharma honeymoon.
News this week from Lupin and Cipla added another dimension to the problem as manufacturing
errors triggered drug recalls in the United States.
Lupin voluntarily recalled a lot of its birth control pills — Mibelas 24 Fe — in the US. A market complaint indicated a packaging error, making the lot number and expiration
date no longer visible. This product is an oral contraceptive for women.
As a result of the
packaging error, the FDA says the first four days of the birth control packet have four
non-hormonal placebo tablets as opposed to the active tablets. This may place
the user at risk for contraceptive failure and unintended pregnancy.
Similarly, Dr. Reddy’s had to recall hundreds of thousands of cartons of a popular acne medicine — Zenatane — manufactured by Cipla’s plant in Pune.
According to FDA enforcement reports, Dr. Reddy’s is recalling 190 lots, consisting of 778,279 cartons of its Zenatane brand isotretinoin capsules, in four dose sizes. The voluntary Class II recall was initiated in late May after the products failed dissolution testing.
During this period of
turmoil, the Indian company which is generating a lot of positive press is Cadila Healthcare.
Cadila’s US
division Zydus Pharmaceuticals’ subsidiary Nesher Pharmaceuticals has received final FDA approval to
market Nystatin Topical Powder, an anti-fungal
antibiotic used to treat skin infections caused by yeast.
There is more good
news from Zydus Cadila. After years of patent battles, the FDA has approved Zydus Cadila’s generic version
of Shire’s ulcerative colitis drug Lialda.
This came as a rude
shock to Shire investors who had believed the US$ 800 million drug was safe for
a few more years. However, there is a chance that instead of a flood of
generics, the Zydus' generic may be the only competition for Lialda for sometime.
Zydus Cadilla has indicated that its version will have a six-month exclusivity.
J&J’s diabetes
drug saves heart at the cost of toes; Sanofi’s insulin slashes hypoglycemia risks for seniors
Would you like to
sacrifice your toes to save yourself from a heart attack? Well, a diabetes drug
made by Johnson & Johnson (J&J), does just that. The drug — Invokana — decreases the risk of heart attacks and strokes, while increasing the risk of amputation,
particularly of toes.
According to the
results of the 10,142-patient study, funded by J&J, for every three heart
attacks, strokes, or cardiovascular deaths prevented by Invokana, there were
two amputations, 71 percent of them of toes or the lower foot.
While this is a setback to J&J, its rivals — Eli Lilly and Boehringer Ingelheim — who make a similar drug called Jardiance, may be cheering the findings of this
study, performed on sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. These
drugs prevent the kidney from absorbing sugar from the blood.
But scientists are not sure why the drugs would prevent cardiovascular disease, and it’s unclear why one of them would lead to amputations. “It justifies the need to test each medicine,” Harlan Krumholz of Yale University said.
Another study
examining an at-risk population of seniors who
had switched to basal insulin found Sanofi’s Toujeo to outdo its peers at cutting the risk of
hypoglycemia in older patients.
During a six-month follow-up, the study found that amongst the ‘at-risk’ seniors, those taking Toujeo were 57 percent less likely to experience hypoglycemia than those who switched to competing insulins—such as Novo Nordisk’s Tresiba and Levemir, and Toujeo’s predecessor, Lantus.
Google ties up
with Indian hospital chain for artificial intelligence eye doctor initiative
Google will soon begin
work on a grand experiment that would use machines to widen access of
healthcare. If successful, this initiative will protect millions of diabetes patients
from an eye disease that leads to blindness.
Last year, researchers at Google had said they had trained image recognition algorithms to detect signs of diabetic retinopathy roughly as accurately as human experts. Left untreated, diabetic retinopathy causes blindness. The software examines photos of a patient’s retina to spot tiny aneurisms that would help detect early stages of the disease.
Google is working
with the Aravind Eye Care System in India, a network of eye hospitals, in order
to integrate this technology.
“This kind of blindness is completely preventable, but because people can’t get screened, half suffer vision loss before they’re detected,” Lily Peng, a product manager with the Google Brain AI research group, said. “One of the promises of this technology is being able to make healthcare more accessible.” There are more than 400 million people worldwide with diabetes, including 70 million in India.
FDA tells Endo to
pull out its opioid pain medication, as Gottlieb attacks addiction
Last week, the US FDA
asked drugmaker Endo Pharmaceuticals to remove its powerful opioid pain medication — Opana ER — from the market, due to “the public health consequences of abuse”.
“We are facing an opioid epidemic — a public health crisis — and we must take all necessary steps to reduce the scope of opioid misuse and abuse,” FDA Commissioner Dr. Scott Gottlieb said. “We will continue to take regulatory steps when we see situations where an opioid product’s risks outweigh its benefits, not only for its intended patient population but also in regard to its potential for misuse and abuse,” he added.
Opioid overdoses killed 33,000
Americans in 2015, with half of those involving a prescription opioid.
Opana ER, which is oxymorphone hydrochloride, is used to manage severe pain. The FDA
approved it for this use in 2006. The drug is about twice as powerful as OxyContin, another often abused opioid.
In 2012, Endo
reformulated the drug to make it more resistant to physical and chemical
tampering. While the drug met the standards for approval, FDA says Endo never
showed that the reformulation would reduce abuse.
Amgen loses bid to delay Novartis’ biosimilar; FDA rejects Coherus’ biosimilar for Neulasta
Amgen lost a case in the Supreme Court of the United States that
sought to delay biosimilars of its rivals. Amgen had argued that its biosimilar rivals
should be forced to delay their 180-day marketing notices until the FDA had
made up its mind on the marketing application.
However, on Monday, the Supreme Court took a decision by determining that the law never imposed a two-tier timing system for these notices. Therefore “the applicant may provide notice either before or after receiving FDA approval.”
This has proven to be
a clear win for Sandoz — the generic unit of Novartis that is fielding an array of copycat biologics. The group is launching a copy of Amgen’s Neupogen. And in the process, Sandoz has
unleashed a fresh wave of biosimilars hitting the US market.
However, Amgen won somewhere else — the FDA rejected Coherus Biosciences’ application for a biosimilar of Amgen’s blockbuster Neulasta (a drug that fights infections in cancer
patients). This action effectively delays any rival until 2018, at the
earliest.
The FDA's response
comes as Amgen gears up for biosimilar competition for Neulasta, which
generated about US$ 4.6 billion in sales last year. The FDA requested Coherus
for a re-analysis of certain data and asked the drug developer for more
manufacturing information.
WHO updates list
of essential medicines; groups antibiotics into three categories
Last week, the World
Health Organization (WHO) released its Essential Medicines List (EML), with a
new advice on which antibiotics to use for common infections and which to
preserve for serious circumstances. Amongst the additions to the WHO Model list of essential medicines
for 2017 are medicines for HIV, hepatitis C, tuberculosis and leukaemia.
The EML is used by
many countries to increase access to medicines. The updated list has added 30
drugs for adults and 25 for children, and specifies new uses for 9
already-listed products. In all, it contains 433 drugs deemed essential to
address the most important public health needs.
This time, WHO has grouped antibiotics into three categories – ACCESS, WATCH and RESERVE – with recommendations on when each category should be used.
Initially, the new
categories apply only to antibiotics used to treat 21 of the most common
general infections. If found useful, it could be broadened in future versions
of the EML to apply to drugs to treat other infections.
Antibiotics in the
ACCESS group must be available at all times as treatments for a wide range of
common infections. It includes drugs like amoxicillin, an antibiotic used to treat infections such as
pneumonia.
The WATCH group
includes antibiotics that are recommended as first- or second-choice treatments
for a small number of infections. For example, the use of ciprofloxacin, used to treat cystitis (a type of
urinary tract infection) and upper respiratory tract infections (such as
bacterial sinusitis and bacterial bronchitis), should be dramatically reduced
to avoid further development of resistance.
The third group, RESERVE, includes antibiotics that should be considered as last resorts, such as colistin and some cephalosporins. These must be used
only in the most severe circumstances when all other alternatives have failed.
Impressions: 3373
This week, Phispers brings you an update on Teva’s continuing woes that include fines, plant closures and layoffs. With Laurus Labs’ Vizag unit clearing the US FDA inspection, we evaluate what Laurus’ expansion plans could mean for Mylan. And then there is some bad news on Pfizer, Amgen and AbbVie. While arthritis patients in Scotland sued Pfizer for its anti-inflammatory painkiller, Amgen suffered a setback over its osteoporosis drug and AbbVie’s Humira lost a patent battle. Read on.
Teva
fined in India; may get foreign CEO; to shut down Hungary plant and layoff 500
Teva’s woes are continuing unabated. On Monday, India’s National Green Tribunal (NGT) slapped a fine of US$ 23,139 (INR 1.5 million) on Teva API India Limited for discharging untreated effluents into the Bagad river. The tribunal found the discharge from the sewage treatment plant of Teva API’s Gajraula-based plant in Uttar Pradesh to be below the permissible
standards.
Last month, the
NGT had ordered closure of 13 industrial units in
Uttar Pradesh, including the Gajraula plant of Teva API.
Globally, the
Israel-based generic giant may get a foreigner as its CEO. During a call with analysts recently, Teva’s chairman Sol Barer said: “We are looking around the world for the best candidate.”
Teva’s CEO Erez Vigodman had stepped down in February this year. The company’s CFO Eyal
Desheh has said he is resigning at the end of June. Teva’s Israeli board members are demanding that an Israeli be appointed CFO
if the CEO is a foreigner.
And then there is
more trouble for Teva in Hungary. Last year, PharmaCompass had reported
on Teva’s newly built sterile manufacturing facility in Godollo, Hungary, the issues highlighted by the
FDA in its warning letter and the product recalls
from this unit. Well, Teva is now
winding
up its sterile injectables plant in Godollo,
and laying off 500 workers
in the next few months.
The plant had halted production last year after the FDA found manufacturing shortcomings. According to a Reuters
report, Teva plans to close down or sell the Godollo plant
by 2018-end. The company says its plans do not affect its other two Hungarian
plants in Debrecen and Sajobabony.
However, Teva isn’t the only one cutting jobs. Novartis announced it will cut 500 traditional production and development roles in Switzerland and another 250 job cuts are planned in the United States. This is part of Novartis’ global restructuring efforts.
As
G20 meets on antibiotic resistance, DSM wins an amoxicillin patent battle in
India
Last week, health ministers of the G20 leading economies met for the first time
and agreed to work together to combat issues such as a growing resistance to
antibiotics. They also agreed on implementing national action plans by the end
of 2018.
According to the member countries, infectious diseases were spreading more quickly than before due to increased globalization. The 20 nations pledged to strengthen health systems and improve their ability to react to pandemics and other health risks. The results of the meeting will provide key inputs for a G20 leaders’ summit in Hamburg in July.
A report last year
found that newly resistant strains of bacteria were responsible for more than
25,000 deaths a year in the 28 member nations in the European Union.
Meanwhile, the
Delhi High Court granted a permanent injunction against Sinopharm Weiqida Pharmaceutical for patent infringement in
India. This was announced by DSM Sinochem
Pharmaceuticals (DSP), a
leading company in the production and commercialization of sustainable,
enzymatic antibiotics, next generation statins and anti-fungals,
This patent, which
is owned by DSP, relates to amoxicillin trihydrate having a low free water content and
processes for the manufacture thereof.
The permanent injunction prevents the manufacture, use, importation, offering for sale and sale of Weiqida’s amoxicillin trihydrate API in India, as well as any drug product that utilizes the API.
Pfizer sued by
70 arthritis patients; study reveals safety risks after drug approvals
The world’s biggest pharma company Pfizer is being sued by 70 arthritis patients in Scotland,
who say they were hit with terrible side effects from Celebrex, an anti-inflammatory painkiller touted
as a wonder drug.
The patients — both men and women in the age group of 60 to 90 years — are collectively seeking US$ 4.54 million (£3.5 million) in damages from the New York-headquartered pharma giant.
They began taking
Celebrex in 2002 to combat the effects of arthritis and muscle and joint
stiffness. However, they went on to suffer health problems, including heart
attacks and strokes.
The Scottish
patients hold good chances of winning the case. A recent study — titled Postmarket Safety Events Among Novel Therapeutics Approved by the US Food and Drug Administration Between 2001 and 2010 — claims that almost a third of drugs cleared
by the American regulator pose safety risks that are identified only after
their approval.
The study, that appeared in The Jama Network
last week, says there is need for ongoing monitoring of new treatments years
after they hit the market.
Among 222 novel therapeutics approved by the FDA from 2001 through 2010, 71 (or 32 percent) were affected by a post-market safety event. Post-market safety events were more frequent among biologics, therapeutics indicated for the treatment of psychiatric disease, those receiving accelerated approval, and those with near–regulatory deadline approval, the study said.
After
Roche and AstraZeneca, Amgen suffers a setback on its osteoporosis drug
Earlier this
month, both Roche and AstraZeneca had faced setbacks in the late-stage
study of their drugs. Roche had
reported its Tecentriq drug failed
to significantly improve overall survival in a late-stage bladder cancer study.
And an experimental biotech drug for severe asthma
from AstraZeneca failed to meet its goal of significantly reducing attacks in a
late-stage study.
As if to continue
the trend, last week Amgen’s top-stage drug prospect aimed at treatment of osteoporosis — romosozumab — faced some serious setbacks.
What initially seemed like happy news — that the late-stage trial comparing romosozumab to Fosamax hit its primary and key secondary endpoints — turned into some serious questions about the future of romosozamub.
The first big setback was a prominent cardio risk imbalance between romosozumab and Fosamax — 2.5 percent for romosozumab and 1.9 percent for Fosamax.
The second big
setback came from the FDA,
which wants to evaluate the new set of head-to-head data before approving
romosozumab. And that means no decision is expected this summer!
Humira loses key patent battle as J&J tries to block Samsung’s Remicade biosimilar
AbbVie’s Humira — the world’s best selling drug which is a treatment for rheumatoid arthritis — received a setback when the US Patent and Trademark Office’s Patent Trial and Appeal Board (PTAB) handed down a verdict in favor of Coherus BioSciences, a biopharma company in the US.
The verdict struck
down AbbVie’s ‘135 methods patent on Humira after an inter partes review. The patent had been labelled as a shield and “one of the cornerstones of the Humira IP estate,” by Barclays analysts.
However, all IPR
decisions are subject to appeal. In a statement, AbbVie said it does plan to
appeal against the verdict.
Meanwhile, a unit
of Johnson & Johnson filed a lawsuit to block the sale of a copy of its rheumatoid arthritis drug Remicade made by South Korea's Samsung Bioepis in the US. Remicade is J&J’s biggest selling drug, with US sales of about US$ 5 billion a year.
Through the law suit, the J&J company — Janssen Biotech Inc — has sought a preliminary or permanent injunction to block Samsung Bioepis' biosimilar of Remicade, from sale in the US.
Frontida BioPharm gets FDA’s ‘all clear’ for Philadelphia plant bought from Sun
In June last year,
Frontida BioPharm had bought Sun Pharmaceuticals’ finished pharmaceutical plant in
Philadelphia. And barely eight months back, it received an FDA warning letter
for this plant, based on an inspection that took place in 2015.
The warning letter had mentioned that Sun Pharma’s quality unit at the time had knowingly released 27 lots of
various strengths of clonidine HCl tablets, despite evidence that the API
used in manufacturing was potentially contaminated.
The warning letter
had been issued in August 2016, and Frontida knew about the regulatory issues
when it acquired the facilities last year from Sun Pharma, India’s largest drugmaker.
The good news is
that Frontida BioPharm says
the US FDA has given the plant an all-clear. Frontida says Sun helped it address these issues.
With the
regulatory issues behind it, Frontida can now move forward with its expansion
plans.
“The positive resolution of our regulatory status with the FDA will stimulate Frontida’s expansion and growth, and enable Frontida to better support our partners to bring new products to the market,” Frontida CEO Song Li said in a statement.
FDA
warns drug makers to check water systems for BCC contamination
The US FDA has warned manufacturers of non-sterile, water-based drug products
of Burkholderia
cepacia complex (BCC
or B cepacia) contamination,
as there have been recent product recalls due to this and other water-borne
opportunistic pathogens found in pharmaceutical water systems.
The regulator’s warning stems from multi-state outbreak of infections. In March this year, Phispers had carried a news item on
Badrivishal Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals, a manufacturer of docusate sodium. It had been placed on FDA’s import alert list in December last.
The FDA warning
letter issued to Badrivishal talks about adulteration with BCC. The facility
used water as a drug component and for cleaning the facility and equipment. The
water source was a river in the vicinity which passes through farmland, where
it is subject to agricultural runoff and animal waste, before it reaches the
Badrivishal manufacturing site.
FDA’s concern was that contaminated water has been the root cause of multi-state outbreak of infections and multiple recalls by other drug manufacturers of non-sterile liquids, including instances of adulteration with BCC.
“BCC can survive or multiply in a variety of non-sterile and water-based products because it is resistant to certain preservatives and antimicrobial agents,” the FDA said.
Detecting BCC
bacteria is a challenge and requires validated testing methods that take into
consideration the unique characteristics of different BCC strains.
Laurus Labs to enter the US generics market;
how will this impact Mylan?
Last week, Laurus Labs
announced that its API facility at Unit 2 in Vizag (India) cleared the US FDA inspection without any Form 483 observations. The unit
manufactures APIs and finished dosage formulations (FDFs).
This successful inspection will help the company
as it plans to foray into the highly regulated US generics market.
Does this suggest trouble for US generic drug
giant Mylan? We think so.
Laurus was started by Dr Satyanarayana Chava in 2007, and is a key manufacturer and supplier of APIs.
With almost US $ 300 million in revenues, it holds its own against better-known
competitors like Mylan.
In fact, Laurus and Mylan have a lot in common.
Both the companies are headed by men who worked together at Matrix
Laboratories. Mylan acquired a controlling stake in Matrix around the time
Chava founded Laurus Labs. Until then, Chava was the chief operating officer of
Matrix, which was being headed by Rajiv Malik, the current president of Mylan.
Laurus has also carved a niche for itself by
supplying antiretroviral or ARVs (used to fight infections caused by
retroviruses like HIV), hepatitis C and oncology drugs. And despite being a relatively new player, its clients include giants like
Pfizer, Teva and Merck.
APIs generally make up for 20 to 35 percent of
the total cost of a drug, but the ones that Laurus develops, like ARVs,
constitute 70 to 75 percent of the cost of the drug.
Both companies have a stronghold in the treatment
of AIDS. Globally, Laurus has achieved a leadership in the manufacture of ARV
APIs. And in the case of Mylan, nearly 50 percent of patients receiving treatment for HIV/AIDS in
the developing world rely on its product, all of which are made in India. In
fact, Mylan is India's third largest pharmaceutical exporter.
So seems like Mylan should watch out for Laurus as
it forward integrates into making finished formulations. Laurus recently filed
2 Abbreviated New Drug Applications in the United States and submitted a
dossier to the WHO (World Health Organization).
Impressions: 4081
In less than three weeks, Donald Trump will assume office as the
President of the United States. He has mentioned that he wants Medicare (a
national social insurance program) to directly negotiate the price it pays for prescription drugs.
Medicare provides health insurance to Americans aged 65 or more, who
have worked and paid into the system through the payroll tax. It also provides
health insurance to younger people with some disabilities or end-stage renal
disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
In 2015, Medicare provided health insurance to over 55 million Americans — including 46 million people aged 65 or more, and nine million younger people.
As we flag off the New Year, PharmaCompass
provides insights into drug prices and prescription patterns in the US in order
to help professionals make informed decisions. We believe that the cost of
medicines in the US, which have been a subject of much public outcry and
discussions in the recent years, will continue to be scrutinized during 2017.
Medicare data for 2014
Medicare Part D, also known as the Medicare prescription drug benefit — the program which subsidizes the costs of prescription drugs and prescription drug insurance premiums for Medicare beneficiaries — published a data set (for calendar year 2014) which contains information from over one million healthcare providers
who collectively prescribed approximately US $121 billion worth of prescription
drugs paid for under this program.
For each prescriber and drug, the dataset
includes the total number of prescriptions that were dispensed (including
original prescriptions and any refills), and the total drug cost.
The total drug cost includes the ingredient cost of the medication, dispensing fees, sales tax, and any applicable administration fees. It’s based on the amounts paid by the Part D plan, the Medicare beneficiary, other government subsidies, and any other third-party payers (such as employers and liability insurers).
The total drug cost does not reflect any manufacturer rebates paid to Part D plan sponsors through direct and indirect remuneration or point-of sale rebates. In order to protect the beneficiary’s privacy, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) did not
include information in cases where 10 or fewer prescriptions were dispensed.
Top
Ten Drugs by Cost, 2014 [Most expensive for Medicare]
Drug Name
Total Claim Count
Beneficiary Count
Prescriber Count
Total Drug Cost
Sofosbuvir
109,543
33,028
7,323
$3,106,589,192
Esomeprazole Magnesium
7,537,736
1,405,570
286,927
$2,660,052,054
Rosuvastatin Calcium
9,072,799
1,752,423
266,499
$2,543,475,142
Aripiprazole
2,963,457
405,048
130,933
$2,526,731,476
Fluticasone/Salmeterol
6,093,354
1,420,515
281,775
$2,276,060,161
Tiotropium Bromide
5,852,258
1,211,919
253,277
$2,158,219,163
Lantus
Solostar
(Insulin Glargine)
4,441,782
972,882
224,710
$2,016,728,436
Sitagliptin Phosphate
4,495,964
789,828
190,741
$1,775,094,282
Lantus
(Insulin Glargine)
4,284,173
787,077
223,502
$1,725,391,907
Lenalidomide
178,373
27,142
9,337
$1,671,610,362
View the Medicare Part D National Prescriber Summary Report, Calendar Year 2014 (Excel version available) for FREE!
Top
Ten Drugs by Average Cost per Claim, 2014 [Most expensive drugs]
Drug Name
Total Claim Count
Beneficiary Count
Prescriber Count
Total Drug Cost
Average Cost Per Claim
Adagen
13
$1,224,835
$94,218
Elaprase
100
$6,560,225
$65,602
Cinryze
1,820
194
196
$96,155,785
$52,833
Carbaglu
60
$2,901,115
$48,352
Naglazyme
129
$6,189,045
$47,977
Berinert
538
73
68
$25,685,311
$47,742
Firazyr
1,568
269
232
$70,948,143
$45,248
H.P. Acthar
9,611
2,932
1,621
$391,189,653
$40,702
Procysbi
314
41
47
$12,542,911
$39,946
Folotyn
15
$598,210
$39,881
Top
Ten Drugs by Claims, 2014 [Most Commonly Used by Patients]
Generic Name
Total Claim Count
Beneficiary Count
Prescriber Count
Total Drug Cost
Lisinopril
38,278,860
7,454,940
464,747
$281,614,340
Levothyroxine Sodium
37,711,869
6,245,507
416,518
$631,855,415
Amlodipine Besylate
36,344,166
6,750,062
451,350
$303,779,661
Simvastatin
34,092,548
6,768,159
387,651
$346,677,118
Hydrocodone-Acetaminophen
33,446,696
8,005,790
677,865
$676,296,988
Omeprazole
33,032,770
6,707,964
475,122
$529,050,385
Atorvastatin Calcium
32,603,055
6,740,061
419,327
$747,635,818
Furosemide
27,133,430
5,176,582
456,047
$135,710,772
Metformin HCl
23,475,787
4,509,978
364,273
$203,948,989
Gabapentin
22,143,641
4,298,609
486,754
$492,557,255
View the Medicare Part D National Prescriber Summary Report, Calendar Year 2014 (Excel version available) for FREE!
Top
Ten Drugs by Prescribers, 2014 [Most Popular with Doctors]
Generic Name
Total Claim Count
Beneficiary Count
Prescriber Count
Total Drug Cost
Hydrocodone/Acetaminophen
33,446,696
8,005,790
677,865
$676,296,988
Ciprofloxacin HCl
7,253,018
4,926,835
568,201
$46,728,353
Amoxicillin
6,298,980
4,384,899
557,614
$31,193,739
Cephalexin
5,040,219
3,529,303
557,048
$36,987,401
Azithromycin
7,339,954
5,274,010
544,625
$70,699,119
Prednisone
11,032,986
4,505,821
536,108
$86,537,932
Tramadol HCl
14,250,227
4,272,724
515,816
$125,343,514
Sulfamethoxazole /Trimethoprim
4,833,758
3,090,944
500,790
$29,231,511
Gabapentin
22,143,641
4,298,609
486,754
$492,557,255
Amoxicillin/Potassium Clav
3,551,452
2,710,244
478,361
$61,713,432
The findings from CMS
data
The CY 2014 data represented a 17 percent
increase compared to the 2013 data set and a substantial part of the total estimated prescription drug spending (as estimated by the Department of Health and Human Services Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation, or ASPE) in the United States — at about US $ 457 billion in 2015, which was 16.7 percent of the overall personal healthcare services.
Of that US $ 457 billion, US $ 328 billion (71.9 percent) was for retail
drugs and US $ 128 billion (28.1 percent) was for non-retail drugs.
The drug pricing process in the US is complex and
reflects the influence of numerous factors, including manufacturer list prices,
confidential negotiated discounts and rebates, insurance plan benefit designs,
and patient choices.
An IMS study found that across 12 therapy classes widely used in Medicare Part D,
medicine costs to plans and patients in Medicare Part D are 35 percent below
list prices.
View the Medicare Part D National Prescriber Summary Report, Calendar Year 2014 (Excel version available) for FREE!
While the CMS does not
currently have an established formulary, Part D drug coverage excludes drugs
not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration, those prescribed for off-label
use, drugs not available by prescription for
purchase in the US, and drugs for which payments would be available under Parts
A or B of Medicare.
Part D coverage
excludes drugs or classes of drugs excluded from Medicaid coverage,
such as:
Drugs used for anorexia, weight loss, or weight gain
Drugs used to promote fertility
Drugs used for erectile dysfunction
Drugs used for cosmetic purposes (hair growth, etc.)
Drugs used for the symptomatic relief of cough and colds
Prescription vitamins and mineral products, except prenatal vitamins and fluoride preparations
Drugs where the manufacturer requires (as a condition of sale) any associated tests or monitoring services to be purchased exclusively from that manufacturer or its designee
Our view
The Medicare program is designed such that the
federal government is not permitted to negotiate prices of drugs with the drug
companies, as federal agencies do under other programs.
For instance, the Department of Veterans Affairs — which is allowed to negotiate drug prices and establish a formulary — has been estimated to pay (on an average) between 40 to 58 percent less for drugs, as opposed to Medicare Part D.
If Trump administration kick starts direct
negotiations on Medicare drug prices with drug companies, 2017 will surely turn
out to be a year for the pharmaceutical industry to remember.
View the Medicare Part D National Prescriber Summary Report, Calendar Year 2014 (Excel version available) for FREE!
Impressions: 7923
This week, Phispers has lots on generics. While the global leader Teva has more troubles at hand, generic players in the US face fresh lawsuits, and Sanofi plans to sell its European generic unit. There is also talk of Novartis buying America’s generic-drugs maker Amneal. In other news, oncologists find problem with clinical trials, and China shuts plants to curb pollution
Teva braces declining sales, lawsuits
and closure of its Mexico plant
There is more bad news from Israel’s Teva Pharmaceutical Industries. First, its Rimsa plant in Mexico is said to be shut, and a lot of employees have been (reportedly) laid off. As per a news report, it’s difficult to make the Rimsa
plant operational anytime soon.
Teva had invested US $ 2.3 billion in the facility. There are reports that the company may
make a write-down on its investment in Rimsa. In September, the global leader
in generics had claimed that the Espinosa brothers, who had controlled Rimsa
until its sale to Teva, had deceived the regulatory authorities and patients
for years and sold defective and illegal drugs.
Teva’s troubles don’t end there. The company is also setting aside US $ 520 million in its bid to settle allegations of paying bribes in Russia, Mexico and Ukraine. In its latest earnings report released Tuesday, Teva noted that “advanced discussions” are under way with the federal courts in the US to resolve the incidents, which took place between 2007 and 2013.
Teva has
completed 12 acquisitions worth US $ 46 billion in the last four years. Teva’s blockbuster Copaxone,
which brings in 19 percent of its overall sales, has lost several patent
challenges in the US and is likely to face generic competition early next year,
putting more than US $ 4 billion in sales at risk. Even without a generic
competitor, sales declined 2.2 percent year-on-year in the third quarter this
year.
To control
pollution, north China industrial hub curbs drug production
If you live in Delhi, and are coping with the hazardous pollution levels, here’s something that will interest you. A wide-ranging ban has
been imposed in a northern Chinese industrial hub on production at drug plants,
steel mills and other businesses.
This is a
last-ditch attempt by the government of Shijiazhuang city to meet this year’s pollution control target — to reduce the levels of PM 2.5 (fine particles that pose a risk to human health) by 10 percent. Shijiazhuang is the capital of the northern Hebei province, which reported economic growth of 6.8 percent in the first three quarters of this year.
Last week,
the government of Shijiazhuang city said for the remaining 45 days of the year,
it will curb output at thermal power plants, halt all production at industries
such as steel and cement, and limit manufacturing of pharmaceuticals, chemicals
and even furniture.
In 2014,
President Xi Jinping had responded to public outrage over high smog levels. As
a result, local officials are trying hard to strike a balance between pollution
control and economic growth.
Shijiazhuang
is home to major active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) producers such as North China Pharmaceutical, CSPC Zhongnuo Pharmaceutical, CSPC Ouyi Pharmaceutical and many others. These companies are critical to the
global antibiotic supply chain as they provide the building blocks for
antibiotic manufacturing, such as 6-APA and 7-ACA, along with commonly used
antibiotics such as Penicillin, Amoxicillin, Amipicillin and Azithromycin.
PharmaCompass has been routinely
covering the Chinese bulk drug industry and its impact on the environment. In April this year, PharmaCompass
had reported how school children in China were wearing gas masks due to pollution concerns. And prior to that, we had
carried an article on how dependent the world has become on bulk drugs from China.
More trouble
for generic drug-makers in the US as unions file lawsuits
In a fresh
salvo at the generic drug industry, a union representing sergeants of the New
York Police Department is attempting to hit some companies with civil penalties. The generic industry is already facing charges from a
two-year US Justice Department antitrust probe.
The union
has filed two lawsuits against two groups of drug-makers, which includes Novartis AG’s generic drug unit, Ireland-based Perrigo Co., India’s Wockhardt and Taro Pharmaceutical Industries (Israeli subsidiary of India’s Sun Pharma). The union has alleged that the companies colluded to
raise prices of two dermatological creams by as much as 1,000 percent since
2013.
Besides
this, at least four other unions
have filed lawsuits of their own, with two of them adding Actavis Inc., acquired in August by Teva, to the list of
defendants. All the unions manage health benefits for their members. The
unions say they overpaid for the drugs due to the price collusion. They point
to data that the drug-makers took price hikes on certain medicines by nearly
the same amounts within months of each other.
A lawyer for
the New York sergeants’ union said he expects a judge will call a conference in December
to decide if the cases can be combined.
Novartis may
buy generic drug-maker Amneal for US $ 8 billion
Swiss
healthcare major Novartis AG is in talks to acquire American generic-drugs maker Amneal Pharmaceuticals. Through this acquisition, Novartis plans to strengthen
its Sandoz
business. According to Bloomberg, Novartis and Amneal may reach an agreement soon. Amneal
makes the antiviral acyclovir (to treat herpes) and gabapentin (for epilepsy and pain). The
acquisition could cost Novartis around US $ 8 billion. Amneal is a family-owned
business led by co-founders Chintu and Chirag Patel and has operations in North
America, Australia, Europe and Asia. Its portfolio of generic treatments
includes around 115 approved molecules in the US.
Sanofi to
sell off European generic drug unit
French drug
maker Sanofi
confirmed it has decided to sell off its generic drug unit in Europe. The decision will affect two
manufacturing plants in the Czech Republic and Romania.
Sanofi CEO Olivier Brandicourt recently informed investors that the company has “made a definitive decision to initiate a carve-out process and divest the generics portfolio in Europe.” The move is part of the company’s 2020 strategic roadmap. He, however, did not provide details.
Sanofi had
acquired Zentiva, a Czech generic business, in 2008 for US $ 2.6 billion. And Sanofi’s generic business is centered around this acquisition. The business is particularly strong in the Czech Republic, Romania and Turkey.
On Monday, Zentiva Romania informed
the Bucharest Stock Exchange that its majority shareholder Sanofi has decided
to sell its Romanian generic drug plant as part of a major divestment plan of
its EU generic drugs business.
A company spokesperson said the planned scope of the divestment is the generics business “related to Europe,” so it excludes Russia, the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) and Turkey. And it includes the two “dedicated manufacturing sites producing and distributing generics for the European market,” one in Prague (Czech Republic), and the other in Bucharest (Romania).
Former
Valeant executives arrested for fraud
Last week,
two former executives of Valeant Pharmaceuticals — Gary Tanner and Andrew Davenport, who had been the CEO of Philidor — were arrested on charges of running a fraud scheme that swindled millions of dollars out of Valeant. The fraud was allegedly conducted with the help of a mail-order pharmacy, that is now defunct.
According to
Preet Bharara, US Attorney for the Southern District of New York, the arrests
were part of an ongoing probe of the scheme.
The criminal
complaint alleges that Tanner and Davenport conspired to enrich themselves with
Valeant funds. The two helped Valeant set up Philidor in early 2013, which was primarily a vehicle to market and distribute
Valeant drugs.
According to
the complaint, Tanner focused on building Philidor’s business, resisted his superiors’ directives to line up other distributors for Valeant’s products and ultimately received a US $10 million kickback from Davenport.
The complaint alleges that in 2014, the two orchestrated Valeant’s agreement to buy an option to purchase Philidor, which cost Valeant at least US $ 133 million. More than US $ 40 million of that went to shell companies controlled by Davenport. One such shell company — called ‘End Game LP — gave a kickback of US $10 million to Tanner.
Homeopathy
products in the US may carry caveats soon
In a report on homeopathic advertising, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) in the US said that homeopathic drugs should “be held to the same truth-in-advertising standards as other products claiming health benefits.”
Only the US
Food and Drug Administration (FDA) can prevent homeopathic marketers from
selling their products. The FTC has no teeth in the matter.
But very soon, homeopathic products could include statements such as ‘there is no scientific evidence backing homeopathic health claims’ and ‘homeopathic claims are based only on theories from the 1700s that are not accepted by modern medical experts.’
However, this may not affect sales of homeopathic products. There are claims that such statements could backfire because homeopaths and those who believe in homoeopathy don’t trust modern medicine. They could also believe that if
homeopathy has been around for that long, it must work.
This is not the first-time homeopathic medicines would carry caveats. In 1988, the FDA had struck a deal where it agreed that homeopaths could be self-regulating, if they include a disclaimer that their claims haven’t been evaluated by the FDA.
In February
this year, PharmaCompass had carried a news nugget on Professor
Paul Glasziou, a leading academic in evidence-based medicine at Bond
University, who had declared homeopathy as a “therapeutic dead-end”
after a systematic review concluded the controversial treatment was no more
effective than placebo drugs.
Cancer
clinical trials exaggerate benefits of new drugs, say oncologists
Two cancer physicians argue that large clinical trials — required for approval of new cancer drugs in the US — often overstate the effectiveness of the treatment in the real world.
During
cancer clinical trials, some volunteers take the experimental drug, while
others receive standard care with existing drugs. The groups are then compared
to see if their tumors have shrunk, how long it takes for the tumors to return,
and how long do the patients survive. This way, the trial sees whether the
experimental drug is safe and effective and can be sold to patients in the US.
The process
is based on the premise that trials give an accurate indication of safety
and efficacy among cancer patients in general, and not only those who are
eligible for and selected for the trial.
The trouble
is, participants in clinical trials are unlike the overall cancer population,
point out oncologists Dr. Sham Mailankody of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer
Center and Dr. Vinay Prasad of the Oregon Health and Science University in JAMA
Oncology. They’re younger, healthier, wealthier, better plugged in to the healthcare system, and better educated.
According to
these oncologists, if cancer patients are similar in age, socio-economic
status, have presence of other (similar) illnesses, and other
characteristics as those in a clinical trial, they might do as well. But for
everyone else, the trial results probably promise more than the drug can
deliver.
Impressions: 4478
This week, Phispers takes you through the EpiPen price hike controversy, and the Indian government’s decision not to adopt a bulk drug policy. There is more news pertaining to Teva’s divestitures, GSK’s new drug for HIV treatment and drug recalls by Cadila, Teva and Sagent. A setback to Indian pharma as minister
says govt against bulk drug policy Earlier this year PharmaCompass had highlighted the ‘inconvenient
truth about Chinese drug manufacturing’ – that a serious imbalance exists in the global supply chain with regard to its dependence on China. India had declared 2015 as the Year of the API, under the ‘Make in India ‘programme. A Cabinet note for a bulk drug policy, based on the recommendations of the Katoch committee, had been floated
earlier this year. Such a policy would have helped the Indian
pharmaceutical sector turn into a US $ 200-billion industry by 2030, and
shifted global dependence away from China.However, the plan suffered a setback as the chemical and fertiliser minister Ananth Kumar announced this week that
the government was against
a bulk drug policy. Instead, states will have to come up with “bulk drug parks” which will help boost manufacturing of bulk drugs.This news comes at a time when a Bloomberg
analysis concluded that China
drug sales grow despite safety concerns at home. Around 700 Chinese firms were told by regulators in China to review their pending applications to sell new drugs and voluntarily withdraw those that were false or incomplete. “Within months, about 75 percent had been retracted by the manufacturers or rejected by Chinese officials,” the Bloomberg report said.Currently, India is dependent on China for APIs. More than 75 per cent of India’s bulk drug imports come from China. And there is concern over quality. Mylan CEO blames system for EpiPen price hike,
announces launch of generic versionLast week, Mylan made headlines as its 400 percent price increase of EpiPen auto-injector came under scrutiny. The furor continued,
even as the Mylan CEO Heather Bresch tried her best to justify the price hikes
in an interview, which generated more negative publicity. In the interview, Bresch blamed the healthcare system for the price hike. According to her, the price of US $ 608 for the life-saving EpiPen reflects a system where there are “four or five hands that the product touches and companies that it goes through before it ever gets to that patient at the counter.” This week, Mylan tried to suppress the furor by
announcing it would launch an authorized generic version of EpiPen for half the price of the brand-name product. The identical generic two-pack of EpiPens, expected to launch in several weeks, will have a list price of US $ 300. This is still significantly higher than the price of the auto-injector prior to Mylan’s acquisition of the EpiPen in 2007. In Canada, the twin pack costs US $ 200, in France it is around US $ 100.In the interview, Bresch acknowledged that the high
retail price in the US was used to subsidize the price of EpiPens in Europe, where
they sold at just US $ 100 or US $ 150.Bresch went onto say: “Congress and the leaders of this country need to quit putting their toe in this topic and really fix this — we have an outdated system.”After the interview, pharma bad boy Martin Shkreli defended the price increase while some Americans turned to Canada for cheaper EpiPens. And Senators questioned if the FDA was to blame for the high drug prices. Meanwhile, analysts said the authorized generic
version of EpiPen may actually make more money for Mylan! Aurobindo, Intas in race to buyout UK and Irish
portfolios of TevaLast week, two Indian drug makers – Aurobindo Pharma and Intas Pharmaceuticals – emerged as the final contenders to buyout the UK and Irish portfolios of Teva. These portfolios of the Israeli generics behemoth have been put up for
sale to comply with the European anti-trust regulations.Both Aurobindo and Intas put
up binding offers of around US $ 1 billion, along with firm financing
commitments, The Economic Times
reported. Last year, Teva had acquired
Allergan Plc’s generic business for US $ 40.5 billion. Teva
is selling assets as part of a broader divestiture process to comply with the
anti-trust regulations for this acquisition.In order to comply with
these regulations, Teva has already sold 80 products in the US to drug makers
like Dr Reddy’s, Sagent, Cipla, Zydus Cadila, Aurobindo, Impax and Perrigo. Glaxo plans to shake up HIV treatment with new drugGlaxoSmithKline plans to capsize the decade-old strategy for treating HIV. Executives at GSK are hoping that the company’s latest HIV pill is powerful enough to suppress the virus, with the help of just one more drug. The drug – Dolutegravir – belongs to a class of HIV drugs known as integrase inhibitors that rapidly reduces the level of virus in the blood. It has already been approved for use as part of traditional triple therapy and hasn’t reported cases of the virus developing resistance to dolutegravir in patients who are new to the treatment.Since the mid-1990s, the treatment of HIV – a virus that causes AIDS – hasn’t changed much. In the mid-1990s, a new class of antiretroviral drugs were introduced. One drug from the new class, along with two other drugs from an earlier class, hindered the virus from developing resistance. This three-drug regimen has been the standard approach for treating HIV for the last two decades.Dolutegravir, according to GSK CEO Andrew Witty, would
be the game changer because taking fewer drugs will lead to fewer side effects.GSK’s majority-owned HIV business – ViiV Healthcare – is undergoing the long process of proving the efficacy of the Dolutegravir. Pfizer and Japan’s Shionogi & Co hold minority shares
in ViiV Healthcare. Japanese wholesaler arrested for illegally selling drugs to Chinese
touristsHidenobu Zaima, president of Tokyo-based drug wholesaler – Biken Pharmacy, was arrested along with four others, on the suspicion of illegally selling
large quantities of prescription drugs to Chinese tourists and violating the
Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Law.Zaima is believed to have sold about 291,000 products
to a Chinese broker for US $ 147,000 between September 2015 and May 2016. Chinese tourists often buy prescription and
over-the-counter products in other countries, such as Japan and Hong Kong,
where they can be cheaper. They also believe that drugs bought in these
countries would be of better quality. Teva, Cadila and Sagent recall drugsThis was a week of drug recalls in the US. Teva issued
a recall of antibiotics for the second time
this year. This time the recall pertained to amoxicillin manufactured at a plant in Canada. The
company is recalling 53,000 bottles of the drug manufactured by Teva Canada Limited in Toronto.Earlier this year, Teva had recalled amikacin sulfate manufactured at its
facility in Hungary due to the potential for the presence of glass particulate.
Meanwhile, India’s Cadila Healthcare recalled 26 batches (or 223,776 bottles)
of an antidepressant -- venlafaxine HCL ER capsules – as well as nine lots for which the company did not specify the bottle count. These drugs were manufactured at the company’s plant in Ahmedabad. The drugs failed dissolution specifications when retained samples were tested. Venlafaxine is used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety and panic disorder.Similarly,
Sagent Pharmaceuticals recalled one lot of oxacillin for injection manufactured by India-based Astral SteriTech. The action was taken after a customer
complained that small, dark particulate matter was found in the solution after
it was reconstituted. The foreign matter found in the vials was identified as iron oxide.
Impressions: 3807
With Novartis shutting two plants in Germany and one in India by 2016-end, the global reliance on China for bulk drugs has increased even further, raising serious concerns over safety, supplies and national security. Which
plants? Last week, Novartis announced it will be shutting three plants of its generic business – Sandoz – by the end of 2016. The first plant is in India and the other two are located in Germany, in Gerlingen and Frankfurt. Frankfurt,
manufacturer of a key antibiotic intermediateThe Frankfurt plant is where Sandoz manufactures
7-ACA
(7-aminocephalosporanic acid), the core chemical structure (building block)
for producing a whole host of cephalosporin antibiotics. The reason given for closure -- prices of the cephalosporin active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and intermediates have collapsed as Asian competitors have dumped excess capacity on the market. The shutdown of the Frankfurt facility
means that the global reliance on China for APIs, used to produce antibiotics
(such as cephalosporin) and especially
7-ACA, will increase only further. Chinese
APIs are already a security threat for India India produces a third of the world's
medicines, mostly in the form of generic drugs. However, according to an Oct 2014 report
by a Boston Consulting Group (BCG) and Confederation of Indian Industry (CII), more
than 90 percent of the key raw materials (intermediates and APIs) that go into
making at least 15-odd essential drugs come from China.The drugs listed include the most commonly used painkiller such as paracetamol, aspirin; antibiotics such as amoxicillin and ampicillin, cephalexin, cefaclor, ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, levofloxacin; first line diabetes drug metformin; and antacid ranitidine. There are no domestic producers left for many drugs such as penicillin-G, and its derivative 6-aminopenicillanic acid, or 6-APA.Since India is still receiving a large quantity of 7-ACA from Germany (confirmed by the import statistics available on the PharmaCompass database), 7-ACA and its derivatives were not mentioned in this report.As per news reports, the Indian government
is now worried about over-dependence on imports from China. "Any
deterioration in relationship with China can potentially result in severe
shortages in the supply of essential drugs to the country. Additionally, China
could easily increase prices of some of these drugs where it enjoys virtual
monopoly," said Bart Janssens, partner, BCG, in a news
report published in The Economic Times. Recognizing the national healthcare
security challenge facing India, the Department of Pharmaceuticals (DoP) has
decided to declare the year 2015 as ‘Year of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients.’ As part of this initiative, the Indian government intends
to build
cluster parks to boost India’s self-reliance on Chinese imports. Quality,
environmental concerns over Chinese AntibioticsChinese supplies of 7-ACA have been plagued
with multiple issues in the past. In 2012, for instance, several Chinese drug
companies were accused of manufacturing 7-ACA using contaminated ‘gutter oil’, instead of more
expensive soybean oil. Gutter oil is reprocessed oil manufactured from waste oil and animal fat collected from restaurants’ fryers, drains, grease traps and slaughterhouses. Chinese restaurants can get through a lot of cooking oil and this waste oil fuels a highly profitable gutter oil black market as there are few other outlets, such as biofuel production, for this by-product.Similarly, antibiotic pollution in the rivers of China is a serious cause of concern for the Chinese. Our previous analysis, “Antibiotic
resistant superbugs: deadlier than cancer and closer to you than you think” provides a detailed overview regarding the challenge being faced. However, with growing focus on antibiotic pollution in China, a shutdown of factories failing pollution norms would be a severe setback for the global antibiotic supply chain. In addition to these challenges, quality concerns have been raised during international regulatory inspections of some of the leading antibiotic producers in China, like Zhuhai
United and North
China Pharmaceutical Company. South
African stock outs of essential drugs a global concernThe outcomes of these challenges are already being felt in countries such as South Africa which are facing an acute shortage of critical drugs. According to a report
published in Groundup, drug shortages in South Africa’s health facilities have become a crisis. The story mentioned the situation in a hospital (Stanger Hospital) in Ilembe District KwaZulu Natal, where 200 products were out of stock. These included various doses of morphine, some antibiotics and antiretrovirals, especially paediatric ones, used to treat HIV. “About a hundred patients per week are going without ranitidine which prevents stomach ulcers. Several Ilembe facilities are even out of stock of paracetamol tablets,” the Groundup report said. There are multiple reasons for the drug stock
outs. However, unprofitability because old, off-patent products are being sold by
manufacturers at prices very close to the cost of production has played a major
role. Firms are abandoning such products and seeking higher return
alternatives. In addition, due to quality failures suppliers are unable to provide lifesaving medications to the South African population. Our
ViewThe problems of stock outs and quality concerns in South Africa can easily expand across the world and can’t be addressed until the global pharmaceutical industry reduces its reliance on China for bulk drugs and intermediates. It remains to be seen if the threat to the global supply chain will make Novartis reconsider its decision or drive a national government to buy the Frankfurt facility.
Impressions: 7491