AbbVie Inc
AbbVie Inc
12 Feb 2026
// FIERCE PHARMA
06 Feb 2026
// BIOSPACE
05 Feb 2026
// PRESS RELEASE

About
euroPLX 90 LisboneuroPLX 90 Lisbon
Industry Trade Show
Not Confirmed
02-03 March, 2026
Industry Trade Show
InterContinental NY Barclay
23-26 March, 2026
Industry Trade Show
Not Confirmed
14-17 February, 2026
CONTACT DETAILS




Events
Webinars & Exhibitions
euroPLX 90 LisboneuroPLX 90 Lisbon
Industry Trade Show
Not Confirmed
02-03 March, 2026
Industry Trade Show
InterContinental NY Barclay
23-26 March, 2026
Industry Trade Show
Not Confirmed
14-17 February, 2026
CORPORATE CONTENT #SupplierSpotlight
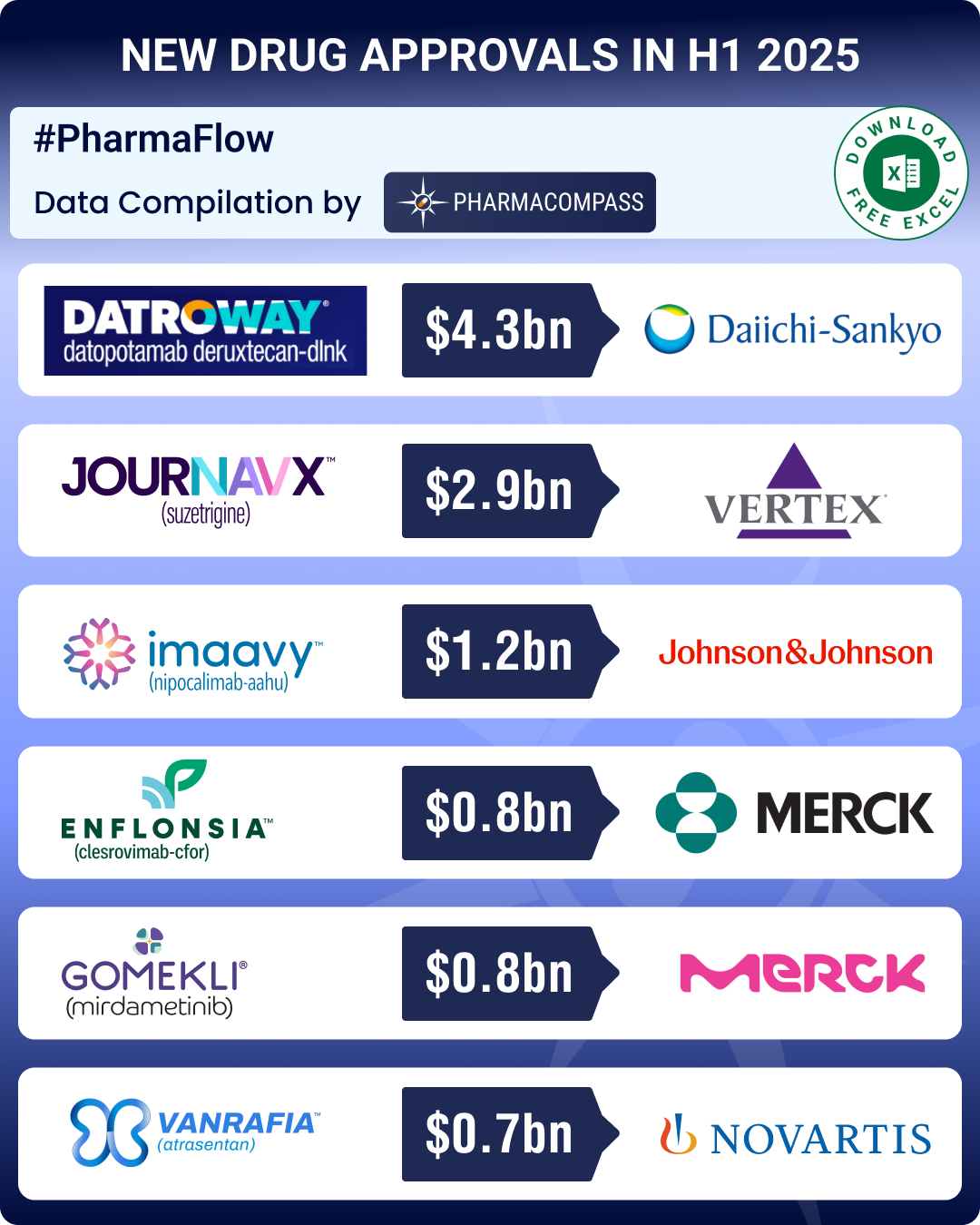
https://www.pharmacompass.com/radio-compass-blog/fda-approvals-drop-24-in-h1-2025-gsk-s-uti-med-vertex-s-non-opioid-painkiller-lead-pack-of-first-in-class-meds
https://www.pharmacompass.com/radio-compass-blog/j-j-s-intra-cellular-buyout-bms-oncology-gambit-sanofi-s-blueprint-acquisition-drive-mega-deals-in-h1-2025
https://www.pharmacompass.com/radio-compass-blog/top-pharma-companies-drugs-in-2024-merck-s-keytruda-maintains-top-spot-as-novo-s-semaglutide-nips-at-its-heels
https://www.pharmacompass.com/radio-compass-blog/molecular-glue-degraders-lilly-abbvie-sign-billion-dollar-deals-bms-leads-with-three-late-stage-drugs
https://www.pharmacompass.com/radio-compass-blog/top-first-in-class-drug-candidates-of-2025-ionis-donidalorsen-sanofi-s-fitusiran-cytokinetics-aficamten-await-fda-approval
https://www.pharmacompass.com/radio-compass-blog/fda-okays-50-new-drugs-in-2024-bms-cobenfy-lilly-s-kisunla-lead-pack-of-breakthrough-therapies
https://www.pharmacompass.com/radio-compass-blog/fda-s-landmark-approvals-of-bms-schizo-med-madrigal-s-mash-drug-us-16-5-bn-catalent-buyout-make-it-to-top-10-news-of-2024
https://www.pharmacompass.com/radio-compass-blog/chinese-fda-registered-generic-facilities-gain-steam-india-maintains-lead-with-396-facilities
https://www.pharmacompass.com/radio-compass-blog/novartis-gsk-sanofi-bms-shell-out-over-us-10-bn-in-dealmaking-as-mid-size-deals-take-centerstage-in-2024
https://www.pharmacompass.com/radio-compass-blog/fda-s-june-2024-list-of-off-patent-off-exclusivity-drugs-sees-rise-in-cancer-hiv-treatments
https://www.pharmacompass.com/radio-compass-blog/fda-approves-record-eight-biosimilars-in-h1-2024-okays-first-interchangeable-biosimilars-for-eylea

12 Feb 2026
// FIERCE PHARMA
https://www.fiercepharma.com/pharma/abbvie-mounts-fresh-ira-legal-challenge-over-botoxs-inclusion-latest-drug-pricing

06 Feb 2026
// BIOSPACE
https://www.biospace.com/drug-development/abbvie-cso-touts-breakthrough-type-therapy-psychedelic-as-j-js-spravato-keeps-growing

05 Feb 2026
// PRESS RELEASE
https://news.abbvie.com/2026-02-04-AbbVie-Reports-Full-Year-and-Fourth-Quarter-2025-Financial-Results

04 Feb 2026
// PRESS RELEASE
https://news.abbvie.com/2026-02-03-AbbVie-Submits-Regulatory-Applications-to-FDA-and-EMA-for-Upadacitinib-RINVOQ-R-in-Adults-and-Adolescents-With-Vitiligo

02 Feb 2026
// FIERCE PHARMA
https://www.fiercepharma.com/marketing/abbvie-has-love-mind-new-migraine-educational-campaign

29 Jan 2026
// PR NEWSWIRE
https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/abbvie-launches-love-in-mind-to-spotlight-the-emotional-impact-of-migraine-on-romantic-relationships-302673336.html
ABOUT THIS PAGE
AbbVie Inc is a supplier offers 22 products (APIs, Excipients or Intermediates).
Find a price of Cyclosporine bulk with DMF, CEP offered by AbbVie Inc
Find a price of Erythromycin bulk with DMF, CEP offered by AbbVie Inc
Find a price of Biperiden Hydrochloride bulk with CEP offered by AbbVie Inc
Find a price of Butorphanol Tartrate bulk with DMF offered by AbbVie Inc
Find a price of Erythromycin Ethyl Succinate bulk with DMF offered by AbbVie Inc
Find a price of Erythromycin Stearate bulk with DMF offered by AbbVie Inc
Find a price of Isoflurane bulk with CEP offered by AbbVie Inc
Find a price of Paricalcitol bulk with DMF offered by AbbVie Inc
Find a price of Ritonavir bulk with CEP offered by AbbVie Inc
Find a price of Atogepant bulk offered by AbbVie Inc
Find a price of Divalproex Sodium bulk offered by AbbVie Inc
Find a price of Elagolix Sodium bulk offered by AbbVie Inc
Find a price of Enflurane bulk offered by AbbVie Inc
Find a price of Erythromycin Thiocyanate bulk offered by AbbVie Inc
Find a price of Foscarbidopa bulk offered by AbbVie Inc
Find a price of Foslevodopa bulk offered by AbbVie Inc
Find a price of Glecaprevir bulk offered by AbbVie Inc
Find a price of Levothyroxine Sodium bulk offered by AbbVie Inc
Find a price of Pibrentasvir bulk offered by AbbVie Inc
Find a price of Terazosin HCl bulk offered by AbbVie Inc
Find a price of Upadacitinib bulk offered by AbbVie Inc
Find a price of Venetoclax bulk offered by AbbVie Inc