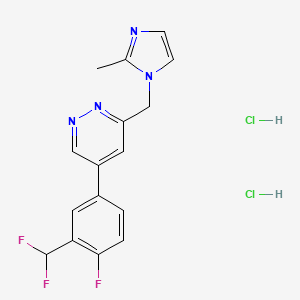

1. 5-(3-(difluoromethyl)-4-fluorophenyl)-3-((2-methyl-1h-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)pyridazine
2. Evt-101
1. Evt-101
2. Evt101
3. B55t45aa8f
4. 1189088-41-2
5. Evt-101 Hydrochloride
6. Evt-101 Dihydrochloride
7. Chembl3545349
8. Dtxsid001336448
9. Db05956
10. Q27274392
11. Pyridazine, 5-(3-(difluoromethyl)-4-fluorophenyl)-3-((2-methyl-1h-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-, Hydrochloride (1:2)
| Molecular Weight | 391.2 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H15Cl2F3N4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 390.0625864 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 390.0625864 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 43.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 25 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 384 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 3 |
Investigated for use/treatment in alzheimer's disease, neurologic disorders, pain (acute or chronic), and parkinson's disease.
EVT 101 penetrates the brain at doses that are well tolerated in man and expected to be clinically relevant, shows activity in areas relevant to pain and, importantly, modulates the activity of specific brain regions during the performance of cognitive tasks relevant to Alzheimer's disease.