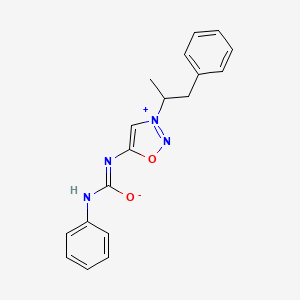

1. N-phenylcarbamoyl-3-(beta-phenylisopropyl)sydnonimine
2. Sidnocarb
3. Sydnocarb
1. Sydnocarb
2. Sidnocarb
3. 34262-84-5
4. Mesocarb [inn]
5. Umt8mp2ndu
6. Mlr-1017
7. Mesocarbum
8. Mesocarbo
9. Sidnokarb
10. Sydnone Imine, 3-(1-methyl-2-phenylethyl)-n-((phenylamino)carbonyl)-
11. N-phenyl-n'-[3-(1-phenylpropan-2-yl)oxadiazol-3-ium-5-yl]carbamimidate
12. Unii-umt8mp2ndu
13. Mesocarbum [inn-latin]
14. Mesocarbo [inn-spanish]
15. Brn 5773701
16. Mesocarb [mart.]
17. Mesocarb [who-dd]
18. Mls000556315
19. Schembl727658
20. 3-(beta-phenylisopropyl)-n-phenyl Carbamoylsidnonimin
21. Chembl2105246
22. Chembl3989800
23. Dtxsid10900961
24. Hms2326a20
25. Sydnone Imine, 3-(.alpha.-methylphenethyl)-n-(phenylcarbamoyl)-
26. Stk548667
27. Akos005476412
28. Ncgc00246489-01
29. Smr000147632
30. 3-(alpha-methylphenethyl)-n-(phenylcarbamoyl)sydnone Imine
31. Sydnone Imine, 3-(alpha-methylphenethyl)-n-(phenylcarbamoyl)-
32. 3-(.alpha.-methylphenethyl)-n-(phenylcarbamoyl)sydnone Imine
33. (5z)-5-[(phenylcarbamoyl)imino]-3-(1-phenylpropan-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1,2,3-oxadiazol-3-ium-4-ide
34. 1,2,3-oxadiazolium, 3-(1-methyl-2-phenylethyl)-5-(((phenylamino)carbonyl)amino)-, Inner Salt
35. 178936-15-7
| Molecular Weight | 322.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H18N4O2 |
| XLogP3 | 4.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 322.14297583 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 322.14297583 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 77.4 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 406 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Anticonvulsants
Drugs used to prevent SEIZURES or reduce their severity. (See all compounds classified as Anticonvulsants.)
Antidepressive Agents
Mood-stimulating drugs used primarily in the treatment of affective disorders and related conditions. Several MONOAMINE OXIDASE INHIBITORS are useful as antidepressants apparently as a long-term consequence of their modulation of catecholamine levels. The tricyclic compounds useful as antidepressive agents (ANTIDEPRESSIVE AGENTS, TRICYCLIC) also appear to act through brain catecholamine systems. A third group (ANTIDEPRESSIVE AGENTS, SECOND-GENERATION) is a diverse group of drugs including some that act specifically on serotonergic systems. (See all compounds classified as Antidepressive Agents.)
Central Nervous System Stimulants
A loosely defined group of drugs that tend to increase behavioral alertness, agitation, or excitation. They work by a variety of mechanisms, but usually not by direct excitation of neurons. The many drugs that have such actions as side effects to their main therapeutic use are not included here. (See all compounds classified as Central Nervous System Stimulants.)
Sympathomimetics
Drugs that mimic the effects of stimulating postganglionic adrenergic sympathetic nerves. Included here are drugs that directly stimulate adrenergic receptors and drugs that act indirectly by provoking the release of adrenergic transmitters. (See all compounds classified as Sympathomimetics.)