
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
API Suppliers
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
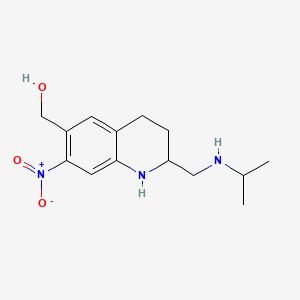

1. Oxaminiquine
2. Uk 4271
3. Uk-4271
4. Uk4271
1. 21738-42-1
2. Mansil
3. Vansil
4. Oxaminiquine
5. Uk-4271
6. Oxamniquinum
7. Uk 4271
8. (+)-oxamniquine
9. Uk 4261
10. Oxamniquine, (+)-
11. Oxamniquine, (-)-
12. Nsc 352888
13. Nsc-352888
14. 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-((isopropylamino)methyl)-7-nitro-6-quinolinemethanol
15. [7-nitro-2-[(propan-2-ylamino)methyl]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolin-6-yl]methanol
16. Mls000756891
17. 00bcy677ot
18. 7gij138h3k
19. Chebi:78416
20. {2-[(isopropylamino)methyl]-7-nitro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolin-6-yl}methanol
21. 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-(((1-methylethyl)amino)methyl)-7-nitro-6-quinolinemethanol
22. 2-((isopropylamino)methyl)-7-nitro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6-quinolinemethanol
23. 6-hydroxymethyl-2-isopropylaminomethyl-7-nitro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline
24. Nsc352888
25. 6-quinolinemethanol, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-(((1-methylethyl)amino)methyl)-7-nitro-
26. 0o977r722d
27. Uk-4261
28. 6-quinolinemethanol, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-((isopropylamino)methyl)-7-nitro-
29. (7-nitro-2-{[(propan-2-yl)amino]methyl}-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolin-6-yl)methanol
30. Oxamniquina
31. Oxamniquinum [inn-latin]
32. Oxamniquina [inn-spanish]
33. (2-((isopropylamino)methyl)-7-nitro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolin-6-yl)methanol
34. 6-quinolinemethanol, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-(((1-methylethyl)amino)methyl)-7-nitro-, (+)-
35. 6-quinolinemethanol, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-(((1-methylethyl)amino)methyl)-7-nitro-, (-)-
36. 119678-90-9
37. Mansil (tn)
38. Vansil (tn)
39. (+/-)-oxamniquine
40. Oxamniquine (usan/inn)
41. Ccris 4113
42. Hsdb 6510
43. [2-[(isopropylamino)methyl]-7-nitro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolin-6-yl]methanol
44. 6-quinolinemethanol, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-[[(1-methylethyl)amino]methyl]-7-nitro-
45. Ncgc00016755-01
46. Einecs 244-556-4
47. (+-)-oxamniquine
48. Cas-21738-42-1
49. Brn 0485597
50. Oxamniquine [mi]
51. Prestwick0_001026
52. Prestwick1_001026
53. Prestwick2_001026
54. Oxamniquine [inn]
55. Dsstox_cid_3398
56. Oxamniquine [hsdb]
57. Oxamniquine [usan]
58. Chembl847
59. Oxamniquine [vandf]
60. Dsstox_rid_77013
61. Oxamniquine [mart.]
62. Unii-00bcy677ot
63. Unii-7gij138h3k
64. Dsstox_gsid_23398
65. Schembl44921
66. Oxamniquine [who-dd]
67. Oxamniquine [who-ip]
68. Spbio_003072
69. Dtxsid3023398
70. Unii-0o977r722d
71. Oxamniquine [orange Book]
72. Hms1571m13
73. Hms2230h11
74. Hms3371n13
75. Oxamniquine [usan:usp:inn:ban]
76. Oxamniquinum [who-ip Latin]
77. Tox21_110593
78. 2-(isopropylaminomethyl)-7-nitro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline-6-methanol
79. Db01096
80. (2-{[(1-methylethyl)amino]methyl}-7-nitro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolin-6-yl)methanol
81. Hy-10416
82. Smr000528982
83. Cs-0002596
84. C07341
85. D00460
86. 5-22-11-00475 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
87. Q682497
88. Sr-01000765728
89. Sr-01000765728-2
90. 1,3,4-tetrahydro-2-[(isopropylamino)methyl]-7-nitro-6-quinolinemethanol
91. 2-(isopropylaminomethyl)-7-nitro-1,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline-6-methanol
92. 6-quinolinemethanol,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-[(isopropylamino)methyl]-7-nitro-
93. (2-[(isopropylamino)methyl]-7-nitro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6-quinolinyl)methanol #
94. {2-[(isopropylamino)methyl]-7-nitro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6-quinolinyl}methanol
95. 6-quinolinemethanol,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-[[(1-methylethyl)amino]methyl]-7-nitro-
96. 119678-89-6
97. 40247-39-0
| Molecular Weight | 279.33 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H21N3O3 |
| XLogP3 | 2.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 279.15829154 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 279.15829154 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 90.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 20 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 332 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Schistosomicides
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Anthemintic (Schistosomiasis)
Budavari, S. (ed.). The Merck Index - Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals. Rahway, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 1989., p. 1094
Oxamniquine is used for the treatment of schistosomiasis (bilharziasis) caused by Schistosoma mansoni /in/ individual patients and in mass treatment and control programs. Oxamniquine is effective against all stages of Schistosoma mansoni infection including the acute phase and the chronic phase which may be associated with hepatosplenic involvement.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 92. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1992 (Plus Supplements 1992)., p. 41
Oxamniquine has been used for suppressive prophylaxis of Schistosoma mansoni infections in animals.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 92. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1992 (Plus Supplements 1992)., p. 41
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for OXAMNIQUINE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
The drug should be used with caution in /patients with a history of seizure disorders/ and they should remain under medical supervision with adequate facilities readily available for the management of seizures should they occur during oxamniquine therapy.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 92. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1992 (Plus Supplements 1992)., p. 42
Patients ... should be warned that /oxamniquine/ may produce an orange to red color in their urine.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 92. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1992 (Plus Supplements 1992)., p. 42
Since the incidence of some adverse effects (eg, dizziness, drowsiness, nausea) may be increased during fasting conditions, patients should be advised to take oxamniquine with food.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 92. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1992 (Plus Supplements 1992)., p. 42
Oxamniquine should be used during pregnancy only when the potential benefits justify the possible risks to the fetus. ... Since it is not known whether oxamniquine is distributed into milk, the drug should be used with caution in nursing women.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 92. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1992 (Plus Supplements 1992)., p. 42
For treatment of Schistosomiasis caused by Schistosoma mansoni
Oxamniquine is an anthelmintic with schistosomicidal activity against Schistosoma mansoni, but not against other Schistosoma spp. Oxamniquine causes worms to shift from the mesenteric veins to the liver where the male worms are retained; the female worms return to the mesentery, but can no longer release egg.
Schistosomicides
Agents that act systemically to kill adult schistosomes. (See all compounds classified as Schistosomicides.)
P - Antiparasitic products, insecticides and repellents
P02 - Anthelmintics
P02B - Antitrematodals
P02BA - Quinoline derivatives and related substances
P02BA02 - Oxamniquine
Absorption
Well absorbed orally
Oxamniquine and its metabolites are excreted mainly in urine. Approximately 40-75% of an oral dose of the drug is excreted in urine within 24 hours of administration, principally as the 6-carboxylic acid metabolite. About 0.5-2% of an oral dose is excreted in urine unchanged; less than 1% of a dose is excreted in urine as the 2-carboxylic acid metabolite.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 92. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1992 (Plus Supplements 1992)., p. 41
Oxamniquine is well absorbed following oral administration. The rate and extent of GI absorption of the drug are decreased by the presence of food. Peak plasma concentrations of oxamniquine occur approximately 1-3 hours after oral administration of usual doses of the drug. ... Interpatient variation in plasma oxamniquine concentrations may result from biodegradation of the drug in the GI mucosa during absorption. ... Oxamniquine undergoes extensive first pass metabolism in the GI lumen before absorption and/or in the GI mucosa during absorption in animals.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 92. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1992 (Plus Supplements 1992)., p. 41
Following oral administration of a single 15 mg/kg dose of oxamniquine in adults and children with Schistosoma mansoni infection in one study, peak serum drug concentrations of 70-2595 and 89-1500 ng/ml, respectively, occurred at 1.5-3 hours. In another study, following oral administration of a single 1 g dose of oxamniquine in patients with advaced hepatosplenic schistosomiasis and in healthy adults, mean peak plasma drug concentrations of 1267 ng/ml at about 1.7 hours and 1983 ng/ml at about 1.4 hours occurred, respectively.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 92. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1992 (Plus Supplements 1992)., p. 41
Probably hepatic
The drug is extensively metabolized, principally in the GI mucosa and/or lumen via enzymatic oxidation of the 6-hydroxymethyl group to the 6-carboxylic acid metabolite. Trace amounts of the 2-carboxylic acid metabolite have also been observed in urine, which reflects oxidation of the side chain. These metabolites do not possess antichistosomal activity.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 92. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1992 (Plus Supplements 1992)., p. 41
1-2.5 hours
Oxamniquine has a plasma half-life of about 1-2.5 hours.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 92. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1992 (Plus Supplements 1992)., p. 41
Oxamniquine may associate with an irreversible inhibition of the nucleic acid metabolism of the parasites. A hypothesis has been put forth that the drug is activated by a single step, in which a schistosome sulfotransferase enzyme converts oxamniquine into an ester (probably acetate, phosphate, or sulfate). Subsequently, the ester spontaneously dissociates, the resulting electrophilic reactant is capable of alkylation of schistosome DNA.
Causes the worms to be dislodged from their usual site of residence in the mesenteric veins to the liver where they are retained and subsequently killed by host tissue reactions (eg, phagocytosis). The dislodgment of worms appears to result principally from contraction and paralysis of their musculature and subsequent immobilization of their suckers, which causes the worms to detach from the blood vessel wall, thereby allowing passive dislodgement by normal blood flow.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 92. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1992 (Plus Supplements 1992)., p. 41
Hycanthone-sensitive and hycanthone-resistant schistosomes (which are also sensitive and resistant to oxamniquine) were exposed in vitro to tritium-labelled oxamniquine. The initial uptake of the drug into the schistosomes was essentially the same for the 2 strains. The homogenate of worms incubated with tritiated oxamniquine was fractionated and a purified DNA fraction was obtained by ethanol precipitation, RNAase and protease digestion, repeated phenolchloroform extractions, cesium chloride gradient centrifugation and extensive dialysis. The DNA fraction from sensitive worms contained radioactive oxamniquine at a level corresponding to about 1 drug molecule per 50,000 base pairs, while the DNA from resistant worms contained essentially no drug. The results support the hypothesis that oxamniquine, like hycanthone, exerts its activity by alkylating macromolecules of sensitive schistosomes.
PMID:2617584 Pica-Mattoccia L et al; Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 83 (3): 373-6 (1989)
ABOUT THIS PAGE
26
PharmaCompass offers a list of Oxamniquine API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Oxamniquine manufacturer or Oxamniquine supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Oxamniquine manufacturer or Oxamniquine supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Oxamniquine API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Oxamniquine API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Oxamniquine Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Oxamniquine Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Mansil manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Mansil, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Mansil manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Mansil API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A Mansil supplier is an individual or a company that provides Mansil active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Mansil finished formulations upon request. The Mansil suppliers may include Mansil API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
Mansil Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Mansil GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Mansil GMP manufacturer or Mansil GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Mansil CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Mansil's compliance with Mansil specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Mansil CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Mansil CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Mansil may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Mansil EP), Mansil JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Mansil USP).
