
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
EU WC
0
VMF
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
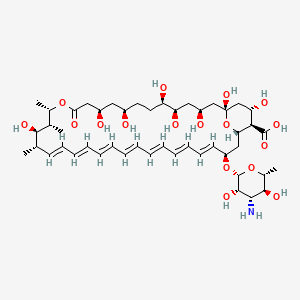

1. Amphocil
2. Amphotericin
3. Amphotericin B Cholesterol Dispersion
4. Amphotericin B Colloidal Dispersion
5. Fungizone
1. 1397-89-3
2. Amphotericin
3. Amphotericine B
4. Fungizone
5. Ambisome
6. Ampho-moronal
7. Halizon
8. Amfotericina B
9. Amphotericinum B
10. Amph-b
11. Liposomal Amphotericin B
12. Amphotericin-b
13. Abelcet
14. Amphotec
15. Fungilin
16. Mfcd00877763
17. 7xu7a7droe
18. Nsc 527017
19. Ncgc00090808-01
20. Dsstox_cid_2601
21. Dsstox_rid_76653
22. Amphotocerin
23. Dsstox_gsid_22601
24. Ambil
25. Ablc
26. Abelecet
27. Amphortericin B
28. Anfotericine B
29. Amphotericin B Liposome
30. (1r,3s,5r,6r,9r,11r,15s,16r,17r,18s,19e,21e,23e,25e,27e,29e,31e,33r,35s,36r,37s)-33-(((2r,3s,4s,5s,6r)-4-amino-3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2h-pyran-2-yl)oxy)-1,3,5,6,9,11,17,37-octahydroxy-15,16,18-trimethyl-13-oxo-14,39-dioxabicyclo[33.3.1]nonatriaconta-19,21,23,25,27,29,31-heptaene-36-carboxylic Acid
31. (1r,3s,5r,6r,9r,11r,15s,16r,17r,18s,19e,21e,23e,25e,27e,29e,31e,33r,35s,36r,37s)-33-[(3-amino-3,6-dideoxy-beta-d-mannopyranosyl)oxy]-1,3,5,6,9,11,17,37-octahydroxy-15,16,18-trimethyl-13-oxo-14,39-dioxabicyclo[33.3.1]nonatriaconta-19,21,23,25,27,29,31-heptaene-36-carboxylic Acid
32. Amphotericin B Liposomal
33. Amphotericin B Trihydrate
34. Iab
35. Unii-7xu7a7droe
36. Fungisome
37. Amfotericina B [inn-spanish]
38. Amphotericine B [inn-french]
39. Amphotericinum B [inn-latin]
40. Ccris 5963
41. Hsdb 3008
42. Amphotericin B [usp:inn:jan]
43. Nsc-527017
44. Fungizone (tn)
45. Amphotec (tn)
46. (1s,3r,4e,6e,8e,10e,12e,14e,16e,18s,19r,20r,21s,25r,27r,30r,31r,33s,35r,37s,38r)-3-[(2r,3s,4s,5s,6r)-4-amino-3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydropyran-2-yl]oxy-19,25,27,30,31,33,35,37-octahydroxy-18,20,21-trimethyl-23-oxo-22,39-dioxabicyclo[33.3.1]nonatriaconta-4,6,8,10,12,14,16-heptaene-38-carboxylic Acid
47. Ambisome (tn)
48. Amp B
49. Cas-1397-89-3
50. Einecs 215-742-2
51. Ns 718
52. Brn 0078342
53. Ai3-26528
54. Prestwick3_000410
55. Amphotericin B (85%)
56. Amphotericin B Solubilized
57. Amphotericin B [mi]
58. Schembl17973
59. Amphotericin B [inn]
60. Amphotericin B [jan]
61. Bspbio_000340
62. 5-18-10-00525 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
63. Amphotericin B [hsdb]
64. Bidd:gt0351
65. Amphotericin B [vandf]
66. Bpbio1_000374
67. Nktr-024
68. Amphotericin B [mart.]
69. Amphotericin B And Cinnamon Oil
70. Amphotericin B [usp-rs]
71. Amphotericin B [who-dd]
72. Amphotericin B [who-ip]
73. Dtxsid9022601
74. Hms2096a22
75. Hms3713a22
76. Amphotericin B (jp17/usp/inn)
77. Hy-b0221
78. Amphotericin B, Streptomyces Nodosus
79. Tox21_111027
80. Tox21_202484
81. Amphotericin B [orange Book]
82. Lmpk06000002
83. S1636
84. Amphotericin B [ep Monograph]
85. Akos024464746
86. Amphotericin B [usp Monograph]
87. Zinc253387843
88. Amphotericin B Liposome [vandf]
89. Ccg-220410
90. Db00681
91. Amphotericinum B [who-ip Latin]
92. Abelcet, Liposomal Amphotericin B
93. Ncgc00260033-01
94. (1r-(1r*,3s*,5r*,6r*,9r*,11r*,15s*,16r*,17r*,18s*,19e,21e,23e,25e,27e,29e,31e,33r*,35s*,36r*,37s*))-33-((3-amino-3,6-dideoxy-beta-d-mannopyranosyl)oxy)-1,3,5,6,9,11,17,37-octahydroxy-15,16,18-trimethyl-13-oxo-14,39-dioxabicyclo(33.3.1)nonatriaconta-19,21,23,25,27,29,31-heptaene-36-carboxylic Acid
95. 14,39-dioxabicyclo(33.3.1)nonatriaconta-19,21,23,25,2 7,29,31-heptaene-36-carboxylic Acid, 33-((3-amino-3,6-dideoxy-beta-d-mannopyranosyl)oxy)-1,3,5,6,9,11,17,37-octahydroxy-15,16,18-trimethyl-13-oxo-(1r-(1r*,3s*,5r*,6r*,9r*,11r*,15s*,16r*,17r*,18s*,19e,21e,23e, 25e-27e,29e,31e,33r*,35s*,36r*,37s*))-
96. Amphotericin B Lipid Complex [mi]
97. Ab00513832
98. Amphotericin B Deoxycholate [who-dd]
99. Amphotericin B Lipid Complex [vandf]
100. Amphotericin B Liposomal Complex [mi]
101. C06573
102. D00203
103. Ab00513832_02
104. 397a893
105. Q412223
106. 1397-89-3, C47h73no17
107. Amphotericin B From Streptomyces Sp., ~80% (hplc), Powder
108. Amphotericin B From Streptomyces Sp., Bioreagent, Suitable For Cell Culture, ~80% (hplc)
109. Amphotericin B Solubilized, Powder, Gamma-irradiated, Bioxtra, Suitable For Cell Culture
110. (1r,3s,5r,6r,9r,11r,15s,16r,17r,18s,19e,21e,23e,25e,27e,29e,31e,33r,35s,36r,37s)-33-[(2r,3s,4s,5s,6r)-4-amino-3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-1,3,5,6,9,11,17,37-octahydroxy-15,16,18-trimethyl-13-oxo-14,39-dioxabicyclo[33.3.1]nonatriaconta-19,21,23,25,
111. (1r,3s,5r,6r,9r,11r,15s,16r,17r,18s,19e,21e,23e,25e,27e,29e,31e,33r,35s,36r,37s)-33-[(2r,3s,4s,5s,6r)-4-amino-3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-1,3,5,6,9,11,17,37-octahydroxy-15,16,18-trimethyl-13-oxo-14,39-dioxabicyclo[33.3.1]nonatriaconta-19,21,23,25,27,29,31-heptaene-36-carboxylic Acid
112. (1r,3s,5r,6r,9r,11r,15s,16r,17r,18s,19e,21e,23e,25e,27e,29e,31e,33r,35s,36r,37s)-33-[(3-amino-3,6-dideoxy-?-d-mannopyranosyl)oxy]-1,3,5,6,9,11,17,37-octahydroxy-15,16,18-trimethyl-13-oxo-14,39-dioxabicyclo[33.3.1]nonatriaconta-19,21,23,25,27,29,31-heptaene-36-carboxylic Acid
113. (1r,3s,5r,6r,9r,11r,15s,16r,17r,18s,19e,21e,23e,25e,27e,29e,31e,33r,35s,36r,37s)-33-[(3-amino-3,6-dideoxy-beta-d-mannopyranosyl)oxy]-1,3,5,6,9,11,17,37-octahydroxy-15,16,18-trimethyl-13-oxo-14,39-dioxabicyclo[33.3.1]nonatriaconta-19,21,23,25,27,29,31-he
114. (1r,3s,5r,6r,9r,11r,15s,16r,17r,18s,19e,21e,23e,25e,27e,29e,31e,33r,35s,36r,37s)-33-[(3-amino-3,6-dideoxy-beta-d-mannopyranosyl)oxy]-1,3,5,6,9,11,17,37-octahydroxy-15,16,18-trimethyl-13-oxo-14,39-dioxabicyclo[33.3.1]nonatriaconta-19,21,23,25,27,29,31-hept
115. (1r,3s,5r,6r,9r,11r,15s,16r,17r,18s,33r,35s,36r,37s)-33-{[(2r,3s,4s,5s,6r)-4-amino-3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy}-1,3,5,6,9,11,17,37-octahydroxy-15,16,18-trimethyl-13-oxo-14,39-dioxabicyclo[33.3.1]nonatriaconta-19,21,23,25,27,29,31-heptaene-36-carbo
116. (1s,3r,4e,6e,8e,10e,12e,14e,16e,18s,19r,20r,21s,25r,27r,30r,31r,33s,35r,37s,38r)-3-[(2r,3s,4s,5s,6r)-4-amino-3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-19,25,27,30,31,33,35,37-octahydroxy-18,20,21-trimethyl-
117. 23-oxo-22,39-dioxabicyclo[33.3.1]nonatriaconta-4,6,8,10,12,14,16-heptaene-38-carboxylic Acid
118. Amphotericin B From Streptomyces Sp., Vetec(tm) Reagent Grade, Bioreagent, Suitable For Cell Culture, ~80%
119. Amphotericin B Solution, 250 Mug/ml In Deionized Water, Sterile-filtered, Bioreagent, Suitable For Cell Culture
| Molecular Weight | 924.1 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C47H73NO17 |
| XLogP3 | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 12 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 18 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 923.48784986 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 923.48784986 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 320 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 65 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1670 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 19 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 7 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Abelcet |
| PubMed Health | Amphotericin B Lipid Complex (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal, Antiprotozoal |
| Active Ingredient | Amphotericin b |
| Dosage Form | Injectable, lipid complex |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 5mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Sigma Tau |
| 2 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ambisome |
| PubMed Health | Amphotericin B Liposome (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal, Antiprotozoal |
| Active Ingredient | Amphotericin b |
| Dosage Form | Injectable, liposomal |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 50mg/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Astellas |
| 3 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Amphotec |
| PubMed Health | Amphotericin B Cholesteryl Sulfate Complex (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal, Antiprotozoal |
| Drug Label | AMPHOTEC is a sterile, pyrogen-free, lyophilized powder for reconstitution and intravenous (IV) administration. AMPHOTEC consists of a 1:1 (molar ratio) complex of amphotericin B and cholesteryl sulfate. Upon reconstitution, AMPHOTEC forms a colloi... |
| Active Ingredient | Amphotericin b |
| Dosage Form | Injectable, lipid complex |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 100mg/vial; 50mg/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Alkopharma Usa |
| 4 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Amphotericin b |
| PubMed Health | Amphotericin B (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal, Antiprotozoal |
| Drug Label | Amphotericin B for Injection USP contains amphotericin B, an antifungal polyene antibiotic obtained from a strain of Streptomyces nodosus. Amphotericin B is designated chemically as [1R- (1R*, 3S*, 5R*, 6R*, 9R*, 11R*, 15S*, 16R*, 17R*, 18S*, 19E, 21... |
| Active Ingredient | Amphotericin b |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 50mg/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | X Gen Pharms |
| 5 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Abelcet |
| PubMed Health | Amphotericin B Lipid Complex (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal, Antiprotozoal |
| Active Ingredient | Amphotericin b |
| Dosage Form | Injectable, lipid complex |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 5mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Sigma Tau |
| 6 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ambisome |
| PubMed Health | Amphotericin B Liposome (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal, Antiprotozoal |
| Active Ingredient | Amphotericin b |
| Dosage Form | Injectable, liposomal |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 50mg/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Astellas |
| 7 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Amphotec |
| PubMed Health | Amphotericin B Cholesteryl Sulfate Complex (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal, Antiprotozoal |
| Drug Label | AMPHOTEC is a sterile, pyrogen-free, lyophilized powder for reconstitution and intravenous (IV) administration. AMPHOTEC consists of a 1:1 (molar ratio) complex of amphotericin B and cholesteryl sulfate. Upon reconstitution, AMPHOTEC forms a colloi... |
| Active Ingredient | Amphotericin b |
| Dosage Form | Injectable, lipid complex |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 100mg/vial; 50mg/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Alkopharma Usa |
| 8 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Amphotericin b |
| PubMed Health | Amphotericin B (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal, Antiprotozoal |
| Drug Label | Amphotericin B for Injection USP contains amphotericin B, an antifungal polyene antibiotic obtained from a strain of Streptomyces nodosus. Amphotericin B is designated chemically as [1R- (1R*, 3S*, 5R*, 6R*, 9R*, 11R*, 15S*, 16R*, 17R*, 18S*, 19E, 21... |
| Active Ingredient | Amphotericin b |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 50mg/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | X Gen Pharms |
Ambecides; Antibiotics, Antifungal; Antibiotics, Macrolide; Antiprotozoal Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
MEDICATION: Antifungal; (VET): Antifungal
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. 13th Edition, Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2001., p. 98
MEDICATION (VET): ... Blastomycosis, histoplasmosis.
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 18
Parenteral amphotericin B is used as a secondary agent in the treatment of paracoccidioidomycosis caused by Paracoccidioide brasillensis. /NOT included in US product labeling/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 131
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for AMPHOTERICIN B (19 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Rash (including maculopapular or vesiculobullous rash), purpura, pruritus, urticaria, sweating, exfoliative dermatitis, erythema multiforme, alopecia, dry skin, and skin discoloration or ulcer, have been reported in patients receiving amphotericin B.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 538
IV administration of conventional amphotericin B, amphotericin B cholesteryl sulfate complex, amphotericin B lipid complex, or amphotericin B liposomal may cause erythema, pain, or inflammation at the injection site. Phlebitis or thrombophlebitis has been reported with conventional IV amphotericin B. The manufacturer of conventional IV amphotericin B and some clinicians suggest that the addition of 500-1000 units of heparin to the amphotericin B infusion, the use of a pediatric scalp-vein needle, or alternate-day therapy may decrease the incidence of thrombophlebitis. Extravasation of the drug causes local irritation.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 538
Conventional IV amphotericin B is associated with a high incidence of adverse effects, and most patients who receive the drug experience potentially severe adverse effects at some time during the course of therapy. Acute infusion reactions (e.g., fever, chills, headache, nausea, vomiting) and nephrotoxicity are the most frequent adverse reactions to conventional IV amphotericin B. Although clinical experience with amphotericin B cholesteryl sulfate complex, amphotericin B lipid complex, and amphotericin B liposomal is limited to date, these drugs appear to be better tolerated than conventional IV amphotericin B. As with conventional IV amphotericin B, the most frequent adverse reactions to amphotericin B cholesteryl sulfate complex, amphotericin B lipid complex, or amphotericin B liposomal are acute infusion reactions; however, data accumulated to date indicate that lipid-based and liposomal formulations of amphotericin B may be associated with a lower overall incidence of adverse effects and a lower incidence of hematologic and renal toxicity than the conventional formulation of the drug.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 537
Acute infusion reactions consisting of fever, shaking chills, hypotension, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, headache, dyspnea, and tachypnea may occur 1-3 hours after initiation of IV infusions of conventional amphotericin B, amphotericin B cholesteryl sulfate, amphotericin B lipid complex, or amphotericin B liposomal. These reactions are most severe and occur most frequently with initial doses and usually lessen with subsequent doses. Fever (with or without shaking chills) may occur as soon as 15-20 minutes after IV infusions of conventional amphotericin B are started. The majority of patients receiving conventional IV amphotericin B (50-90%) exhibit some degree of intolerance to initial doses of the drug, even when therapy is initiated with low doses. Although these reactions become less frequent following subsequent doses or administration of the drug on alternate days, they recur if conventional IV amphotericin B therapy is interrupted and then reinstituted.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 537
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for AMPHOTERICIN B (18 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Used to treat potentially life threatening fungal infections.
FDA Label
Amphotericin B shows a high order of in vitro activity against many species of fungi. Histoplasma capsulatum, Coccidioides immitis, Candida species, Blastomyces dermatitidis, Rhodotorula, Cryptococcus neoformans, Sporothrix schenckii, Mucor mucedo, and Aspergillus fumigatus are all inhibited by concentrations of amphotericin B ranging from 0.03 to 1.0 mcg/mL in vitro. While Candida albicans is generally quite susceptible to amphotericin B, non-albicans species may be less susceptible. Pseudallescheria boydii and Fusarium sp. are often resistant to amphotericin B. The antibiotic is without effect on bacteria, rickettsiae, and viruses.
Amebicides
Agents which are destructive to amebae, especially the parasitic species causing AMEBIASIS in man and animal. (See all compounds classified as Amebicides.)
Antiprotozoal Agents
Substances that are destructive to protozoans. (See all compounds classified as Antiprotozoal Agents.)
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
Antifungal Agents
Substances that destroy fungi by suppressing their ability to grow or reproduce. They differ from FUNGICIDES, INDUSTRIAL because they defend against fungi present in human or animal tissues. (See all compounds classified as Antifungal Agents.)
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A01 - Stomatological preparations
A01A - Stomatological preparations
A01AB - Antiinfectives and antiseptics for local oral treatment
A01AB04 - Amphotericin B
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A07 - Antidiarrheals, intestinal antiinflammatory/antiinfective agents
A07A - Intestinal antiinfectives
A07AA - Antibiotics
A07AA07 - Amphotericin B
G - Genito urinary system and sex hormones
G01 - Gynecological antiinfectives and antiseptics
G01A - Antiinfectives and antiseptics, excl. combinations with corticosteroids
G01AA - Antibiotics
G01AA03 - Amphotericin B
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J02 - Antimycotics for systemic use
J02A - Antimycotics for systemic use
J02AA - Antibiotics
J02AA01 - Amphotericin B
Absorption
Bioavailability is 100% for intravenous infusion.
Clearance
39 +/- 22 mL/hr/kg [febrile neutropenic cancer and bone marrow transplant patients receiving infusion of 1 mg/kg/day at Day 1]
17 +/- 6 mL/hr/kg [febrile neutropenic cancer and bone marrow transplant patients receiving infusion of 1 mg/kg/day 3-20 days later]
51 +/- 44 mL/hr/kg [febrile neutropenic cancer and bone marrow transplant patients receiving infusion of 2.5 mg/kg/day at Day 1]
22 +/- 15 mL/hr/kg [febrile neutropenic cancer and bone marrow transplant patients receiving infusion of 2.5 mg/kg/day 3-20 days later]
21 +/- 14 mL/hr/kg [febrile neutropenic cancer and bone marrow transplant patients receiving infusion of 5 mg/kg/day at Day 1]
11 +/- 6 mL/hr/kg [febrile neutropenic cancer and bone marrow transplant patients receiving infusion of 5 mg/kg/day 3-20 days later]
The pharmacokinetics of amphotericin B vary substantially depending on whether the drug is administered as conventional amphotericin B (formulated with sodium desoxycholate), amphotericin B cholesteryl sulfate complex, amphotericin B lipid complex, or amphotericin B liposomal, and pharmacokinetic parameters reported for one amphotericin B formulation should not be used to predict the pharmacokinetics of any other amphotericin B formulation.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 541
Amphotericin B is poorly absorbed from the GI tract and must be given parenterally to treat systemic fungal infections. In one study, immediately after completion of iv infusion of 30 mg of amphotericin B (administered over a period of several hours), average peak serum concentrations were about 1 ug/ml; when the dose was 50 mg, average peak serum concentrations were approximately 2 ug/ml. Immediately after infusion, no more than 10% of the amphotericin B dose can be accounted for in serum. Average minimum serum concentrations (recorded just prior to the next drug infusion) of approximately 0.4 ug/ml have been reported when doses of 30 mg were given daily or when doses of 60 mg were given every other day.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 541
Information on the distribution of amphotericin B is limited, although distribution is apparently multicompartmental. The volume of distribution of the drug following administration of conventional amphotericin B has been reported to be 4 L/kg; the volume of distribution at steady state after administration of amphotericin B cholesteryl sulfate is reported to be 3.8-4.1 L/kg. Amphotericin B concentrations attained in inflamed pleura, peritoneum, synovium, and aqueous humor following IV administration of conventional amphotericin B reportedly are about 60% of concurrent plasma concentrations; the drug also is distributed into vitreous humor, pleural, pericardial, peritoneal, and synovial fluid. Amphotericin B reportedly crosses the placenta and low concentrations are attained in amniotic fluid.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 541
Following IV administration of conventional amphotericin B, CSF concentrations of the drug are approximately 3% of concurrent serum concentrations. To achieve fungistatic CSF concentrations, the drug must usually be administered intrathecally. In patients with meningitis, intrathecal administration of 0.2-0.3 mg of conventional amphotericin B via a subcutaneous reservoir has produced peak CSF concentrations of 0.5-0.8 ug/mL; 24 hours after the dose, CSF concentrations were 0.11-0.29 ug/mL. Amphotericin B is removed from the CSF by arachnoid villi and appears to be stored in the extracellular compartment of the brain, which may act as a reservoir for the drug.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 541
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for AMPHOTERICIN B (14 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Exclusively renal
An elimination half-life of approximately 15 days follows an initial plasma half-life of about 24 hours.
Amphotericin B cholesteryl sulfate complex has a distribution half-life of 3.5 minutes and an elimination half-life of 27.5-28.2 hours. /Amphotericin B cholesteryl sulfate complex/
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 541
Following IV administration of conventional amphotericin B in patients whose renal function is normal prior to therapy, the initial plasma half-life is approximately 24 hours. After the first 24 hours, the rate at which amphotericin B is eliminated decreases and an elimination half-life of approximately 15 days has been reported.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 541
Elimination, half life: Neonates: Variable (range, 18 to 62.5 hours). Children: Variable (range, 5.5 to 40.3 hours). Adults: Approximately 24 hours. Terminal half life: Approximately 15 days. NOTE: There is large interindividual variation among neonates in the elimination of amphotericin B. Amphotericin B may persist in the circulation of neonates for up to 17 days after it has been discontinued.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 131
. The half life of elimination of amphotericin B from the lungs /of rats/ was 4.8 days according to serial sacrifices done after a single dose of 3.2 mg of aerosol doses of amphotericin B per kg.
PMID:2327759 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC171515 Niki Y et al; Antimicrob Agents Chemother 34 (1): 29-32 (1990)
Amphotericin B is fungistatic or fungicidal depending on the concentration obtained in body fluids and the susceptibility of the fungus. The drug acts by binding to sterols (ergosterol) in the cell membrane of susceptible fungi. This creates a transmembrane channel, and the resultant change in membrane permeability allowing leakage of intracellular components. Ergosterol, the principal sterol in the fungal cytoplasmic membrane, is the target site of action of amphotericin B and the azoles. Amphotericin B, a polyene, binds irreversibly to ergosterol, resulting in disruption of membrane integrity and ultimately cell death.
Amphotericin B usually is fungistatic in action at concentrations obtained clinically, but may be fungicidal in high concentrations or against very susceptible organisms. Amphotericin B exerts its antifungal activity principally by binding to sterols (e.g., ergosterol) in the fungal cell membrane. As a result of this binding, the cell membrane is no longer able to function as a selective barrier and leakage of intracellular contents occurs. Cell death occurs in part as a result of permeability changes, but other mechanisms also may contribute to the in vivo antifungal effects of amphotericin B against some fungi. Amphotericin B is not active in vitro against organisms that do not contain sterols in their cell membranes (eg, bacteria).
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 540
Binding to sterols in mammalian cells (such as certain kidney cells and erythrocytes) may account for some of the toxicities reported with conventional amphotericin B therapy. At usual therapeutic concentrations of amphotericin B, the drug does not appear to hemolyze mature erythrocytes, and the anemia seen with conventional IV amphotericin B therapy may result from the action of the drug on actively metabolizing and dividing erythropoietic cells.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 540
...Nephrotoxicity associated with conventional IV amphotericin B appears to involve several mechanisms, including a direct vasoconstrictive effect on renal arterioles that reduces glomerular and renal tubular blood flow and a lytic action on cholesterol-rich lysosomal membranes of renal tubular cells. ...
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 537
 ChemWerth works in generic API development & supply, non-infringement patent strategy development and regulatory support.
ChemWerth works in generic API development & supply, non-infringement patent strategy development and regulatory support.
 LGM Pharma accelerates & optimizes the new product pathway from early development through commercialization.
LGM Pharma accelerates & optimizes the new product pathway from early development through commercialization.
 Century has been an API manufacturer for over 40 years & is the partner of choice for multipurpose custom manufacturing projects.
Century has been an API manufacturer for over 40 years & is the partner of choice for multipurpose custom manufacturing projects.
 Shanghai Minbiotech is the leading producer of biopharmaceuticals and a variety of high-end generic & innovative drugs.
Shanghai Minbiotech is the leading producer of biopharmaceuticals and a variety of high-end generic & innovative drugs.

GDUFA
DMF Review : N/A
Rev. Date :
Pay. Date :
DMF Number : 9564
Submission : 1992-03-06
Status : Active
Type : II

GDUFA
DMF Review : N/A
Rev. Date :
Pay. Date :
DMF Number : 2578
Submission : 1975-12-17
Status : Inactive
Type : II

GDUFA
DMF Review : N/A
Rev. Date :
Pay. Date :
DMF Number : 7514
Submission : 1988-06-03
Status : Inactive
Type : II

GDUFA
DMF Review : N/A
Rev. Date :
Pay. Date :
DMF Number : 10126
Submission : 1987-06-26
Status : Inactive
Type : II

 FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]
FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]
 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.

Certificate Number : R1-CEP 2005-212 - Rev 04
Status : Valid
Issue Date : 2023-08-17
Type : Chemical
Substance Number : 1292

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.

Certificate Number : R1-CEP 2002-079 - Rev 09
Status : Valid
Issue Date : 2023-05-12
Type : Chemical
Substance Number : 1292

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.

Certificate Number : CEP 2023-150 - Rev 01
Status : Valid
Issue Date : 2025-05-14
Type : Chemical
Substance Number : 1292

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.

Amphotericin B, Process II, For Use In The Manuf...
Certificate Number : CEP 2023-152 - Rev 00
Status : Valid
Issue Date : 2024-07-03
Type : Chemical
Substance Number : 1292

 FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]
FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results] 
API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Details:
The funds will be used the Company’s antifungal drug candidate MAT2203 (Amphotericin B) for the treatment of invasive fungal infections.
Lead Product(s): Amphotericin B,Fluocytosine
Therapeutic Area: Infections and Infectious Diseases Brand Name: MAT2203
Study Phase: Phase IIIProduct Type: Other Small Molecule
Sponsor: Undisclosed
Deal Size: $3.3 million Upfront Cash: Undisclosed
Deal Type: Private Placement February 13, 2025

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Lead Product(s) : Amphotericin B,Fluocytosine
Therapeutic Area : Infections and Infectious Diseases
Highest Development Status : Phase III
Partner/Sponsor/Collaborator : Undisclosed
Deal Size : $3.3 million
Deal Type : Private Placement
Matinas BioPharma Acquires Preferred Stock, Appoints Dr. Robin L. Smith
Details : The funds will be used the Company’s antifungal drug candidate MAT2203 (Amphotericin B) for the treatment of invasive fungal infections.
Product Name : MAT2203
Product Type : Other Small Molecule
Upfront Cash : Undisclosed
February 13, 2025

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Details:
MAT2203 (Amphotericin B) is a potential oral broad-spectrum treatment for invasive deadly fungal infections, which is being evaluated in patients with Limb-threatening mucor infection.
Lead Product(s): Amphotericin B
Therapeutic Area: Infections and Infectious Diseases Brand Name: MAT2203
Study Phase: PreclinicalProduct Type: Other Small Molecule
Sponsor: Inapplicable
Deal Size: Inapplicable Upfront Cash: Inapplicable
Deal Type: Inapplicable June 24, 2024

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Lead Product(s) : Amphotericin B
Therapeutic Area : Infections and Infectious Diseases
Highest Development Status : Preclinical
Partner/Sponsor/Collaborator : Inapplicable
Deal Size : Inapplicable
Deal Type : Inapplicable
Matinas Bio Reports Successful Treatment of Limb-Threatening Mucor Infection with MAT2203
Details : MAT2203 (Amphotericin B) is a potential oral broad-spectrum treatment for invasive deadly fungal infections, which is being evaluated in patients with Limb-threatening mucor infection.
Product Name : MAT2203
Product Type : Other Small Molecule
Upfront Cash : Inapplicable
June 24, 2024

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Details:
MAT2203 (amphotericin B) is an orally administered lipid nanocrystal (LNC) formulation of amphotericin B, which is being evaluated for the treatment of invasive fusarium infection.
Lead Product(s): Amphotericin B
Therapeutic Area: Infections and Infectious Diseases Brand Name: MAT2203
Study Phase: Phase IProduct Type: Other Small Molecule
Sponsor: Inapplicable
Deal Size: Inapplicable Upfront Cash: Inapplicable
Deal Type: Inapplicable March 22, 2024

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Lead Product(s) : Amphotericin B
Therapeutic Area : Infections and Infectious Diseases
Highest Development Status : Phase I
Partner/Sponsor/Collaborator : Inapplicable
Deal Size : Inapplicable
Deal Type : Inapplicable
Three Patients in Matinas BioPharma's Program Achieve Complete Response to Infection
Details : MAT2203 (amphotericin B) is an orally administered lipid nanocrystal (LNC) formulation of amphotericin B, which is being evaluated for the treatment of invasive fusarium infection.
Product Name : MAT2203
Product Type : Other Small Molecule
Upfront Cash : Inapplicable
March 22, 2024

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Details:
MAT2203 (amphotericin B), an oral formulation using LNC technology, is in preclinical studies for invasive aspergillosis with limited treatment options.
Lead Product(s): Amphotericin B
Therapeutic Area: Infections and Infectious Diseases Brand Name: MAT2203
Study Phase: IND EnablingProduct Type: Other Small Molecule
Sponsor: Inapplicable
Deal Size: Inapplicable Upfront Cash: Inapplicable
Deal Type: Inapplicable February 26, 2024

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Lead Product(s) : Amphotericin B
Therapeutic Area : Infections and Infectious Diseases
Highest Development Status : IND Enabling
Partner/Sponsor/Collaborator : Inapplicable
Deal Size : Inapplicable
Deal Type : Inapplicable
Matinas BioPharma Updates Outcomes on MAT2203 Compassionate Use Program
Details : MAT2203 (amphotericin B), an oral formulation using LNC technology, is in preclinical studies for invasive aspergillosis with limited treatment options.
Product Name : MAT2203
Product Type : Other Small Molecule
Upfront Cash : Inapplicable
February 26, 2024

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Details:
MAT2203 (amphotericin B) acts by binding to the sterol component of a cell membrane leading to alterations in cell permeability & cell death. It is being evaluated for invasive aspergillosis.
Lead Product(s): Amphotericin B
Therapeutic Area: Infections and Infectious Diseases Brand Name: MAT2203
Study Phase: IND EnablingProduct Type: Other Small Molecule
Sponsor: Inapplicable
Deal Size: Inapplicable Upfront Cash: Inapplicable
Deal Type: Inapplicable February 20, 2024

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Lead Product(s) : Amphotericin B
Therapeutic Area : Infections and Infectious Diseases
Highest Development Status : IND Enabling
Partner/Sponsor/Collaborator : Inapplicable
Deal Size : Inapplicable
Deal Type : Inapplicable
Matinas Reaches Agreement with FDA for Phase 3 to Support NDA for MAT2203 in Aspergillosis
Details : MAT2203 (amphotericin B) acts by binding to the sterol component of a cell membrane leading to alterations in cell permeability & cell death. It is being evaluated for invasive aspergillosis.
Product Name : MAT2203
Product Type : Other Small Molecule
Upfront Cash : Inapplicable
February 20, 2024

Details:
The partnership allows Cipla to scale up amphotericin, conducting studies and seeking regulatory approvals for commercialization in treating fungal keratitis.
Lead Product(s): Amphotericin B
Therapeutic Area: Infections and Infectious Diseases Brand Name: Undisclosed
Study Phase: PreclinicalProduct Type: Other Small Molecule
Sponsor: Cipla
Deal Size: Undisclosed Upfront Cash: Undisclosed
Deal Type: Partnership February 15, 2024

Lead Product(s) : Amphotericin B
Therapeutic Area : Infections and Infectious Diseases
Highest Development Status : Preclinical
Partner/Sponsor/Collaborator : Cipla
Deal Size : Undisclosed
Deal Type : Partnership
Cipla Partners with CSIR-CDRI to Develop Formulation for Fungal Keratitis
Details : The partnership allows Cipla to scale up amphotericin, conducting studies and seeking regulatory approvals for commercialization in treating fungal keratitis.
Product Name : Undisclosed
Product Type : Other Small Molecule
Upfront Cash : Undisclosed
February 15, 2024

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Details:
MAT2203 (amphotericin B) is an oral formulation based on the LNC platform delivery technology. It is being evaluated in preclinical studies for the treatment of invasive aspergillosis with limited or no treatment options.
Lead Product(s): Amphotericin B
Therapeutic Area: Infections and Infectious Diseases Brand Name: MAT2203
Study Phase: PreclinicalProduct Type: Other Small Molecule
Sponsor: Inapplicable
Deal Size: Inapplicable Upfront Cash: Inapplicable
Deal Type: Inapplicable December 21, 2023

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Lead Product(s) : Amphotericin B
Therapeutic Area : Infections and Infectious Diseases
Highest Development Status : Preclinical
Partner/Sponsor/Collaborator : Inapplicable
Deal Size : Inapplicable
Deal Type : Inapplicable
Details : MAT2203 (amphotericin B) is an oral formulation based on the LNC platform delivery technology. It is being evaluated in preclinical studies for the treatment of invasive aspergillosis with limited or no treatment options.
Product Name : MAT2203
Product Type : Other Small Molecule
Upfront Cash : Inapplicable
December 21, 2023

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Details:
MAT2203 is a potential oral formulation broad-spectrum treatment for invasive deadly fungal infections. Although amphotericin B is a fungicidal agent, it is currently only available through an intravenous, while MAT2203 has oral route of administration.
Lead Product(s): Amphotericin B
Therapeutic Area: Urology Brand Name: MAT2203
Study Phase: PreclinicalProduct Type: Other Small Molecule
Sponsor: Inapplicable
Deal Size: Inapplicable Upfront Cash: Inapplicable
Deal Type: Inapplicable November 10, 2023

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Lead Product(s) : Amphotericin B
Therapeutic Area : Urology
Highest Development Status : Preclinical
Partner/Sponsor/Collaborator : Inapplicable
Deal Size : Inapplicable
Deal Type : Inapplicable
Details : MAT2203 is a potential oral formulation broad-spectrum treatment for invasive deadly fungal infections. Although amphotericin B is a fungicidal agent, it is currently only available through an intravenous, while MAT2203 has oral route of administration.
Product Name : MAT2203
Product Type : Other Small Molecule
Upfront Cash : Inapplicable
November 10, 2023

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Details:
Late-breaking data demonstrate that MAT2203 achieves impressive in vivo efficacy and has in vitro killing activity 5 to 10-fold higher than liposomal amphotericin B against two clinical isolates of pulmonary mucormycosis.
Lead Product(s): Amphotericin B
Therapeutic Area: Infections and Infectious Diseases Brand Name: MAT2203
Study Phase: Phase IIIProduct Type: Other Small Molecule
Sponsor: University of Minnesota
Deal Size: Inapplicable Upfront Cash: Inapplicable
Deal Type: Inapplicable December 10, 2022

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Lead Product(s) : Amphotericin B
Therapeutic Area : Infections and Infectious Diseases
Highest Development Status : Phase III
Partner/Sponsor/Collaborator : University of Minnesota
Deal Size : Inapplicable
Deal Type : Inapplicable
Matinas BioPharma to Present New MAT2203 (Oral Amphotericin B) Data During IDWeek 2022
Details : Late-breaking data demonstrate that MAT2203 achieves impressive in vivo efficacy and has in vitro killing activity 5 to 10-fold higher than liposomal amphotericin B against two clinical isolates of pulmonary mucormycosis.
Product Name : MAT2203
Product Type : Other Small Molecule
Upfront Cash : Inapplicable
December 10, 2022

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Details:
MAT2203 (amphotericin B) is an oral, LNC formulation of the highly effective, but also highly toxic, antifungal medicine amphotericin B, primarily used as a first-line treatment for invasive fungal infections.
Lead Product(s): Amphotericin B
Therapeutic Area: Infections and Infectious Diseases Brand Name: MAT2203
Study Phase: Phase I/ Phase IIProduct Type: Other Small Molecule
Sponsor: Inapplicable
Deal Size: Inapplicable Upfront Cash: Inapplicable
Deal Type: Inapplicable October 21, 2022

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Lead Product(s) : Amphotericin B
Therapeutic Area : Infections and Infectious Diseases
Highest Development Status : Phase I/ Phase II
Partner/Sponsor/Collaborator : Inapplicable
Deal Size : Inapplicable
Deal Type : Inapplicable
Details : MAT2203 (amphotericin B) is an oral, LNC formulation of the highly effective, but also highly toxic, antifungal medicine amphotericin B, primarily used as a first-line treatment for invasive fungal infections.
Product Name : MAT2203
Product Type : Other Small Molecule
Upfront Cash : Inapplicable
October 21, 2022

 FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]
FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]Related Excipient Companies

Global Sales Information

Company : Astellas Pharma
Amphotericin B Liposome
Drug Cost (USD) : 1,411,630
Year : 2023
Prescribers : 144
Prescriptions : 463

Portfolio PDF
Product Web Link
Virtual Booth
Digital Content
Website
Corporate PDF
Company : X-Gen Pharmaceu
Amphotericin B
Drug Cost (USD) : 2,148
Year : 2023
Prescribers : 12
Prescriptions : 50

Portfolio PDF
Product Web Link
Virtual Booth
Digital Content
Website
Corporate PDF
Company : Auromedics-Eugi
Amphotericin B Liposome
Drug Cost (USD) : 425,340
Year : 2023
Prescribers : 66
Prescriptions : 141

Portfolio PDF
Product Web Link
Virtual Booth
Digital Content
Website
Corporate PDF
Company : Sun Pharmaceuti
Amphotericin B Liposome
Drug Cost (USD) : 545,987
Year : 2023
Prescribers : 102
Prescriptions : 240

Portfolio PDF
Product Web Link
Virtual Booth
Digital Content
Website
Corporate PDF
Company : Leadiant Biosci
Amphotericin B Lipid Complex
Drug Cost (USD) : 297,179
Year : 2022
Prescribers : 113
Prescriptions : 350

Portfolio PDF
Product Web Link
Virtual Booth
Digital Content
Website
Corporate PDF
Company : Sun Pharmaceuti
Amphotericin B Liposome
Drug Cost (USD) : 371,249
Year : 2022
Prescribers : 48
Prescriptions : 107

Portfolio PDF
Product Web Link
Virtual Booth
Digital Content
Website
Corporate PDF
Company : X-Gen Pharmaceu
Amphotericin B
Drug Cost (USD) : 69,254
Year : 2022
Prescribers : 87
Prescriptions : 263

Portfolio PDF
Product Web Link
Virtual Booth
Digital Content
Website
Corporate PDF
Company : Astellas Pharma
Amphotericin B Liposome
Drug Cost (USD) : 2,022,792
Year : 2022
Prescribers : 147
Prescriptions : 660

Portfolio PDF
Product Web Link
Virtual Booth
Digital Content
Website
Corporate PDF
Company : Leadiant Biosci
Amphotericin B Lipid Complex
Drug Cost (USD) : 504,545
Year : 2021
Prescribers : 199
Prescriptions : 697

Portfolio PDF
Product Web Link
Virtual Booth
Digital Content
Website
Corporate PDF
Company : X-Gen Pharmaceu
Amphotericin B
Drug Cost (USD) : 87,641
Year : 2021
Prescribers : 112
Prescriptions : 379

Portfolio PDF
Product Web Link
Virtual Booth
Digital Content
Website
Corporate PDF
 FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]
FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]Dosage Form :
Dosage Strength : Os Suspe 60 Ml 500 Mg/5 Ml
Price Per Pack (Euro) : 5.97
Published in :
Country : Italy
RX/OTC/DISCN : Class C

Dosage Form : Amphotericin B 100Mg 20Ml 1 Unit...
Dosage Strength : 10 VIALS EV 100 mg 20 ml + 10 needles
Price Per Pack (Euro) : 1,421.90
Published in :
Country : Italy
RX/OTC/DISCN : Class H

Dosage Form : Amphotericin B 50Mg 10Ml 1 Units...
Dosage Strength : 1 ampoule EV 50 mg 10 ml
Price Per Pack (Euro) : 11.49
Published in :
Country : Italy
RX/OTC/DISCN : Class H

Gilead Sciences Switzerland S?rl
Dosage Form : Dry Sub
Dosage Strength : 50mg
Price Per Pack (Euro) : 136.24
Published in :
Country : Switzerland
RX/OTC/DISCN : Class A

Gilead Sciences Switzerland S?rl
Dosage Form : Dry Sub
Dosage Strength : 50mg
Price Per Pack (Euro) : 1362.4
Published in :
Country : Switzerland
RX/OTC/DISCN : Class A

Dosage Form : Lozenges
Dosage Strength : 10mg
Price Per Pack (Euro) : 3.77
Published in :
Country : Switzerland
RX/OTC/DISCN : Class B

Gilead Sciences International Ltd
Dosage Form : Powder for infusion fluid, resol...
Dosage Strength : 50 mg
Price Per Pack (Euro) : 1,550.27
Published in :
Country : Norway
RX/OTC/DISCN :

Dosage Form : Susp
Dosage Strength : 10%
Price Per Pack (Euro) : 8.68
Published in :
Country : Switzerland
RX/OTC/DISCN : Class B

Dosage Form : Tabl
Dosage Strength : 100mg
Price Per Pack (Euro) : 11.2
Published in :
Country : Switzerland
RX/OTC/DISCN : Class B

 FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]
FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]Main Therapeutic Indication : Infectious Diseases
Currency : USD
2020 Revenue in Millions : 112
2019 Revenue in Millions : 110
Growth (%) : 2

Main Therapeutic Indication : Infectious Diseases
Currency : USD
2020 Revenue in Millions : 36
2019 Revenue in Millions : 40
Growth (%) : -12

Main Therapeutic Indication : Infectious Diseases
Currency : USD
2020 Revenue in Millions : 436
2019 Revenue in Millions : 407
Growth (%) : 7

Main Therapeutic Indication : Infectious Diseases
Currency : USD
2021 Revenue in Millions : 139
2020 Revenue in Millions : 111
Growth (%) : 35

Main Therapeutic Indication : Infectious Diseases
Currency : USD
2021 Revenue in Millions : 540
2020 Revenue in Millions : 436
Growth (%) : 24

Main Therapeutic Indication : Infectious Diseases
Currency : USD
2022 Revenue in Millions : 497
2021 Revenue in Millions : 540
Growth (%) : -8

Main Therapeutic Indication : Infectious Diseases
Currency : USD
2022 Revenue in Millions : 115
2021 Revenue in Millions : 138
Growth (%) : -17

Main Therapeutic Indication : Infectious Diseases
Currency : USD
2023 Revenue in Millions : 492
2022 Revenue in Millions : 497
Growth (%) : -1

Main Therapeutic Indication : Infectious Diseases
Currency : USD
2024 Revenue in Millions : 533
2023 Revenue in Millions : 492
Growth (%) : 8

Main Therapeutic Indication : Infectious Diseases (HIV, Hepatitis...
Currency : USD
2018 Revenue in Millions : 115
2017 Revenue in Millions : 97
Growth (%) : 18%

 FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]
FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
74
PharmaCompass offers a list of Amphotericin B API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Amphotericin B manufacturer or Amphotericin B supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Amphotericin B manufacturer or Amphotericin B supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Amphotericin B API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Amphotericin B API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Amphotericin B Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Amphotericin B Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Fungisome manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Fungisome, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Fungisome manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Fungisome API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Fungisome manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Fungisome supplier is an individual or a company that provides Fungisome active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Fungisome finished formulations upon request. The Fungisome suppliers may include Fungisome API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Fungisome suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Fungisome DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Fungisome active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Fungisome DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Fungisome USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Fungisome DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Fungisome USDMF includes data on Fungisome's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Fungisome USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Fungisome suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) established the Japan Drug Master File (JDMF), also known as the Master File (MF), to permit Japanese and foreign manufacturers of drug substances, intermediates, excipients, raw materials, and packaging materials (‘Products’) to voluntarily register confidential information about the production and management of their products in Japan.
The Fungisome Drug Master File in Japan (Fungisome JDMF) empowers Fungisome API manufacturers to present comprehensive information (e.g., production methods, data, etc.) to the review authority, i.e., PMDA (Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Agency).
PMDA reviews the Fungisome JDMF during the approval evaluation for pharmaceutical products. At the time of Fungisome JDMF registration, PMDA checks if the format is accurate, if the necessary items have been included (application), and if data has been attached.
click here to find a list of Fungisome suppliers with JDMF on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a Fungisome Drug Master File in Korea (Fungisome KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of Fungisome. The MFDS reviews the Fungisome KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the Fungisome KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a Fungisome KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their Fungisome API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of Fungisome suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Fungisome CEP of the European Pharmacopoeia monograph is often referred to as a Fungisome Certificate of Suitability (COS). The purpose of a Fungisome CEP is to show that the European Pharmacopoeia monograph adequately controls the purity of Fungisome EP produced by a given manufacturer. Suppliers of raw materials can prove the suitability of Fungisome to their clients by showing that a Fungisome CEP has been issued for it. The manufacturer submits a Fungisome CEP (COS) as part of the market authorization procedure, and it takes on the role of a Fungisome CEP holder for the record. Additionally, the data presented in the Fungisome CEP (COS) is managed confidentially and offers a centralized system acknowledged by numerous nations, exactly like the Fungisome DMF.
A Fungisome CEP (COS) is recognised by all 36 nations that make up the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. Fungisome CEPs may be accepted in nations that are not members of the Ph. Eur. at the discretion of the authorities there.
click here to find a list of Fungisome suppliers with CEP (COS) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Fungisome as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Fungisome API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Fungisome as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Fungisome and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Fungisome NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Fungisome suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Fungisome Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Fungisome GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Fungisome GMP manufacturer or Fungisome GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Fungisome CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Fungisome's compliance with Fungisome specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Fungisome CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Fungisome CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Fungisome may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Fungisome EP), Fungisome JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Fungisome USP).
