Acquisitions and spin-offs dominated headlines in 2019 and the tone was set very early with Bristol-Myers Squibb acquiring
New Jersey-based cancer drug company Celgene in a US$ 74 billion deal announced on
January 3, 2019. After factoring
in debt, the deal value ballooned to about US$ 95 billion, which according
to data compiled by Refinitiv, made it the largest healthcare deal on
record.
In the summer, AbbVie Inc,
which sells the world’s best-selling drug Humira, announced its acquisition of Allergan Plc, known for Botox and other cosmetic
treatments, for US$ 63 billion. While the companies are still awaiting
regulatory approval for their deal, with US$ 49 billion in combined 2019
revenues, the merged entity would rank amongst the biggest in the industry.
View Our Interactive Dashboard on Top drugs by sales in 2019 (Free Excel Available)
The big five by pharmaceutical sales — Pfizer,
Roche, J&J, Novartis and Merck
Pfizer
continued
to lead companies by pharmaceutical sales by reporting annual 2019 revenues of
US$ 51.8 billion, a decrease of US$ 1.9 billion, or 4 percent, compared to
2018. The decline was primarily attributed to the loss of exclusivity of Lyrica in 2019,
which witnessed its sales drop from US$ 5 billion in 2018 to US$ 3.3 billion in
2019.
In 2018, Pfizer’s then incoming CEO Albert Bourla had mentioned that the company did not see the need for any large-scale M&A activity as Pfizer had “the best pipeline” in its history, which needed the company to focus on deploying its capital to keep its pipeline flowing and execute on its drug launches.
Bourla stayed true to his word and barring the acquisition of Array Biopharma for US$ 11.4 billion and a spin-off to merge Upjohn, Pfizer’s off-patent branded and generic established medicines business with
Mylan, there weren’t any other big ticket deals which were announced.
The
Upjohn-Mylan merged entity will be called Viatris and is expected to have 2020
revenues between US$ 19 and US$ 20 billion
and could outpace Teva to
become the largest generic company in the world, in term of revenues.
Novartis, which had
followed Pfizer with the second largest revenues in the pharmaceutical industry
in 2018, reported its first full year earnings after spinning off its Alcon eye
care devices business division that
had US$ 7.15 billion in 2018 sales.
In 2019,
Novartis slipped two spots in the ranking after reporting total sales of US$
47.4 billion and its CEO Vas Narasimhan continued his deal-making spree by buying New
Jersey-headquartered The Medicines Company (MedCo) for US$ 9.7
billion to acquire a late-stage cholesterol-lowering
therapy named inclisiran.
As Takeda Pharmaceutical Co was
busy in 2019 on working to reduce its debt burden incurred due to its US$ 62
billion purchase of Shire Plc, which was announced in 2018, Novartis also purchased
the eye-disease medicine, Xiidra, from the Japanese drugmaker for US$ 5.3 billion.
Novartis’ management also spent a considerable part of 2019 dealing with data-integrity concerns which emerged from its 2018 buyout of AveXis, the
gene-therapy maker Novartis had acquired for US$ 8.7 billion.
The deal gave Novartis rights to Zolgensma,
a novel treatment intended for children less than two years of age with the
most severe form of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). Priced at US$ 2.1 million,
Zolgensma is currently the world’s most expensive drug.
However,
in a shocking announcement, a month after approving the drug, the US Food and
Drug Administration (FDA) issued a press release on
data accuracy issues as the agency was informed by AveXis that
its personnel had manipulated data which
the FDA used to evaluate product comparability and nonclinical (animal)
pharmacology as part of the biologics license application (BLA), which was
submitted and reviewed by the FDA.
With US$
50.0 billion (CHF 48.5 billion) in annual pharmaceutical sales, Swiss drugmaker
Roche came in at number two position in 2019
as its sales grew 11 percent driven by
its multiple sclerosis medicine Ocrevus, haemophilia drug Hemlibra and cancer medicines Tecentriq and Perjeta.
Roche’s newly introduced medicines generated US$ 5.53 billion (CHF 5.4 billion) in growth, helping offset the impact of the competition from biosimilars for its three best-selling drugs MabThera/Rituxan, Herceptin and Avastin.
In late 2019, after months of increased
antitrust scrutiny, Roche completed
its US$ 5.1 billion acquisition of Spark Therapeutics to strengthen its presence in
gene therapy.
Last year, J&J reported almost flat worldwide sales of US$ 82.1 billion. J&J’s pharmaceutical division generated US$ 42.20 billion and its medical devices and consumer health divisions brought in US$ 25.96 billion and US$ 13.89 billion respectively.
Since J&J’s consumer health division sells analgesics, digestive health along with beauty and oral care products, the US$ 5.43 billion in consumer health sales from over-the-counter drugs and women’s health products was only used in our assessment of J&J’s total pharmaceutical revenues. With combined pharmaceutical sales of US$ 47.63 billion, J&J made it to number three on our list.
While the sales of products like Stelara, Darzalex, Imbruvica, Invega Sustenna drove J&J’s pharmaceutical business to grow by 4 percent over 2018, the firm had to contend with generic competition against key revenue contributors Remicade and Zytiga.
US-headquartered Merck, which is known as
MSD (short for Merck Sharp & Dohme) outside the United States and
Canada, is set to significantly move up the rankings next year fueled by its
cancer drug Keytruda, which witnessed a 55
percent increase in sales to US$ 11.1 billion.
Merck reported total revenues of US$ 41.75 billion and also
announced it will spin off its women’s health drugs,
biosimilar drugs and older products to create a new pharmaceutical
company with US$ 6.5 billion in annual revenues.
The firm had anticipated 2020 sales between US$ 48.8 billion and US$ 50.3 billion however this week it announced that the coronavirus pandemic will reduce 2020 sales by more than $2 billion.
View Our Interactive Dashboard on Top drugs by sales in 2019 (Free Excel Available)
Humira holds on to remain world’s best-selling drug
AbbVie’s acquisition of Allergan comes as the firm faces the expiration of patent protection for Humira, which brought in a staggering US$ 19.2 billion in sales last year for
the company. AbbVie has failed to successfully acquire or develop a major new
product to replace the sales generated by its flagship drug.
In 2019, Humira’s US revenues increased 8.6 percent to US$ 14.86 billion while internationally, due
to biosimilar competition, the sales dropped 31.1 percent to US$ 4.30 billion.
Bristol Myers Squibb’s Eliquis, which is also marketed by Pfizer, maintained its number two position
and posted total sales of US$ 12.1 billion, a 23 percent increase over 2018.
While Bristol Myers Squibb’s immunotherapy treatment Opdivo, sold in partnership with Ono in Japan, saw sales increase from US$ 7.57 billion to US$ 8.0 billion, the growth paled in comparison to the US$ 3.9
billion revenue increase of Opdivo’s key immunotherapy competitor Merck’s Keytruda.
Keytruda took the number three spot in drug sales that
previously belonged to Celgene’s Revlimid, which witnessed a sales decline from US$ 9.69 billion to US$ 9.4 billion.
Cancer treatment Imbruvica, which is marketed
by J&J and AbbVie, witnessed a 30 percent increase in sales. With US$ 8.1
billion in 2019 revenues, it took the number five position.
View Our Interactive Dashboard on Top drugs by sales in 2019 (Free Excel Available)
Vaccines – Covid-19 turns competitors into partners
This year has been dominated by the single biggest health emergency in years — the novel coronavirus (Covid-19) pandemic. As drugs continue to fail to meet expectations, vaccine development has received a lot of attention.
GSK reported the highest vaccine sales of all drugmakers with
total sales of US$ 8.4 billion (GBP 7.16 billion), a significant portion of its
total sales of US$ 41.8 billion (GBP 33.754 billion).
US-based Merck’s vaccine division also reported a significant increase in sales to US$ 8.0 billion and in 2019 received FDA and EU approval to market its Ebola vaccine Ervebo.
This is the first FDA-authorized vaccine against the deadly virus which causes
hemorrhagic fever and spreads from person to person through direct contact with
body fluids.
Pfizer and Sanofi also reported an increase in their vaccine sales to US$ 6.4
billion and US$ 6.2 billion respectively and the Covid-19 pandemic has recently
pushed drugmakers to move faster than ever before and has also converted
competitors into partners.
In a rare move, drug behemoths — Sanofi and GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) —joined hands to develop a vaccine for the novel coronavirus.
The two companies plan to start human trials
in the second half of this year, and if things go right, they will file
for potential approvals by the second half of 2021.
View Our Interactive Dashboard on Top drugs by sales in 2019 (Free Excel Available)
Our view
Covid-19 has brought the world economy to a grinding halt and shifted the global attention to the pharmaceutical industry’s capability to deliver solutions to address this pandemic.
Our compilation shows that vaccines and drugs
for infectious diseases currently form a tiny fraction of the total sales of
pharmaceutical companies and few drugs against infectious diseases rank high on
the sales list.
This could well explain the limited range of
options currently available to fight Covid-19. With the pandemic currently infecting
over 3 million people spread across more than 200 countries, we can safely
conclude that the scenario in 2020 will change substantially. And so should our
compilation of top drugs for the year.
View Our Interactive Dashboard on Top drugs by sales in 2019 (Free Excel Available)
Impressions: 54752
Now that it has been
established that the novel coronavirus is going to globally impact the drug
supply chain, it becomes imperative to analyze the extent of the impact.
Since the outbreak of
the novel coronavirus — COVID-19 — in December, PharmaCompass has been constantly reaching out to
manufacturers around the world to assess the current state of the drug supply
chain. This week, we share our preliminary analysis based on the feedback we
have received from drug manufacturers around the world.
Drug shortages are
for real
Last week, the US
Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced the first human drug shortage
as a result of the coronavirus outbreak. In addition, the FDA announced it was
tracking 20 drugs that could face shortages. Some generic drugmakers are predicting shortages
as early as in June or July, due to the novel coronavirus.
The FDA did not disclose the name of the drug in shortage or the 20 drugs it is tracking, as this is considered ‘confidential commercial information’.
In India, a committee constituted by the country’s Department of Pharmaceuticals started monitoring the availability of 58 active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) to take preventive measures
against illegal hoarding and black-marketing in the country.
According to a report published in The Economic Times, after
reviewing the list of drugs, 34 were found to have no alternatives which
include critical and essential drugs like potassium clavulanate, ceftriaxone sodium sterile, piperacillin tazobactam, meropenem, vancomycin, gentamycin and ciprofloxacin.
This was immediately
followed by the Indian government restricting the exports of 13
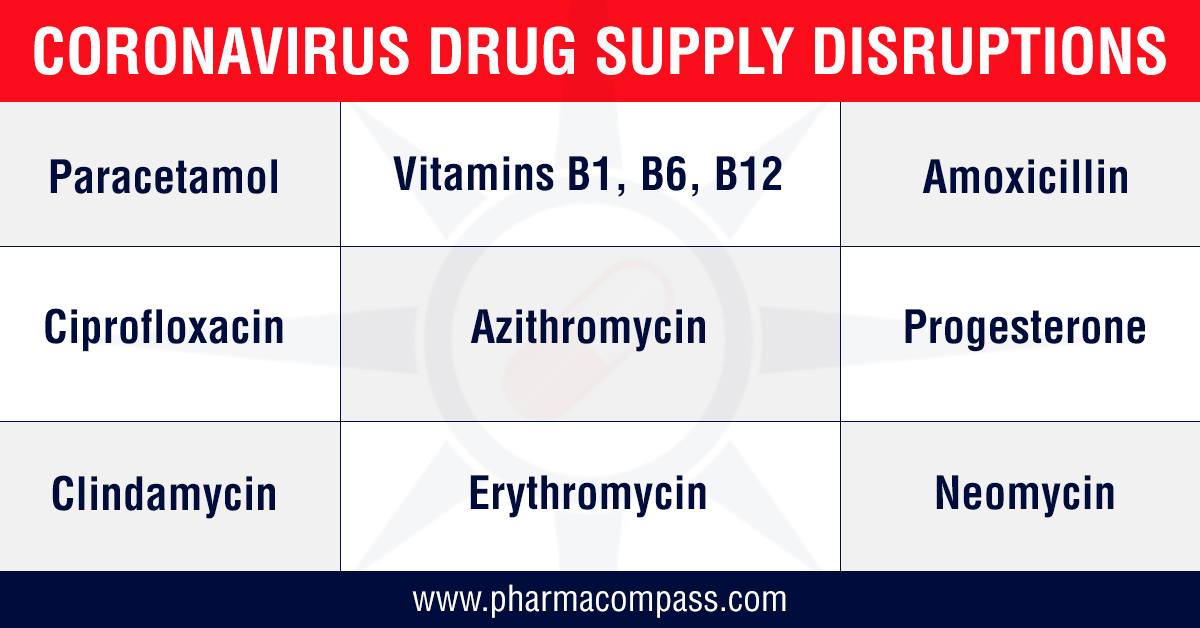
APIs along with some of their finished formulations. The list includes paracetamol, tinidazole, metronidazole, acyclovir, vitamin B1, vitamin B6, vitamin B12, progesterone, chloramphenicol and neomycin. For most
of the products on this list, India is a net importer, as there is little
domestic manufacturing of these APIs.
COVID-19 is also
likely to impact bottomlines. Leading generic drugmaker Mylan said it expects the coronavirus outbreak to impact its financial results
while some of the largest drugmakers — including AstraZeneca, Merck and Pfizer — have said that the coronavirus outbreak could affect their supplies or sales.
Paracetamol
affected; prices double in less regulated markets
The decline in industrial activity in China is certainly taking its toll, as drugs which are on the World Health Organization’s Model list of Essential Medicines are beginning to face significant price increases in the wake of disruption of key starting raw materials for bulk drugs.
The export
restriction out of India on commonly used analgesic, Paracetamol — sold under the brand names such as Tylenol (in the US), Panadol (in the UK), Dafalgan (France) and Crocin
(India) — is not surprising as the API has witnessed almost doubling of prices in less regulated markets because exports of its key building block para-amino phenol (PAP) have dramatically reduced from China.
While there are only
a few manufacturers who produce paracetamol without being dependent on Chinese
PAP, a few major manufacturers in India depend almost completely on Chinese PAP
for their paracetamol production and usually only keep three to four months of
inventory.
By the end of
February, their inventory stockpiles had halved and in the event of a continued
supply disruption, their entire inventory pipeline is likely to dry out. In
addition, Chinese paracetamol manufacturers, who export a significant amount of
their bulk ingredient production globally, including to India, are also
currently unable to export. This is beginning to create the potential of panic
among sourcing executives across the world.
Several
antibiotics also in danger of acute shortages
While paracetamol was listed on the API watch list circulated by India’s Department of Pharmaceuticals, our survey has revealed that other products on the list like ciprofloxacin, amoxicillin and azithromycin are also facing severe raw material
shortages. As a result, the prices of these bulk drugs have also increased
sharply.
In a statement to The Economic Times, leading Indian generic manufacturer Mankind Pharma’s chairman and managing director said
amoxicillin is the most commonly used API to manufacture antibiotics and the
company has invested Rs 1 billion (US$ 14 million) in placing irregular orders
with vendors to try and address the potential shortage that is expected. He
went on to say that if the situation continues until April, there will be an
acute shortage.
In a statement to the US House of Representatives last October, Janet Woodcock, the FDA’s Director of Center of Drug Evaluation and Research, said the FDA has determined that there are three WHO Essential Medicines whose API manufacturers are based only in China. The three medicines are: capreomycin, streptomycin (both indicated to treat Mycobacterium
tuberculosis) and sulfadiazine (used to treat chancroid and trachoma).
Streptomycin is also on the watch list published by India’s Department of Pharmaceuticals along with commonly used anti-hypertensives like losartan, valsartan, telmisartan and olmesartan and diabetes treatment metformin.
Intermediates
becoming a problem for generic drugmakers
PharmaCompass’ discussions have also revealed that in many cases while API manufacturing factories in China have returned to work, there are disruptions in the availability of raw materials and/or logistics at sea ports and airports which have led to unavailability of supplies.
While the FDA has a
list of the number of API facilities in China which are in a position to supply
to the United States, Woodcock said in her statement that the FDA “cannot determine with any precision the volume of API that China is actually producing, or the volume of APIs manufactured in China that is entering the US market.”
This visibility
reduces drastically when one has to assess the dependence of each API
manufacturer around the world on China for intermediates. Our discussions have
revealed that it is these intermediates which are becoming a problem for most
API manufacturers, even those based in India.
It was worth
highlighting that a manufacturing process change at an intermediate stage of
commonly used blood pressure medicine valsartan resulted in the recall of
millions of pills as it was found to contain a cancer causing impurity above
acceptable levels. Similarly, in 2008, the adulteration of heparin in China,
which killed 81 people and left 785 severely injured, was an outcome of the
subcontracting of precursor chemicals of Heparin.
Our view
The over-dependence
on China for key starting materials has been the subject of discussion ever
since we launched PharmaCompass. Rosemary Gibson explored this subject
in detail in her book China Rx: Exposing the Risks of America’s Dependence on
China for Medicine.
The restrictions imposed on industrial activity and transportation in China in the first two months of this year has resulted in NASA’s satellite images showing a decline in pollution levels over China.
While China works
towards getting its industrial and transportation engine up and running to 2019
levels, the outbreak has spread to other countries which will further increase
the demand for drugs to fight the virus.
This is a time when
the pharmaceutical industry needs to act responsibly and make decisions which
are in the best interests of patients globally.
Sharing information is one such step — it will allow for drug stockpiles and inventories that exist to be re-distributed to areas which need them most. For, in the event of an urgent need, drugs will become available to those who are most in need.
Impressions: 8184
This week in Phispers, we look at the contrasting 2017 forecasts of Mylan and Teva, resulting from the FDA approval of Mylan’s generic Copaxone. Valeant decides to return the female libido pill business to Sprout Pharma. In India, two Lupin facilities receive FDA warning letters. And Torrent Pharma’s imminent acquisition of Unichem is set to make it the country’s fifth largest drug company. Meanwhile, Pfizer admits to have faltered on integrating Hospira and QuintilesIMS rebrands itself as IQVIA.
Teva’s credit rating nosedives, as Mylan raises 2017 forecast with approval of Copaxone
Here’s the tale of two drug makers — Teva Pharmaceutical Industries
and Mylan NV. Both have been facing tough times — Teva due to the declining prices of drugs and the high debt it incurred due to its US$ 40 billion acquisition of Allergan Plc’s generics business last
year; and Mylan due to its struggles with its blockbuster emergency allergy
shot EpiPen.
But
last week clearly favored Mylan. Teva saw its credit rating cut to junk by Fitch Ratings after the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved two doses of Mylan’s generic version of Teva’s Copaxone. This multiple sclerosis drug happens to be Teva’s biggest product. As a result, Teva slashed its 2017 profit forecast for a third time.
Fitch
predicted that Teva will have to either sell assets or find external sources of
financing to meet its obligations. Mylan, on the other hand, raised its 2017 forecast as it expects to benefit from the ‘earlier-than-expected approval’ of its generic Copaxone.
Even
as Mylan hopes to benefit from its generic Copaxone, its challenges
continue unabated. Its third-quarter results highlighted the company's struggles with
declining sales of EpiPen. Sales of EpiPen fell by US$ 245.1 million on increased
competition and higher governmental rebates following a settlement with the US
Department of Justice.
EpiPens,
which contain the hormone epinephrine, are used to stave off allergic
reactions that can be fatal. However, since mid-September this year, seven
people have died as a result of failure of EpiPens to deploy correctly. In all, the FDA has
received 228 reports of EpiPen or EpiPen Jr failures since mid-September.
Teva’s JV with Guangzhou:
Meanwhile, Teva is exploring growth through the world’s second-largest market for drugs — China. It is setting
up a joint venture with Guangzhou Pharmaceutical Holdings
to manufacture and sell its drugs in the Chinese market. It is awaiting
approval from the local government.
Two years after buying ‘female-Viagra’, Valeant plans to sell it back to Sprout
After
buying the female libido pill business from Sprout Pharmaceuticals two years
back for US$ 1 billion, this week Valeant Pharmaceuticals International
said it plans to sell the business back to its original
owner.
The controversial pink pill — Addyi — made by Sprout was said to be a blockbuster drug, expected to command a US$ 2 billion market. However, Addyi proved to be a commercial disaster, with its sales being sluggish last year. What was worse, Valeant was sued on behalf of the former Sprout investors for
its alleged failure to market Addyi successfully. The complaint had said that
sales of the pill may have totaled less than US$ 10 million in 2016, far short
of the US$ 1 billion targeted by July, 2017.
Addyi, approved by the US FDA in August 2015 under intense pressure from patient advocacy groups, is meant to be taken daily. It is prescribed to activate sexual impulses, but carries a strong warning about its potential side effects — such as low blood pressure and fainting, especially when taken with alcohol. Many in the industry believe that the drug should never have been approved.
Valeant has agreed to sell its subsidiary and Addyi to a new company “associated” with Sprout’s founders, for a royalty stream of only 6 percent on global sales of Addyi. In addition, Valeant said it will provide a US$ 25 million loan to fund initial operating expenses to the new company to get things started. And in exchange, Sprout is dropping its lawsuit claiming Valeant mismanaged the launch by pricing the drug too high.
Valeant’s glaucoma drug:
Last week, the US FDA approved Valeant’s long-delayed glaucoma drug — latanoprostene bunod ophthalmic solution.
Christened Vyzulta, the solution was approved for the reduction of
intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with open-angle glaucoma. Valeant hopes
to have the drug in the market before 2017-end, Joseph Papa, CEO of Valeant,
said in a statement.
Valeant
acquired the drug through its US$ 8.7 billion buyout of Bausch + Lomb in 2013. The drug was
licensed to Bausch + Lomb by France-based Nicox.
Torrent to emerge fifth-largest Indian drug player after
Unichem buyout
In
India, Ahmedabad-headquartered Torrent Pharmaceuticals plans to acquire Unichem Laboratories’ domestic business for US$ 558 million (Rs 36 billion) by the end of this week.
The
deal would make Torrent the fifth largest player in the Indian market with
a market share of 3.4 percent. According to a Reuters report, Torrent
would buy more than 120 brands from Unichem in India and Nepal,
along with its manufacturing plant in Sikkim.
The
board of Torrent is meeting on November 10 to approve the second quarter
results. A formal announcement on the acquisition of Unichem is likely to come on
that day.
Unichem has not been able to leverage its slow-growing, mature brands. The deal includes the purchase of the brands like Unienzyme, Losar, Ampoxin and Telsar.
The
acquisition is likely to deliver synergies in both cost and revenues for Torrent’s branded drugs business in India. Torrent is expected to turnaround Unichem’s mature brand, just the way it had turned around Elder Pharma’s branded formulations,
which it had acquired in 2014 for US$ 308 million (Rs 20 billion).
Analysts expect Unichem to use the proceeds from the deal to ramp up its unprofitable international business. The transaction will strengthen Torrent’s position in cardiology, diabetology, gastro-intestinals and central nervous systems therapies, Torrent chairman Samir Mehta said.
Despite record profits, Pfizer’s CEO says troubles with Hospira persist
American pharmaceutical giant Pfizer reported third-quarter profits
last week, which more than doubled as its new drugs to treat cancer and other
illnesses made up for the hit the company took due to patent expirations.
Pfizer’s net income from the
quarter stood at US$ 2.8 billion, compared with just under US$ 1.4 billion in
the year-ago period.
However, Pfizer’s Essential Health unit remained an area of concern, into which Hospira was folded. The third quarter
revenue of this unit was down 11 percent, at US$ 5.06 billion. Pfizer had
acquired Hospira in 2015 for US$ 15
billion.
While praising other parts of the Essential Health unit (such as biosimilars and emerging markets), Pfizer CEO Ian Read pointed his finger at Hospira. “Within our Essential Health portfolio, we have been experiencing supply shortages with some products. The shortages are primarily for products from the legacy Hospira portfolio and are largely driven by capacity constraints and technical issues,” Read said.
Pfizer
has attributed a 12 percent operational decline from its sterile injectable products on “capacity constraints and technical issues” stemming from the former Hospira facilities.
At
the time of acquisition, the sterile injectables player Hospira was facing
regulatory challenges. The executives of Pfizer had assured
investors and regulators that they would quickly resolve issues at
the plants. However, two years on, the problems still persist.
Pfizer has sold or closed some of the troubled operations of Hospira. But one that has continued to bother the company is a facility in McPherson, Kansas. Earlier this year, Pfizer’s fill/finish manufacturing facility in McPherson received a warning letter from the US FDA. The manufacturing problems at the McPherson plant also derailed the launch of a generic version of Teva’s Copaxone, that was being developed by Sandoz and Momenta. The drug
was being finished at the McPherson plant, which was slapped the FDA warning
letter.
Goodbye
QuintilesIMS, Hello IQVIA
QuintilesIMS has rebranded itself and changed its name to IQVIA. Last year, Quintiles and IMS Health had merged. The merged entity — QuintilesIMS — had emerged as the world's largest pharma services provider, with a market value of almost US$ 18 billion and around 50,000 employees.
The name change (to IQVIA) is effective from November 6, 2017; and beginning November 15, 2017, equity shares of the company will trade on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) under the new name and new ticker symbol ‘IQV’.
“IQVIA may be grounded in the intelligence and capabilities of I and Q, but it is ‘via’ the path forward that we hope to inspire and ignite real change for healthcare stakeholders,” a spokesperson told Endpoints News.
Two Lupin facilities receive FDA warning letters
In another setback to Indian generic manufacturers trying to
overcome concerns of non-compliance with good manufacturing practices (GMPs),
Lupin informed the bourses that it had received a warning
letter for its formulation manufacturing facilities in Goa
and Indore (Pithampur Unit II).
In April 2017, Lupin had received three Form 483 observations for its Goa facility, and a month later six Form 483 observations for Pithampur.
In June last year, a PharmaCompass article had asked the question — “Lupin’s FDA inspections, how serious are the concerns?”. In our review of FDA observations of previous inspections at Lupin, we had highlighted concerns over “instances where batches that generated ‘out of specification (OOS)’ results and failed in-process specifications, had the finished product released by the quality control unit (QCU) and distributed” without invalidating the OOS results.
The recent warning letters indicate continued
concerns at Lupin.
The observations of the recent inspections specifically highlight Lupin’s continued “failure to thoroughly review any unexplained discrepancy” as Lupin invalidated approximately 96 percent of all OOS results obtained at Pithampur and over 75 percent of them in Goa.
While Lupin does not expect any disruption
in supplies, the company does anticipate a delay of new product approvals.
Impressions: 3809
Over
700 commonly used generic medicines were
recommended for suspension by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) based on data
integrity concerns, over clinical studies conducted at GVK Biosciences in
Hyderabad, India.What
will be the global fallout of the European decision? The European decision has
impacted products from companies such as:Abbott Laboratories, Accord Healthcare (Intas), Actavis, Alembic, Apotex, Betapharm (Dr. Reddy’s), Brown & Burk UK, Fair Med Healthcare AG, Glenmark, Lupin, Micro Labs, Mylan, Orion Corporation, Ranbaxy, Ratiopharm, Sandoz, Sanofi-Aventis, Stada, Teva, Torrent, Wockhardt, Zydus… and many, many more.The
original recommendation of suspending
some of the medicines
made in January 2015, was an outcome of an inspection of GVK Biosciences’ site in Hyderabad (GVK BIO is a Clinical Research Organization-
CRO) by the
French medicines agency (ANSM) through the EMA. The EMA stated in their official release: “The
inspection revealed data manipulations of electrocardiograms (ECGs) during the
conduct of some studies of generic medicines, which appeared to have taken
place over a period of at least five years. Their systematic nature, the
extended period of time during which they took place and the number of members
of staff involved cast doubt on the integrity of the conduct of trials at the
site.” 1000 drugs reviewed// 700
rejectedWhile
over 1,000 pharmaceutical forms and strengths were reviewed at the GVK site,
over 300 of them had sufficient supporting data available from other sources.
As a result, these medicines were allowed to remain on the market in the EU.However, for the over 700 other medicines, the EMA after its second review, maintained its previous recommendation of January 2015, to suspend medicines, where no additional supporting data from other studies was available. Only one exception after that second review was spared from suspension, as the company was able to address the EMA’s concerns: it was Bivolet Nebivolol (5 mg tablets/ marketing authorisation holder: Neo Balkanika EOOD).While the agency noted that “there is no evidence of harm or
lack of effectiveness linked to the conduct of studies by GVK Biosciences at
Hyderabad. Some of these medicines may remain on the market” if they are of critical importance for patients. However, the recommendation
will now be sent to the European Commission for a legally binding decision,
which will apply to Member States regardless of the decision taken in the
interim period.The updated list of medicines for which, the CHMP (Committee
for Medicinal Products for Human Use) recommends suspension, is available on the EMA website. Companies
are given 12 months to submit additional data. The potential global impact of the European
suspensions?The GVK Biosciences
scandal is almost as severe in magnitude and impact, as the data falsification
concerns, which were discovered at Ranbaxy (Katherine Eban’s stunning investigation in Fortune, “Dirty Medicine” covers this extensively). One of the main promoters of GVK Biosciences is Mr. D.S. Brar who was CEO & Managing Director of Ranbaxy from 1999-2004. The impact of GVK
Biosciences’ misdeeds is already being felt on new product launches. Mylan recently withdrew its European application for generic
Abilify (aripiprazole) (2014 sales US$6.2x billion) citing “identification of major GCP issues (Good
Clinical Practices).” What about the impact on the US market?In 2010, FDA discovered data integrity
violations, which bankrupted
clinical research organization, Cetero Research/PRACS. Based on the Cetero findings
in the United States, the EMA suspended seven drugs. Now it remains to
be seen, how the FDA will handle the data integrity concerns found in Europe
since products like repaglinide & candesartan cilexitil (Mylan), levetiracetam (Dr. Reddy’s), clonazepam (Sandoz), metformin hydrochloride (Actavis), tacrolimus (Panacea Biotech) all have U.S. FDA approvals. Leading GVK Biosciences’ defense is the Indian government, who warned last month that if the European Union does not reconsider their decision, it may go to the World Trade Organization. The Indian government’s position is based on an appeal by GVK Biosciences, which made the “Indian government set up a panel of experts last year to investigate
the matter and found no manipulation”, GVK Biosciences CEO Manni Kantipudi told Reuters.However, globally reputed GMP expert, Lachman Consultants, believes that the GVK Bioscience episode “could potentially impact data integrity, similar to the Cetero/PRACS
case”.It’s clear for us that this is not the end of the story…
Impressions: 4081
Unrelated to the inspection of
the USFDA at the Dr. Reddys Srikakulam facility, Dr. Reddys sought permission from the Ministry of Environment,
Forests & Climate Change to expand
their drug and intermediate manufacturing at three locations.
All three chemical technical operation (CTO) units, CTO-I, CTO-II & CTO-III are located in Medak district and the announced planned capacity increases along with the anticipated capital investment were
Existing Capacity
Planned Capacity
Anticipated Investment
CTO I
14.7 TPM
45.5 TPM
Rs 30 crores
CTO II
21.9 TPM
68.9 TPM
Rs 45 crores
CTO - III
4.45 TPM
28.1 TPM
Rs 12 crores
*$1 million is approximately about Rs 6.2
crores & TPM is tons per month
In addition, the declaration given by Dr. Reddys also mentions the various products which will be produced at each facility (table below).
Needless to say, the plans are ambitious however with the growth witnessed by the Indian pharmaceutical industry over the past decade, one can understand Dr. Reddys commitment to investing further in their business.
Table Dr. Reddys production plans at various facilities
Product
Name
Planned
Capacity (TPM)
Facility
Location
Alendronate
Sodium Trihydrate
6.67
CTO
- III
Alfuzosin
2.33
CTO
- I
Altretamine
0.03
CTO
- I
Amlodipine
Besylate
33.33
CTO
- II
Amlodipine
Besylate
133.33
CTO
- III
Amlodipine
Besylate ( Ethyl 4 [2- (pthalamide)ethoxy] aceto acetate (TDM-2)
100
CTO
- II
Amlodipine
Maleate
30
CTO
- III
Amsacrine
0.07
CTO
- I
Anastrazole
0.83
CTO
- II
Aprepitant
3.33
CTO
- III
Aripiprazole
0.33
CTO
- II
Atomoxetine
1.67
CTO
- III
Atorvastatin
375.83
CTO
- II
Azacitidine
0.67
CTO
- I
Bicalutamide
0.03
CTO
- II
Bivalirudin
0.03
CTO
- II
Bivalirudin
Trifluoro Acetate
0.03
CTO
- I
Bortezomib
0.03
CTO
- I
Cabazitaxel
0.02
CTO
- I
Candesartan
cilexetil
6.67
CTO
- II
Cetirizine
Hydrochloride
66.67
CTO
- I
Cetirizine
16.67
CTO
- II
Ciprofloxacin
176.67
CTO
- II
Ciprofloxacin
HCl
533.33
CTO
- II
Ciprofloxacin Lactate
33.33
CTO
- II
Clopidogrel
Bisulfate
500
CTO
- I
Clopidogrel Premix
166.67
CTO
- II
Diluted
Everolimus 5% (Everolimus)
0.33
CTO
- II
Disodium
Pamidronate
0.33
CTO
- III
Docetaxel
1.9
CTO
- I
Dutasteride
3.33
CTO
- II
Esomeprazole
magnesium
66.67
CTO
- III
Ezetimibe
3.33
CTO
- II
Fexofenadine
Hydrochloride
500
CTO
- I
Finasteride
10
CTO
- II
Fluoxetine
110
CTO
- I
Fondaparinux
Sodium
0.33
CTO
- II
Galantamine
0.03
CTO
- II
Gemcitabine
13.33
CTO
- I
Glimepiride
13.33
CTO
- II
Imatinib
0.17
CTO
- I
Irinotecan
0.33
CTO
- I
Ketorolac
66.67
CTO
- II
Lacidipine
5
CTO
- III
Lamotrigine
33.33
CTO
- I
Lansoprozole
8.33
CTO
- III
Letrozole
0.03
CTO
- II
Levocetrizine
Di HCl
10
CTO
- III
Levofloxacin
200
CTO
- II
Lomustine
1.33
CTO
- I
Losartan
Postassium
150
CTO
- I
Meloxicam
0.03
CTO
- I
Memantine
HCl
3.33
CTO
- II
Mesalamine
0.03
CTO
- II
Metoprolol
Succinate
266.67
CTO
- II
Moxifloxacin
116.67
CTO
- II
Norfloxacin
0.03
CTO
- I
Omeprazole
133.33
CTO
- III
Omeprazole
Magnesium
50
CTO
- III
Omeprazole
Sodium
10
CTO
- III
Omerprazole Form B
33.33
CTO
- III
Paclitaxel
0.33
CTO
- I
Pantoprazole
Sodium
100
CTO
- III
paroxetine
HCl
0.03
CTO
- II
Pemetrexed
0.67
CTO
- I
Rabeprazole
Sodium
83.33
CTO
- III
Raloxifene
33.33
CTO
- II
Ramipril
100
CTO
- III
Repaglinide
6.67
CTO
- II
Rivastigmine
6.67
CTO
- II
Risperidone
13.33
CTO
- I
Rivastigmine
6.667
CTO
- I
Rizatriptan
Benzoate
1.33
CTO
- II
Rocuronium
Bromide
0.03
CTO
- II
Ropinrole
HCl
1.83
CTO
- III
Rosiglitazone
3.33
CTO
- II
Sparfloxacin
3.33
CTO
- I
Tacrolimus
5
CTO
- II
Tadalafil
3.33
CTO
- II
Telmisartan
100
CTO
- II
Temozolamide
0.03
CTO
- I
Terbinafine
HCl
133.33
CTO
- III
Tizanidine
HCl
16.67
CTO
- III
Topotecan
0.07
CTO
- I
valganciclovir
0.03
CTO
- I
Vardenafil
3.33
CTO
- II
Voriconazole
8.33
CTO
- III
Ziprasidone
Hydrochloride
100
CTO
- I
Zoledronic
acid
0.33
CTO
- III
Zolmitriptan
0.83
CTO
- I
Zonisamide
0.03
CTO
- II
Impressions: 3086