

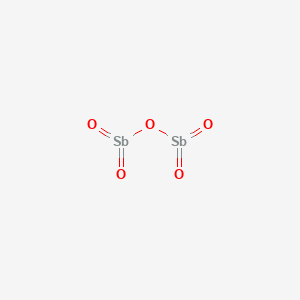

1. Antimony Pentaoxide
1. 1314-60-9
2. Antimony(v) Oxide
3. Antimonic Oxide
4. Diantimony Pentaoxide
5. Stibic Anhydride
6. Antimony Pentaoxide
7. Apox S
8. Antimony Oxide (sb2o5)
9. Nyacol Ago 40
10. Nyacol Adp 480
11. Nyacol Adp 494
12. Suncolloid Ame 130
13. Suncolloid Amt 130
14. Anchimonzol A 2550
15. Nyacol 1550
16. Sun Epoch Na 100
17. Nyacol A 1590
18. Sun Epoch Na 3070p
19. Sun Epoch Na 3080p
20. A 1530 (metal Oxide)
21. Sanka Anchimonzol A 2550m
22. Ago 40
23. Hfr 201
24. A 1550
25. A 2550
26. Dtxsid6050467
27. 756ocg058b
28. Refchem:113170
29. ((dioxostibanyl)oxy)stibanedione
30. Dtxcid6029468
31. 215-237-7
32. Mfcd00011216
33. (dioxo-lambda5-stibanyl)oxy-dioxo-lambda5-stibane
34. Ccris 4497
35. Einecs 215-237-7
36. Unii-756ocg058b
37. Ec 215-237-7
38. Schembl63324
39. Antimony(v) Oxide, Elec. Gr.
40. Antimony(v) Oxide - 99.9%
41. Antimony(v) Oxide, Puratronic?
42. Akos015903586
43. Fa163898
44. Ns00112453
45. Antimony(v) Oxide, 99.995% Trace Metals Basis
46. Q419889
| Molecular Weight | 323.52 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | O5Sb2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | Da |
| Monoisotopic Mass | Da |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 77.5 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 7 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 123 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Antimony is widely distributed throughout the body. The hair and skin contain the highest levels of antimony. The adrenal glands, lung, large intestine, trachea, cerebellum, and kidneys also contain relatively high levels of antimony. Blood is the main vehicle for the transport of absorbed antimony to various tissue compartments of the body. Antimony is a metal and, therefore, does not undergo catabolism. Antimony can covalently interact with sulfhydryl groups and phosphate, as well as numerous reversible binding interactions with endogenous ligands (e.g., proteins). It is not known if these interactions are toxicologically significant. Antimony is excreted via the urine and feces. Some of the fecal antimony may represent unabsorbed antimony that is cleared from the lung via mucociliary action into the esophagus to the gastrointestinal tract. (L741)
