
Synopsis
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
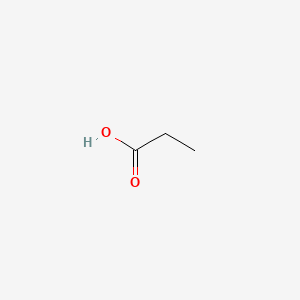

1. Chromium Propionate
2. Ethylformic Acid
3. Lithium Propanoate
4. Monoprop
5. Potassium Propionate
6. Propionic Acid, Zinc Salt
7. Zinc Propionate
1. Propanoic Acid
2. 79-09-4
3. Ethylformic Acid
4. Methylacetic Acid
5. Carboxyethane
6. Metacetonic Acid
7. Ethanecarboxylic Acid
8. Pseudoacetic Acid
9. Luprosil
10. Monoprop
11. Propionate
12. Prozoin
13. Antischim B
14. Propionoic Acid
15. Acide Propionique
16. Methyl Acetic Acid
17. Sentry Grain Preserver
18. C3 Acid
19. Tenox P Grain Preservative
20. Caswell No. 707
21. Propionic Acid Grain Preserver
22. Fema No. 2924
23. Propionsaeure
24. Propcorn
25. Propkorn
26. Propoic Acid
27. Propioic Acid
28. Acide Propanoique
29. Propionic Acid (natural)
30. Kyselina Propionova
31. Carboxylic Acids, C1-5
32. Acide Propionique [french]
33. Kyselina Propionova [czech]
34. Ccris 6096
35. Proprionic Acid
36. C1-5 Carboxylic Acids
37. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 077702
38. Fatty Acids, C3-24
39. Hsdb 1192
40. N-propionic Acid
41. Toxi-check
42. Ai3-04167
43. Ch3-ch2-cooh
44. Un1848
45. Brn 0506071
46. Propionic Acid [nf]
47. Chebi:30768
48. Jhu490rvyr
49. Chembl14021
50. Ins No.280
51. 68937-68-8
52. Ins-280
53. Metacetonate
54. Propanate
55. Pseudoacetate
56. Ethanecarboxylate
57. 68990-37-4
58. Propionic Acid (nf)
59. Propionic Acid [un1848] [corrosive]
60. E-280
61. Propionic Acid, >=99.5%
62. Propanyl Acid
63. Fema Number 2924
64. Einecs 201-176-3
65. Unii-jhu490rvyr
66. Mfcd00002756
67. Luprisol
68. Proponic Acid
69. 1-propanoic Acid
70. 2-methylacetic Acid
71. Einecs 273-079-4
72. Etco2h
73. Propionic Acid Solution
74. Propionic Acid, 99%
75. Propanoic Acid (9ci)
76. C2h5cooh
77. Dsstox_cid_5961
78. Bmse000179
79. Epitope Id:139981
80. Propionic Acid, >=99%
81. Propionic Acid, 99.5%
82. Ec 201-176-3
83. Propionic Acid [mi]
84. Dsstox_gsid_25961
85. Propionic Acid Reagent Grade
86. Natural Propionic Acid
87. Propionic Acid (6ci,8ci)
88. Propionic Acid [fcc]
89. 4-02-00-00695 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
90. Propionic Acid, 99%, Fcc
91. Propionic Acid [fhfi]
92. Propionic Acid [hsdb]
93. Propionic Acid [inci]
94. Propionic Acid [vandf]
95. Gtpl1062
96. Propionic Acid [mart.]
97. Dtxsid8025961
98. Propionic Acid [usp-rs]
99. Propionic Acid [who-dd]
100. Amy4114
101. Top Distillation Cut By-product Acids, Monobasic (c1-c5)
102. Methylacetic Acid, Propanoic Acid
103. Dtxsid001015846
104. Propionic Acid, Acs Reagent Grade
105. Carboxymethoxylaminehemihydrochloride
106. Propionic Acid, Analytical Standard
107. Zinc6050663
108. Propionic Acid, Natural, 99%, Fg
109. Tox21_304030
110. Bdbm50082199
111. Lmfa01010003
112. Stl168039
113. Propionic Acid, Feed Grade, 98.7%
114. Akos000118853
115. Db03766
116. Un 1848
117. Cas-79-09-4
118. Propionic Acid, For Synthesis, 99.5%
119. Ncgc00357239-01
120. Propionic Acid, >=99.5%, Fcc, Fg
121. Bp-20411
122. E280
123. Propionic Acid 100 Microg/ml In Ethanol
124. Propionic Acid, Acs Reagent, >=99.5%
125. Ft-0637136
126. Ft-0658557
127. P0500
128. Propionic Acid 100 Microg/ml In Cyclohexane
129. Propionic Acid, Saj First Grade, >=98.0%
130. C00163
131. D02310
132. Propionic Acid 1000 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
133. Propionic Acid, Puriss. P.a., >=99.5% (gc)
134. Q422956
135. F2191-0098
136. Propionic Acid, Bioreagent, Suitable For Insect Cell Culture, ~99%
137. Propionic Acid, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
| Molecular Weight | 74.08 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C3H6O2 |
| XLogP3 | 0.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 74.036779430 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 74.036779430 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 37.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 5 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 40.2 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
VET: Useful orally in ruminants as an antiketogenic agent ... it also stimulates rumen development in calves. /Propionic acid and salts/
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 493
VET: ... As topical antifungal agents in various dermatoses.
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 492
... Treating dermatophytic infections ... /Sodium Propionate/
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 822
/VET:/ Propionic acid ... has been used to treat dermatomycoses. Propionic acid is also incorporated in manufactured animal feeds to help control fungal growth. At concentrations above 3 ug/ml it is fungicidal against a toxigenic strain of Aspergillus parasiticus.
Booth, N.H., L.E. McDonald (eds.). Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 5th ed. Ames, Iowa: Iowa State University Press, 1982., p. 772
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for PROPIONIC ACID (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Both their low efficacy and exaggerated price make /propionic acid and sodium propionate/ irrational choices for treatment /of dermatomycoses/...
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 1310
Propanoic acid and various direct sodium or calcium salt formulations of the acid are currently most commonly approved and indicated by organizations like the FDA and EMA for use as an antibacterial food additive preservative in animal feed and food for human consumption. Similarly, although the use of propanoic acid or any of its direct sodium or calcium salt formulations as excipient ingredients in pharmaceuticals is not necessarily a major role for the compound today, sodium propionate was used in some vaginal cream preparations indicated for cervicitis, cervical tears, and/or postcauterization, postcryosurgery, and postconization of the cervix. In such products, the sodium propionate was primarily used to elicit a preservative, bacteriostatic effect while other active ingredients combined in the formulation like urea, benzalkonium chloride, inositol, and methionine and cystine amino acids facilitated debridement, enhanced medication spread, epithelialization promotion, and wound healing, respectively. Nevertheless, a great variety of propionic acid derivatives exist as separate pharmaceuticals, each with their own unique therapeutic categories, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics.
As a naturally occurring carboxylic acid, propionic acid typically undergoes metabolism via conversion to propionyl coenzyme A (propionyl-CoA), which is part of the usual metabolic pathway that carboxylic acids participate within in the human body. Most of propionic acid's antibacterial and preservative activities subsequently stem from this metabolic pathway as the metabolic fate of propionates varies in different microorganisms, resulting in antimicrobial mechanisms of action that may revolve around differing propionate metabolites causing competition, inhibition, and/or interference effects along other metabolic pathways in the various microorganisms affected. In the human body, however, propionic acid is generally metabolized with little ill effect and ultimately becomes a chemical intermediate in the citric acid cycle.
Absorption
Some propionic acid is oxidized to lactic acid during absorption, but most passes to the liver, which removes nearly all of it from the portal blood. Propionic acid represents 20-25% of absorbed volatile fatty acids. Propionic acid is rapidly absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract.
Route of Elimination
Most absorbed propionic acid is passed to the liver, which removes nearly all of it from the portal blood. Three days after a single oral administration of labeled sodium propionate, 77% of the radioactivity was found in expired air, and 7% in urine and feces.
Volume of Distribution
Three days after a single oral administration of labeled sodium propionate, 77% of the radioactivity was found in expired air, and 7% in urine and feces. The radioactivity found in skin, liver, intestine, and adipose tissue was 3.9, 1.1, 0.9, and 0.7%, respectively. Readily accessible data regarding the volume of distribution of propionic acid is not available.
Clearance
Readily accessible data regarding the clearance of propionic acid is not available.
Some propionic acid is oxidized to lactic acid during absorption but most passes to the liver, which removes nearly all of it from the portal blood ... propionic acid ... represents 20-25% of absorbed volatile fatty acids.
Jones, L.M., et al. Veterinary Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 4th ed. Ames: Iowa State University Press, 1977., p. 736
Three days after a single oral admin of labeled sodium propionate, 77% of the radioactivity was found in expired air, and 7% in urine and feces. The radioactivity found in skin, liver, intestine, and adipose tissue was 3.9, 1.1, 0.9, and 0.7%, respectively.
KOZUKA H ET AL; EISEI KAGAKU 27 (5): 303-8 (1981)
Propionic acid is rapidly absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract and, even after large doses, very little is excreted in the urine.
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. 5:706
... In the forestomachs of rats fed 4% PA in powdered diet, the amount of PA in hyperplasias (1553 | 508 mug PA/g tissue) was three times higher than that in the remainder of the tissue (479 | 247 mug PA/g tissue). The PA content decreased progressively towards the glandular parts.
PMID:8473000 Bueld JE, Netter KJ; Food Chem Toxicol 31 (3): 169-176 (1993)
Propionic acid is first converted to propionyl coenzyme A (propionyl-CoA), however, it directly enter either beta oxidation or the citric acid cycles. As propionic acid has three carbons, propionyl-CoA. In the majority of vertebrates, propionyl-CoA is carboxylated to D-methylmalonyl-CoA, which is then isomerised to L-methylmalonyl-CoA. A vitamin B12-dependent enzyme catalyzes rearrangement of L-methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA, which can then be used as a substrate in the citric acid cycle.
Propionate is formed as the terminal three-carbon fragment (as propionyl-coenzyme A) in the oxidation of odd-number carbon fatty acids and from oxidation of the side chain of cholesterol. Radioactivity from propionate admin to fasting rats may appear in glycogen, glucose, citric acid cycle intermediates, amino acids, and proteins. The route of metabolism of propionic acid involves interaction with coenzyme A, carboxylation to form methylmalonyl-coenzyme A, and conversion to succinic acid, which enters the citric acid cycle. Propionic acid may be oxidized without forming ketone bodies and in contrast to acetic acid, is incorporated into a carbohydrate as well as lipid.
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. 5:706
The metab of radiolabeled sodium propionate was studied in rats three days after a single oral admin. Among the liver extracts, 89% of the liver radioactivity was found in trichloroacetic acid precipitated fraction, and 10% in glycogen.
KOZUKA H ET AL; EISEI KAGAKU 27 (5): 303-8 (1981)
Treatment with L-carnitine greatly enhanced the formation and excretion of short-chain acylcarnitines in three patients with propionic acidemia and in three normal controls. Mass spectrometry ... identified the acylcarnitine as propionylcarnitine in patients with propionic acidemia. The normal children excreted mostly acetylcarnitine. Propionic acidemia and other organic acidurias are characterized by the intramitochondrial accumulation of short-chain acyl-Coenzyme A (CoA) compounds. The substrate specificity of the carnitine acetyltransferase enzyme and its steady state nature appears to facilitate elimination of propionyl groups while restoring the acyl-acyl-Coenzyme A:free acyl-CoenzymeA ratio in the mitochondrion. L-carnitine may be a useful therapeutic approach for elimination of toxic acyl acyl-Coenzyme A compounds in several of these disorders.
PMID:6725560 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC437091 Roe CR et al; J Clin Invest 73 (6): 1785-8 (1984)
Propionic acid (10 mM) inhibited hepatocyte oxidation of 1-(14)C-pyruvate (10 mM) by 60%. This inhibition was not the result of substrate competition, as butyric acid had minimal effects on pyruvate oxidation. ... Propionic acid also inhibited oxidation of 1-(14)C palmitic acid (0.8 mM) by hepatocytes isolated from fed rats. ... These results demonstrate that propionic acid interferes with oxidative metabolism in intact hepatocytes.
PMID:3790065 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1146796 Brass EP et al; Biochem J 236 (1): 131-6 (1986)
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for PROPIONIC ACID (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
The half-life of iv sodium propionate administered in the sheep animal model is about 6.9 +/- 0.4 minutes.
The t1/2 of the iv sodium propionate load ... from 6.9 +/- 0.4 min in the control sheep ... . /Sodium propionate/
PMID:4014846 Grohn Y et al; Am J Vet Res 46 (4): 952-8 (1985)
The metabolic fate of propionates varies in different microorganisms. Some have enzyme systems that can convert succinate to propionyl-coenzyme A and through various further steps to propionate, CO2, or propionyl phoshpate. Still others can convert propionic acid to B-alanine or directly to CO2. Whatever the case, the inhibiting effect for microbials is likely related to competition with acetate in the acetokinase system, to the blockage of pyruvate conversion to acetyl-coenzyme A and to interference with B-alanine in pantothenic acid syntheses. Moreover, other studies suggest the antimicrobial activity of propionic acid revolves around its ability to reduce the pH of its immediate environment to levels of acidity that are harmful to pathogenic microbes as well as its ability to dissociate such that its lipid soluble undissociated form is capable of entering microbial cells. Additionally, there are also studies that suggest that propionic acid's antifungal activity may be the result of propionyl-CoA inhibiting glucose metabolism in certain species of fungus via the accumulation of the CoA-derivative.

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Market Place

ABOUT THIS PAGE
41
PharmaCompass offers a list of Propionic Acid API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Propionic Acid manufacturer or Propionic Acid supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Propionic Acid manufacturer or Propionic Acid supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Propionic Acid API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Propionic Acid API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Propionic Acid Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Propionic Acid Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Propionic Acid manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Propionic Acid, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Propionic Acid manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Propionic Acid API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Propionic Acid manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Propionic Acid supplier is an individual or a company that provides Propionic Acid active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Propionic Acid finished formulations upon request. The Propionic Acid suppliers may include Propionic Acid API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Propionic Acid suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
Propionic Acid Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Propionic Acid GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Propionic Acid GMP manufacturer or Propionic Acid GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Propionic Acid CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Propionic Acid's compliance with Propionic Acid specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Propionic Acid CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Propionic Acid CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Propionic Acid may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Propionic Acid EP), Propionic Acid JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Propionic Acid USP).

