
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
VMF
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
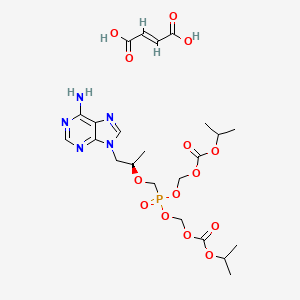

1. (r)-9-(2-phosphonylmethoxypropyl)adenine
2. 9-(2-phosphonomethoxypropyl)adenine
3. 9-(2-phosphonylmethoxypropyl)adenine
4. 9-(2-phosphonylmethoxypropyl)adenine, (+-)-isomer
5. 9-(2-phosphonylmethoxypropyl)adenine, (r)-isomer - T357098
6. 9-(2-phosphonylmethoxypropyl)adenine, (s)-isomer
7. 9-pmpa (tenofovir)
8. Disoproxil Fumarate, Tenofovir
9. Disoproxil, Tenofovir
10. Fumarate, Tenofovir Disoproxil
11. Tenofovir
12. Tenofovir Disoproxil
13. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate
1. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate
2. 202138-50-9
3. Tenofovir Df
4. Virea
5. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate [usan]
6. Pmpa-prodrug
7. Gs-4331-05
8. Gsk548470
9. Gsk-548470
10. Ott9j7900i
11. Tenofovir Disoproxil (fumarate)
12. Tenofovir (disoproxil Fumarate)
13. Chebi:63718
14. Gs-4331-05-
15. 9-((r)-2-((bis(((isopropoxycarbonyl)oxy)methoxy)phosphinyl)methoxy)propyl)adenine Fumarate
16. (r)-(((((1-(6-amino-9h-purin-9-yl)propan-2-yl)oxy)methyl)phosphoryl)bis(oxy))bis(methylene) Diisopropyl Dicarbonate Fumarate
17. (r)-5-((2-(6-amino-9h-purin-9-yl)-1-methylethoxy)methyl)-2,4,6,8-tetraoxa-5-phosphanonanedioic Acid, Bis(1-methylethyl) Ester, 5-oxide, (e)-2-butenedioate (1:1)
18. 2,4,6,8-tetraoxa-5-phosphanonanedioic Acid, 5-[[(1r)-2-(6-amino-9h-purin-9-yl)-1-methylethoxy]methyl]-, 1,9-bis(1-methylethyl) Ester, 5-oxide, (2e)-2-butenedioate (1:1)
19. 9-((r)-2-((bis(((isopropoxycarbonyl)oxy)methoxy)phosphinyl)methoxy)propyl)adenine Fumarate (1:1)
20. Bis(hydroxymethyl) (((r)-2-(6-amino-9h-purin-9-yl)-1-methylethoxy)methyl)phosphonate, Bis(isopropyl Carbonate) (ester), Fumarate (1:1)
21. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate
22. (2e)-but-2-enedioic Acid Bis({[(propan-2-yloxy)carbonyl]oxy}methyl) {[(2r)-1-(6-amino-9h-purin-9-yl)propan-2-yl]oxy}methanephosphonate
23. [[(2r)-1-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)propan-2-yl]oxymethyl-(propan-2-yloxycarbonyloxymethoxy)phosphoryl]oxymethyl Propan-2-yl Carbonate;(e)-but-2-enedioic Acid
24. Hsdb 7165
25. Tenofovirdisoproxilfumarate
26. Unii-ott9j7900i
27. Mfcd08141829
28. Gs 4331-05
29. Viread (tn)
30. Tenofovir-disoproxil-fumarate
31. Chembl1486
32. Schembl40021
33. Tenofoviri Disoproxili Fumaras
34. Mls004774141
35. Gs-1278 Disoproxil Fumarate
36. Schembl2670560
37. Dtxsid5050426
38. Ex-a590
39. S1400
40. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate- Bio-x
41. Akos016340707
42. Akos025149493
43. Ccg-270300
44. Cs-1346
45. Gs-us-104-0321
46. Ks-1246
47. 9-((r)-2-((bis(((isopropoxycarbonyl)oxy)methoxy)phosphinyl)methoxy)propyl)adenine, Fumarate
48. Bt164457
49. Hy-13782
50. Smr003500786
51. Tenofovir (as Disoproxil Fumarate)
52. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate (jan/usan)
53. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate [mi]
54. Bcp0726000258
55. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate [jan]
56. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate [hsdb]
57. Am20090676
58. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate [mart.]
59. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate [vandf]
60. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate [usp-rs]
61. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate [who-dd]
62. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate [who-ip]
63. D01982
64. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate, >=98% (hplc)
65. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate [ema Epar]
66. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate [orange Book]
67. Q-201788
68. Atripla Component Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate
69. Eviplera Component Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate
70. Odefsey Component Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate
71. Q27132754
72. Stribild Component Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate
73. Temixys Component Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate
74. Tenofoviri Disoproxili Fumaras [who-ip Latin]
75. Truvada Component Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate
76. Delstrigo Component Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate
77. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Component Delstrigo
78. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Component Of Atripla
79. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Component Of Odefsey
80. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Component Of Temixys
81. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Component Of Truvada
82. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Component Of Eviplera
83. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Component Of Stribild
84. (r)-(((((1-(6-amino-9h-purin-9-yl)propan-2-yl)oxy)methyl)phosphoryl)bis(oxy))bis(methylene)diisopropyldicarbonatefumarate
85. [[(1r)-2-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-1-methyl-ethoxy]methyl-(isopropoxycarbonyloxymethoxy)phosphoryl]oxymethyl Isopropyl Carbonate; Fumaric Acid
86. 9-((r)-2-((bis(((isopropoxycarbonyl)oxy)-methoxy)phosphinyl)methoxy)propyl)adenine Fumarate (1:1)
87. 9-[(r)-2[[bis[[(isopropoxycarbonyl)oxy]methoxy]phosphinyl]methoxy]propyl]adenine Fumarate (1:1)
88. Bis({[(propan-2-yloxy)carbonyl]oxy}methyl) ({[(2r)-1-(6-amino-9h-purin-9-yl)propan-2-yl]oxy}methyl)phosphonate (2e)-but-2-enedioate
89. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
| Molecular Weight | 635.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C23H34N5O14P |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 18 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 19 |
| Exact Mass | 635.18398777 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 635.18398777 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 260 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 43 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 817 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate |
| PubMed Health | Tenofovir (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiretroviral Agent |
| Drug Label | VIREAD is the brand name for tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (a prodrug of tenofovir) which is a fumaric acid salt of bis-isopropoxycarbonyloxymethyl ester derivative of tenofovir. In vivo tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is converted to tenofovir, an acy... |
| Active Ingredient | Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | 300mg |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval |
| Company | Macleods Pharma; Aurobindo Pharma; Invagen Pharms; Cipla; Matrix Labs; Teva Pharms; Strides Arcolab |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Viread |
| Drug Label | VIREAD is the brand name for tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (a prodrug of tenofovir) which is a fumaric acid salt of bis-isopropoxycarbonyloxymethyl ester derivative of tenofovir. In vivo tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is converted to tenofovir, an acy... |
| Active Ingredient | Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Powder |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 40mg/scoopful; 200mg; 250mg; 150mg; 300mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Gilead Sciences |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate |
| PubMed Health | Tenofovir (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiretroviral Agent |
| Drug Label | VIREAD is the brand name for tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (a prodrug of tenofovir) which is a fumaric acid salt of bis-isopropoxycarbonyloxymethyl ester derivative of tenofovir. In vivo tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is converted to tenofovir, an acy... |
| Active Ingredient | Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | 300mg |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval |
| Company | Macleods Pharma; Aurobindo Pharma; Invagen Pharms; Cipla; Matrix Labs; Teva Pharms; Strides Arcolab |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Viread |
| Drug Label | VIREAD is the brand name for tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (a prodrug of tenofovir) which is a fumaric acid salt of bis-isopropoxycarbonyloxymethyl ester derivative of tenofovir. In vivo tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is converted to tenofovir, an acy... |
| Active Ingredient | Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Powder |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 40mg/scoopful; 200mg; 250mg; 150mg; 300mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Gilead Sciences |
Anti-HIV Agents, Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 2012)
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is used in conjunction with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infections in adults. /Included in US product labeling/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2012; Drug Information 2012. Bethesda, MD. 2012, p. 747
Tenofovir is used for the management of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in adults. This indication is based on histologic, virologic, biochemical, and serologic responses in adults with hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg)-positive or -negative chronic HBV with compensated liver function.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2012; Drug Information 2012. Bethesda, MD. 2012, p. 748
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF), emtricitabine (FTC), and efavirenz (EFV) are the three components of the once-daily, single tablet regimen (Atripla) for treatment of HIV-1 infection. Previous cell culture studies have demonstrated that the double combination of tenofovir (TFV), the parent drug of TDF, and FTC were additive to synergistic in their anti-HIV activity, which correlated with increased levels of intracellular phosphorylation of both compounds. In this study, /researchers/ demonstrated the combinations of TFV+FTC, TFV+EFV, FTC+EFV, and TFV+FTC+EFV synergistically inhibit HIV replication in cell culture and synergistically inhibit HIV-1 reverse transcriptase (RT) catalyzed DNA synthesis in biochemical assays. Several different methods were applied to define synergy including median-effect analysis, MacSynergyII and quantitative isobologram analysis. We demonstrated that the enhanced formation of dead-end complexes (DEC) by HIV-1 RT and TFV-terminated DNA in the presence of FTC-triphosphate (TP) could contribute to the synergy observed for the combination of TFV+FTC, possibly through reduced terminal NRTI excision. Furthermore, /researchers/ showed that EFV facilitated efficient formation of stable, DEC-like complexes by TFV- or FTC-monophosphate (MP)-terminated DNA and this can contribute to the synergistic inhibition of HIV-1 RT by TFV-diphosphate (DP)+EFV and FTC-TP+EFV combinations. This study demonstrated a clear correlation between the synergistic antiviral activities of TFV+FTC, TFV+EFV, FTC+EFV, and TFV+FTC+EFV combinations and synergistic HIV-1 RT inhibition at the enzymatic level. /Researchers/ propose the molecular mechanisms for the TFV+FTC+EFV synergy to be a combination of increased levels of the active metabolites TFV-DP and FTC-TP and enhanced DEC formation by a chain-terminated DNA and HIV-1 RT in the presence of the second and the third drug in the combination. This study furthers the understanding of the longstanding observations of synergistic anti-HIV-1 effects of many NRTI+NNRTI and certain NRTI+NRTI combinations in cell culture, and provides biochemical evidence that combinations of anti-HIV agents can increase the intracellular drug efficacy, without increasing the extracellular drug concentrations.
PMID:19439089 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2693498 Feng JY et al; Retrovirology 6: 44 (2009)
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: LACTIC ACIDOSIS/SEVERE HEPATOMEGALY WITH STEATOSIS and POST TREATMENT EXACERBATION OF HEPATITIS. Lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis, including fatal cases, have been reported with the use of nucleoside analogs, including Viread, in combination with other antiretrovirals. Severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis have been reported in HBV-infected patients who have discontinued anti-hepatitis B therapy, including Viread. Hepatic function should be monitored closely with both clinical and laboratory follow-up for at least several months in patients who discontinue anti-hepatitis B therapy, including Viread. If appropriate, resumption of anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for VIREAD (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) tablet, coated VIREAD (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) powder (November 2012). Available from, as of November 14, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=33fd6418-fbdc-42ca-a50d-ce2a476a5418
Lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis (sometimes fatal) have been reported rarely in patients receiving nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors alone or in conjunction with other antiretroviral agents. Most reported cases have involved women; obesity and long-term therapy with a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor also may be risk factors. Caution should be observed when nucleoside analogs are used in patients with known risk factors for liver disease; however, lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis have been reported in patients with no known risk factors. Tenofovir therapy should be interrupted in any patient with clinical or laboratory findings suggestive of lactic acidosis or pronounced hepatotoxicity (signs of hepatotoxicity include hepatomegaly and steatosis even in the absence of marked increases in serum aminotransferase concentrations).
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2012; Drug Information 2012. Bethesda, MD. 2012, p. 749
Redistribution or accumulation of body fat, including central obesity, dorsocervical fat enlargement (buffalo hump), peripheral wasting, facial wasting, breast enlargement, and general cushingoid appearance, has been reported with antiretroviral therapy.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2012; Drug Information 2012. Bethesda, MD. 2012, p. 750
The most common adverse effects in HIV-infected patients receiving tenofovir disoproxil fumarate are rash, diarrhea, headache, pain, depression, asthenia, and nausea. The most common adverse effect in HIV-infected patients receiving tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is nausea.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2012; Drug Information 2012. Bethesda, MD. 2012, p. 750
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for TENOFOVIR DISOPROXIL FUMARATE (14 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
* HIV 1 infection:
Viread 123 mg film coated tablets are indicated in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products for the treatment of HIV 1 infected paediatric patients, with NRTI resistance or toxicities precluding the use of first line agents, aged 6 to < 12 years who weigh from 17 kg to less than 22 kg.
The choice of Viread to treat antiretroviral experienced patients with HIV 1 infection should be based on individual viral resistance testing and/or treatment history of patients.
* Hepatitis B infection:
Viread 123 mg film coated tablets are indicated for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B in paediatric patients aged 6 to < 12 years who weigh from 17 kg to less than 22 kg, with
compensated liver disease and evidence of immune active disease, i. e. active viral replication and persistently elevated serum ALT levels, or histological evidence of moderate to severe inflammation and/or fibrosis. With respect to the decision to initiate treatment in paediatric patients, see sections 4. 2, 4. 4, 4. 8 and 5. 1.
* HIV 1 infection:
Viread 163 mg film coated tablets are indicated in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products for the treatment of HIV 1 infected paediatric patients, with NRTI resistance or toxicities precluding the use of first line agents, aged 6 to < 12 years who weigh from 22 kg to less than 28 kg.
The choice of Viread to treat antiretroviral experienced patients with HIV 1 infection should be based on individual viral resistance testing and/or treatment history of patients.
* Hepatitis B infection:
Viread 163 mg film coated tablets are indicated for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B in paediatric patients aged 6 to < 12 years who weigh from 22 kg to less than 28 kg, with:
compensated liver disease and evidence of immune active disease, i. e. active viral replication and persistently elevated serum ALT levels, or histological evidence of moderate to severe inflammation and/or fibrosis. With respect to the decision to initiate treatment in paediatric patients, see sections 4. 2, 4. 4, 4. 8 and 5. 1.
* HIV 1 infection:
Viread 204 mg film coated tablets are indicated in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products for the treatment of HIV 1 infected paediatric patients, with NRTI resistance or toxicities precluding the use of first line agents, aged 6 to < 12 years who weigh from 28 kg to less than 35 kg.
The choice of Viread to treat antiretroviral experienced patients with HIV 1 infection should be based on individual viral resistance testing and/or treatment history of patients.
* Hepatitis B infection:
Viread 204 mg film coated tablets are indicated for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B in paediatric patients aged 6 to < 12 years who weigh from 28 kg to less than 35 kg, with:
compensated liver disease and evidence of immune active disease, i. e. active viral replication and persistently elevated serum ALT levels or histological evidence of moderate to severe inflammation and/or fibrosis. With respect to the decision to initiate treatment in paediatric patients, see sections 4. 2, 4. 4, 4. 8 and 5. 1.
* HIV 1 infection:
Viread 245 mg film coated tablets are indicated in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products for the treatment of HIV 1 infected adults.
In adults, the demonstration of the benefit of Viread in HIV 1 infection is based on results of one study in treatment nave patients, including patients with a high viral load (> 100,000 copies/ml) and studies in which Viread was added to stable background therapy (mainly tritherapy) in antiretroviral pre-treated patients experiencing early virological failure (< 10,000 copies/ml, with the majority of patients having < 5,000 copies/ml).
Viread 245 mg film coated tablets are also indicated for the treatment of HIV 1 infected adolescents, with NRTI resistance or toxicities precluding the use of first line agents, aged 12 to < 18 years.
The choice of Viread to treat antiretroviral experienced patients with HIV 1 infection should be based on individual viral resistance testing and/or treatment history of patients.
* Hepatitis B infection:
Viread 245 mg film coated tablets are indicated for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B in adults with:
compensated liver disease, with evidence of active viral replication, persistently elevated serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels and histological evidence of active inflammation and/or fibrosis (see section 5. 1). evidence of lamivudine resistant hepatitis B virus (see sections 4. 8 and 5. 1). decompensated liver disease (see sections 4. 4, 4. 8 and 5. 1). Viread 245 mg film coated tablets are indicated for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B in adolescents 12 to < 18 years of age with:
compensated liver disease and evidence of immune active disease, i. e. active viral replication and persistently elevated serum ALT levels, or histological evidence of moderate to severe inflammation and/or fibrosis. With respect to the decision to initiate treatment in paediatric patients, see sections 4. 2, 4. 4, 4. 8 and 5. 1.
* HIV 1 infection:
Viread 33 mg/g granules are indicated in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products for the treatment of HIV 1 infected paediatric patients, with NRTI resistance or toxicities precluding the use of first line agents, from 2 to < 6 years of age, and above 6 years of age for whom a solid dosage form is not appropriate.
Viread 33 mg/g granules are also indicated in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products for the treatment of HIV 1 infected adults for whom a solid dosage form is not appropriate.
In adults, the demonstration of the benefit of Viread in HIV 1 infection is based on results of one study in treatment nave patients, including patients with a high viral load (> 100,000 copies/ml) and studies in which Viread was added to stable background therapy (mainly tritherapy) in antiretroviral pre-treated patients experiencing early virological failure (< 10,000 copies/ml, with the majority of patients having < 5,000 copies/ml).
The choice of Viread to treat antiretroviral experienced patients with HIV 1 infection should be based on individual viral resistance testing and/or treatment history of patients.
Hepatitis B infectionViread 33 mg/g granules are indicated for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B in adults for whom a solid dosage form is not appropriate with:
compensated liver disease, with evidence of active viral replication, persistently elevated serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels and histological evidence of active inflammation and/or fibrosis (see section 5. 1). evidence of lamivudine resistant hepatitis B virus (see sections 4. 8 and 5. 1). decompensated liver disease (see sections 4. 4, 4. 8 and 5. 1).
Viread 33 mg/g granules are also indicated for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B in paediatric patients2 to < 18 years of age for whom a solid dosage form is not appropriate with:
compensated liver disease and evidence of immune active disease, i. e. active viral replication, and persistently elevated serum ALT levels, or histological evidence of moderate to severe inflammation and/or fibrosis. With respect to the decision to initiate treatment in paediatric patients, see sections 4. 2, 4. 4, 4. 8 and 5. 1.
Antiviral Agents
Agents used in the prophylaxis or therapy of VIRUS DISEASES. Some of the ways they may act include preventing viral replication by inhibiting viral DNA polymerase; binding to specific cell-surface receptors and inhibiting viral penetration or uncoating; inhibiting viral protein synthesis; or blocking late stages of virus assembly. (See all compounds classified as Antiviral Agents.)
Anti-HIV Agents
Agents used to treat AIDS and/or stop the spread of the HIV infection. These do not include drugs used to treat symptoms or opportunistic infections associated with AIDS. (See all compounds classified as Anti-HIV Agents.)
Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors
Inhibitors of reverse transcriptase (RNA-DIRECTED DNA POLYMERASE), an enzyme that synthesizes DNA on an RNA template. (See all compounds classified as Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors.)
J05AF07
Following IV administration of tenofovir, approximately 70-80% of the dose is recovered in the urine as unchanged tenofovir within 72 hours of dosing. Following single dose, oral administration of tenofovir, the terminal elimination half-life of tenofovir is approximately 17 hours. After multiple oral doses of tenofovir 300 mg once daily (under fed conditions), 32 + or - 10% of the administered dose is recovered in urine over 24 hours. Tenofovir is eliminated by a combination of glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion. There may be competition for elimination with other compounds that are also renally eliminated.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for VIREAD (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) tablet, coated VIREAD (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) powder (November 2012). Available from, as of November 14, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=33fd6418-fbdc-42ca-a50d-ce2a476a5418
In vitro binding of tenofovir to human plasma or serum proteins is less than 0.7 and 7.2%, respectively, over the tenofovir concentration range 0.01 to 25 ug/mL. The volume of distribution at steady-state is 1.3 + or - 0.6 L/kg and 1.2 + or - 0.4 L/kg, following intravenous administration of tenofovir 1.0 mg/kg and 3.0 mg/kg.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for VIREAD (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) tablet, coated VIREAD (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) powder (November 2012). Available from, as of November 14, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=33fd6418-fbdc-42ca-a50d-ce2a476a5418
Viread is a water soluble diester prodrug of the active ingredient tenofovir. The oral bioavailability of tenofovir from Viread in fasted subjects is approximately 25%. Following oral administration of a single dose of Viread 300 mg to HIV-1 infected subjects in the fasted state, maximum serum concentrations (Cmax) are achieved in 1.0 + or - 0.4 hr. Cmax and AUC values are 0.30 + or - 0.09 ug/mL and 2.29 + or - 0.69 ug hr/mL, respectively.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for VIREAD (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) tablet, coated VIREAD (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) powder (November 2012). Available from, as of November 14, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=33fd6418-fbdc-42ca-a50d-ce2a476a5418
Administration of Viread 300 mg tablets following a high-fat meal (approximately 700 to 1000 kcal containing 40 to 50% fat) increases the oral bioavailability, with an increase in tenofovir AUC of approximately 40% and an increase in Cmax of approximately 14%. However, administration of Viread with a light meal did not have a significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of tenofovir when compared to fasted administration of the drug. Food delays the time to tenofovir Cmax by approximately 1 hour. Cmax and AUC of tenofovir are 0.33 + or - 0.12 ug/mL and 3.32 + or - 1.37 ug hr/mL following multiple doses of Viread 300 mg once daily in the fed state, when meal content was not controlled.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for VIREAD (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) tablet, coated VIREAD (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) powder (November 2012). Available from, as of November 14, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=33fd6418-fbdc-42ca-a50d-ce2a476a5418
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for TENOFOVIR DISOPROXIL FUMARATE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is a prodrug and is not active until it undergoes diester hydrolysis in vivo to tenofovir and subsequently is metabolized to the active metabolite (tenofovir diphosphate).
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2012; Drug Information 2012. Bethesda, MD. 2012, p. 751
Following single dose, oral administration of Viread, the terminal elimination half-life of tenofovir is approximately 17 hours.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for VIREAD (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) tablet, coated VIREAD (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) powder (November 2012). Available from, as of November 14, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=33fd6418-fbdc-42ca-a50d-ce2a476a5418
Like nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, the antiviral activity of tenofovir depends on intracellular conversion to an active metabolite; however, tenofovir is a nucleotide containing a phosphonate group and the steps and enzymes involved in enzymatic conversion to the active metabolite differ from those involved in the conversion of nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Tenofovir is phosphorylated by cellular nucleotide kinases to tenofovir diphosphate; tenofovir diphosphate is a structural analog of deoxyadenosine-5-triphosphate, the usual substrate for viral RNA-directed DNA polymerase. Although other mechanisms may be involved in the antiretroviral activities of the drug, tenofovir diphosphate appears to compete with deoxyadenosine-5-triphosphate for viral RNA-directed DNA polymerase and for incorporation into viral DNA. Following incorporation of tenofovir diphosphate into the viral DNA chain, DNA synthesis is prematurely terminated because the absence of the 3-hydroxy group on the drug prevents further 5 to 3 phosphodiester linkages.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2012; Drug Information 2012. Bethesda, MD. 2012, p. 751
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, a synthetic antiretroviral agent, is a nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor. Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is a prodrug and is not active until it undergoes diester hydrolysis in vivo to tenofovir and subsequently is metabolized to the active metabolite (tenofovir diphosphate). Following conversion to the pharmacologically active metabolite, tenofovir apparently inhibits replication of retroviruses, including human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1), by interfering with viral RNA-directed DNA polymerase (reverse transcriptase). In vitro studies indicate that tenofovir is active against HIV-1, HIV-2, and hepatitis B virus (HBV); the drug also has some activity against HIV-2.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2012; Drug Information 2012. Bethesda, MD. 2012, p. 751
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) is an oral prodrug and acyclic nucleotide analog of adenosine monophosphate that inhibits HIV-1 (HIV) reverse transcriptase. A growing subset of TDF-treated HIV(+) individuals presented with acute renal failure, suggesting tenofovir-associated kidney-specific toxicity. ... Previous studies using an HIV transgenic mouse model (TG) demonstrated specific changes in renal proximal tubular mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) abundance. Nucleosides are regulated in biological systems via transport and metabolism in cellular compartments. In this study, the role(s) of organic anion transporter type 1 (OAT1) and multidrug-resistant protein type 4 (MRP4) in transport and regulation of tenofovir in proximal tubules were assessed. Renal toxicity was assessed in kidney tissues from OAT1 knockout (KO) or MRP4 KO compared with wild-type (WT, C57BL/6) mice following treatment with TDF (0.11 mg/day), didanosine (ddI, a related adenosine analog, 0.14 mg/day) or vehicle (0.1 M NaOH) daily gavage for 5 weeks. Laser-capture microdissection (LCM) was used to isolate renal proximal tubules for molecular analyses. mtDNA abundance and ultrastructural pathology were analyzed. mtDNA abundance in whole kidneys from both KO and WT was unchanged regardless of treatment. Renal proximal tubular mtDNA abundance from OAT1 KO also remained unchanged, suggesting prevention of TDF toxicity due to loss of tenofovir transport into proximal tubules. In contrast, renal proximal tubules from MRP4 KO exhibited increased mtDNA abundance following TDF treatment compared with WT littermates, suggesting compensation. Renal proximal tubules from TDF-treated WT and MRP4 KO exhibited increased numbers of irregular mitochondria with sparse, fragmented cristae compared with OAT1 KO. Treatment with ddI had a compensatory effect on mtDNA abundance in OAT1 KO but not in MRP4 KO. Both OAT1 and MRP4 have a direct role in transport and efflux of tenofovir, regulating levels of tenofovir in proximal tubules. Disruption of OAT1 activity prevents tenofovir toxicity but loss of MRP4 can lead to increased renal proximal tubular toxicity. These data help to explain mechanisms of human TDF renal toxicity.
PMID:21403643 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3103636 Kohler JJ et al; Lab Invest 91 (6): 852-8 (2011)a
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (tenofovir DF) use has been associated with renal dysfunction and Fanconi syndrome. Tenofovir is taken up into renal tubules by anion transporters where high intracellular drug concentration may induce a functionally relevant depletion of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). /The researchers/ investigated if tenofovir may induce renal mtDNA depletion and respiratory chain dysfunction. Rats (n = 8) were gavaged daily with 100 mg x kg(-1) x d(-1) of tenofovir DF or didanosine. Kidneys and livers were examined after 8 weeks of treatment. The tenofovir group had significantly lower body and kidney weights than rats exposed to water or didanosine. Proximal but not distal tubules were of increased diameter and contained small lipid droplets. Tubular mitochondria were enlarged, and their crystal architecture was disrupted. Tenofovir-exposed kidneys contained low mtDNA copy numbers and impaired expression of mtDNA-encoded cytochrome c oxidase (COX) I but not nucleus-encoded COX IV subunits. Histochemistry demonstrated low tubular COX and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide dehydrogenase (NADH-DH) activities, whereas succinate dehydrogenase activity was preserved. COX activity was preserved in the glomeruli of tenofovir-exposed rats. Didanosine did not elicit renal effects but, unlike tenofovir, depleted mtDNA in liver (by 52%). Tenofovir DF induces an organ-specific nephrotoxicity with mtDNA depletion and dysfunction of mtDNA-encoded respiratory chain subunits. The data do not support nephrotoxicity of didanosine.
PMID:19582894 Lebrecht D et al; J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 51 (3): 258-63 (2009)

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS

Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ANALYTICAL

ABOUT THIS PAGE
33
PharmaCompass offers a list of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate manufacturer or Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate manufacturer or Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate supplier is an individual or a company that provides Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate finished formulations upon request. The Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate suppliers may include Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate USDMF includes data on Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Drug Master File in Korea (Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate. The MFDS reviews the Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate written confirmation (Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate APIs or Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate GMP manufacturer or Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate's compliance with Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate EP), Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate USP).

