
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
EU WC
0
VMF
0
Australia
Annual Reports
NA
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
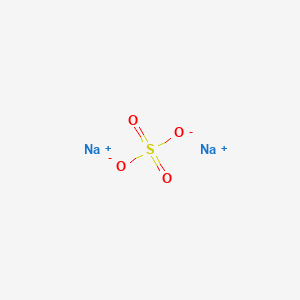

1. Disodium Sulfate
2. Mangxiao
3. Mirabilitum
4. Natrii Sulphas
5. Puxiao
6. Sodium Bisulfate
7. Sodium Bisulfate, Monohydrate
8. Sodium Hydrosulfate
9. Sodium Sulfate, 35s-labeled Cpd
10. Sodium Sulfate, Decahydrate
11. Sulfuric Acid, Monosodium Salt
12. Thenardite
1. 7757-82-6
2. Disodium Sulfate
3. Sodium Sulfate, Anhydrous
4. Sodium Sulfate Anhydrous
5. Sodium Sulphate
6. Salt Cake
7. Sodiumsulfate
8. Sulfuric Acid Disodium Salt
9. Disodium Sulphate
10. Disodium;sulfate
11. 15124-09-1
12. Sulfuric Acid, Sodium Salt
13. Sulfate, Sodium
14. Sodium Sulphate Anhydrous
15. Sodium Sulfate, Dried [jan]
16. Sodium Sulfate, Dried
17. Na2so4
18. Mfcd00003504
19. Sodium Sulphate, Anhydrous
20. Chebi:32149
21. 36kcs0r750
22. Nsc-403914
23. Sulfuric Acid, Mono-c14-18-alkyl Esters, Sodium Salts
24. 13759-07-4
25. Sodium Sulfate, Dried (jan)
26. Dibasic Sodium Sulfate
27. Natriumsulfat (german)
28. Na Sulphate
29. Caswell No. 793
30. Hsdb 5042
31. Sodium Sulfate Anyhdrous
32. Sulfuric Acid Sodium Salt (1:2)
33. Sodium Sulfate (solution)
34. Thenardite (na2(so4))
35. Natriumsulfat
36. Sodium Tallow Alcohol Sulfate
37. Unii-36kcs0r750
38. Einecs 231-820-9
39. Einecs 268-366-6
40. Einecs 268-773-9
41. Einecs 270-211-2
42. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 005604
43. Nsc 403914
44. Sodium Sulfate Acs He
45. Ai3-02398
46. Sda 17-062-04
47. Sulfuric Acid Sodium Salt
48. Dsstox_cid_1291
49. Ec 231-820-9
50. Dsstox_rid_76063
51. Sodium Sulfate [mi]
52. Dsstox_gsid_21291
53. Sodium Sulfate, Acs Reagent
54. Sodium Sulfate, Dried (tn)
55. Sodium Sulfate [hsdb]
56. Chembl233406
57. Dtxsid1021291
58. Anhydous Sodium Sulfate (jp17)
59. Sodium Sulfate - Drilling Grade
60. Bcp13313
61. Sodium Sulfate, For Residue Analysis
62. Tox21_201045
63. Sodium Sulfate Anhydrous [ii]
64. Akos015833463
65. Anhydrous Sodium Sulfate [jan]
66. Sodium Sulfate Anhydrous Granular Acs
67. Sodium Sulfate, Bioxtra, >=99.0%
68. Sulfuric Acid Disodium Salt, Anhydrous
69. Db09472
70. Anhydrous Sodium Sulfate [mart.]
71. Ncgc00258598-01
72. Sodium Sulfate, Lr, Anhydrous, >=99%
73. E514
74. Sodium Sulfate Anhydrous [usp-rs]
75. Sodium Sulfate Anhydrous [who-dd]
76. Sodium Sulfate Anhydrous; Sodium Sulphate
77. Cas-7757-82-6
78. Sodium Sulfate, Anhydrous [who-ip]
79. Sodium Sulfate, Ar, Anhydrous, >=99.5%
80. Ft-0645112
81. S0566
82. Sodium Sulfate, 99.9955% (metals Basis)
83. Sodium Sulfate, Reagentplus(r), >=99.0%
84. Sodium Sulfate Anhydrous [orange Book]
85. Sodium Sulfate, For Pesticide Residue Analysis
86. Sodium Sulfate, Trace Metals Grade, 99.99%
87. D01732
88. Natrii Sulfas Anhydricus [who-ip Latin]
89. Sodium Sulfate, >=99.99% Trace Metals Basis
90. Sodium Sulfate, Jis Special Grade, >=99.0%
91. Sodium Sulfate, Vetec(tm) Reagent Grade, 99%
92. Sodium Sulfate Anhydrous [usp Monograph]
93. Sodium Sulfate, Anhydrous [ep Monograph]
94. Sodium Sulfate, Meets Usp Testing Specifications
95. Q211737
96. Sodium Sulfate, For Hplc, 99.0-101.0% (t)
97. Sodium Sulfate, Purum, Anhydrous, >=99.0% (t)
98. Sodium Sulfate, Saj First Grade, >=99.0%, Beads
99. Sodium Sulfate, Saj First Grade, >=99.0%, Powder
100. Sodium Sulfate, >=99.0%, Plant Cell Culture Tested
101. Sodium Sulfate, Bioultra, Anhydrous, >=99.0% (t)
102. Sodium Sulfate, P.a., 99.0-101.0%, Reag. Iso
103. Sodium Sulfate, For Pesticide Residue Analysis, 99.0%
104. Sodium Sulfate, Tested According To Ph.eur., Anhydrous
105. Sulfuric Acid Disodium Salt, Anhydrous [who-ip]
106. Sodium Sulfate, Acs Reagent, >=99.0%, Anhydrous, Powder
107. Sodium Sulfate, Acs Reagent, >=99.0%, Anhydrous, Granular
108. Sodium Sulfate, Anhydrous, Free-flowing, Redi-dri(tm), Acs Reagent, >=99%
109. Sodium Sulfate Anhydrous, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
110. Sodium Sulfate, Anhydrous, Free-flowing, Redi-dri(tm), Reagentplus(r), >=99%
111. Sodium Sulfate, Anhydrous, Granular, Free-flowing, Redi-dri(tm), Acs Reagent, >=99%
112. Sodium Sulfate, Puriss. P.a., Acs Reagent, Reag. Iso, Reag. Ph. Eur., Anhydrous, >=99.0%
113. Sodium Sulfate, Puriss., Meets Analytical Specification Of Ph. Eur., Bp, Usp, Anhydrous, 99.0-100.5% (calc. To The Dried Substance)
| Molecular Weight | 142.04 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | Na2O4S |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 141.93126821 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 141.93126821 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 88.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 7 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 62.2 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 3 |
Cathartics
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
EXPL THER /The purpose of the study was/ to evaluate the early bone response to a nanotextured dental implant treated with sodium sulfate (Na2SO4), using a rabbit model. Twelve animals were randomly divided into group 1 (Control) - machined implants and group 2 (Test) - nanotextured implants. Extra-oral incision was performed to provide access to intended surgical site where the dental implant was inserted immediately after the extraction of the mandibular first premolar. Implant surface characterization was performed by scanning electron microscopy attached to energy dispersive spectroscopy and interferometry. Three weeks after surgery, the animals were induced to death and undecalcified sections of the samples were prepared for histological and histomorphometrical analysis. Surface characterization of the implant demonstrated enhanced surface area of anodized group compared to Control group with 19.2% +/- 6.2 versus 1.6 +/- 0.7, respectively. Histological evaluation demonstrated new bone formation starting from the buccal and lingual cortical walls on both groups. After three weeks, significant higher bone contact of 27% (p<0.05) was observed to nanotextured compared to machined implants (Control group). The anodization with sodium sulfate nanostructures to the implant surface that resulted in faster osseointegration.
PMID:24919046 Pinheiro FA et al; Acta Cir Bras 29 (6): 376-82 (2014)
/EXPL THER/ ... 2-16 mmol/kg of sodium sulfate and sulfur-containing amino acids (cysteine or methionine) were infused intravenously for 2 hr into pentobarbital-anesthetized rats. ... Hepatic 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate concentrations increased significantly (30-35%) only when infused with the higher doses (8 or 16 mmol/kg/2 hr) of sodium sulfate.
PMID:7493551 Kim HJ et al; Drug Metab Dispos 23 (8): 840-5 (1995)
VET: Cathartic
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. Cambridge, UK: Royal Society of Chemistry, 2013., p. 1607
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Sodium sulfate (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Sodium sulfate used in treatment of hypercalcemia may result in hypokalemia and hypernatremia. Thus, the progress of patients with cardiovascular disease should be watched closely when ... infusions are administered.
Hansten, P.D. Drug Interactions. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Lea and Febiger, 1979., p. 396
indicated for bowel cleansing prior to colonoscopy or barium enema X-ray examination.
Induces catharsis by the osmotic effects of the unabsorbed sulfate salts and polyethylene glycol (PEG) in the GI tract. Specifically, sulfate salts provide sulfate anions, which are poorly absorbed, and PEG, which is primarily unabsorbed, causes water to be retained in the GI tract resulting in watery diarrhea.
Cathartics
Agents that are used to stimulate evacuation of the bowels. (See all compounds classified as Cathartics.)
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A06 - Drugs for constipation
A06A - Drugs for constipation
A06AD - Osmotically acting laxatives
A06AD13 - Sodium sulfate
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A12 - Mineral supplements
A12C - Other mineral supplements
A12CA - Sodium
A12CA02 - Sodium sulfate
Absorption
Absorption of sodium sulfate after ingestion in rats was investigated. 35)S-Radioactivity excreted in urine during 24 hr indicated almost complete absorption from GI tract. Determination in serum 2 hr after admin revealed 3-fold increase in sulfate concentration rapid and almost complete absorption of inorganic sulfate occurs after oral admin in rats.
Route of Elimination
Rectal effluent if unabsorbed sulfates ; urine (predominant route for absorbed sulfates )
The importance of tissue sulfate concentrations in regulating 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate (PAPS) synthesis is not known. Therefore, this study was conducted to determine the influence of increased availability of inorganic sulfate on steady-state PAPS concentrations in various tissues. To increase tissue sulfate concentrations, 2-16 mmol/kg of sodium sulfate and sulfur-containing amino acids (cysteine or methionine) were infused intravenously for 2 hr into pentobarbital-anesthetized rats. Serial blood samples were taken during the infusion and analyzed for sulfate concentrations. After 2 hr of infusion, liver, kidney, and brain were removed for quantification of tissue PAPS and sulfate concentrations. Infusion of sodium sulfate, cysteine, and methionine increased serum and tissue sulfate concentrations in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Serum sulfate concentrations increased from 0.8 to 14 mM during the infusion of sodium sulfate, whereas infusions of cysteine and methionine increased serum sulfate concentrations to 4.8 and 2.0 mM, respectively. Tissue sulfate concentrations also increased during sulfate infusion. Liver sulfate concentration increased from 0.8 to 4.8 mM, kidney concentration increased from 0.6 to 31 mM, and brain concentration increased from 0.1 to 0.6 mM. Similar to the serum sulfate concentrations, sulfate infusion was the most effective in increasing tissue sulfate concentrations, cysteine was intermediate, and methionine the least effective. Although sulfate concentrations in liver, kidney, and brain increased 6-, 50-, and 6-fold by infusing sulfate, respectively; tissue PAPS levels were not altered markedly. Hepatic PAPS concentrations increased significantly (30-35%) only when infused with the higher doses (8 or 16 mmol/kg/2 hr) of sodium sulfate.
PMID:7493551 Kim HJ et al; Drug Metab Dispos 23 (8): 840-5 (1995)
The absorption of inorganic sulfate after ingestion was investigated in rats. After oral administration of Na235SO4, 35S radioactivity was measurable in plasma already after 15 min and its plasma concentration reached a peak after about 1.5-2 hr. The 35S-radioactivity excreted in urine during 24 hr after ingestion of Na235SO4 together with varying amounts of unlabelled Na2SO4 (0.25-5.0 mmol Na2SO4 per rat) indicated an almost complete absorption of inorganic sulfate from the gastrointestinal tract. Determination of the inorganic sulfate concentration in rat serum 2 hr after oral administration of 5.0 mmol Na2SO4 revealed a three-fold increase in serum sulfate concentration. The data suggest a rapid and almost complete absorption of inorganic sulfate after oral administration in the rat. Its importance in relation to the sulfate availability for sulfate conjugation of drugs is discussed.
PMID:476150 Krijgsheld KR et al; Biochim Biophys Acta 586 (3): 492-500 (1979)
Sodium sulfate can be used to enhance the conjugation of phenolic drugs with sulfate and to treat hypercalcemia. It is thought that sulfate in is absorbed slowly and incompletely from the digestive tract. The purposes of this investigation were to determine the absorption of large amount of sodium sulfate(18.1 g as the decahydrate, equivalent to 8.0 g of the anhydrous salt) and to compare the bioavailability when this amount is administered orally to normal subjects as a single dose and as four equally divided hourly doses. The 72-hr urinary recovery of free sulfate following single and divided doses was 53.4 +/- 15.8 and 61.8 +/- 7.8%, respectively (mean +/- SD, n=5, p > 0.2). The single dose produced severe diarrhea while the divided doses caused only mild or no diarrhea. Thus, a large amount of sodium sulfate, when administered orally in divided doses over 3 hr, is well tolerated and is absorbed to a significant extent. Orally administered sodium sulfate may be useful for the early treatment of acetaminophen overdose.
PMID:7264905 Cocchetto DM, Levy G; J Pharm Sci 70 (3): 331-3 (1981)
The renal excretion of potassium by unanesthetized sheep was studied in clearance studies in which water and sodium excretion were elevated by intravenous infusion of isotonic sodium chloride, hypertonic sodium phosphate, or hypertonic sodium sulfate. Aldosterone was infused at 10 ug/hr in some experiments with sodium sulfate. Sodium excretion increased in all experiments, rising at times to equal 25% of the filtered load. Urine flow increased in most experiments. Glomerular filtration rate increased only with infusion of isotonic saline. No consistent change in potassium excretion occurred under any of these loading conditions. This finding contrasts with the increase in potassium excretion commonly seen in man, dogs, and rats intravenously loaded with sodium salts.
PMID:645906 Rabinowitz L, Gunther RA; Am J Physiol 234 (5): F371-5 (1978)
Serum sulfate: 8.5 hours
MoviPrep produces a watery stool leading to cleansing of the colon. The osmotic activity of polyethylene glycol 3350, sodium sulfate, sodium chloride, potassium chloride, sodium ascorbate, and ascorbic acid, when taken with 1 liter of additional clear fluid, usually results in no net absorption or excretion of ions or water.

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS

Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
81
PharmaCompass offers a list of Sodium Sulfate API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Sodium Sulfate manufacturer or Sodium Sulfate supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Sodium Sulfate manufacturer or Sodium Sulfate supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Sodium Sulfate API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Sodium Sulfate API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Sodium Sulfate Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Sodium Sulfate Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Disodium sulphate manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Disodium sulphate, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Disodium sulphate manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Disodium sulphate API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Disodium sulphate manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Disodium sulphate supplier is an individual or a company that provides Disodium sulphate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Disodium sulphate finished formulations upon request. The Disodium sulphate suppliers may include Disodium sulphate API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Disodium sulphate suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Disodium sulphate DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Disodium sulphate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Disodium sulphate DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Disodium sulphate USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Disodium sulphate DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Disodium sulphate USDMF includes data on Disodium sulphate's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Disodium sulphate USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Disodium sulphate suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) established the Japan Drug Master File (JDMF), also known as the Master File (MF), to permit Japanese and foreign manufacturers of drug substances, intermediates, excipients, raw materials, and packaging materials (‘Products’) to voluntarily register confidential information about the production and management of their products in Japan.
The Disodium sulphate Drug Master File in Japan (Disodium sulphate JDMF) empowers Disodium sulphate API manufacturers to present comprehensive information (e.g., production methods, data, etc.) to the review authority, i.e., PMDA (Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Agency).
PMDA reviews the Disodium sulphate JDMF during the approval evaluation for pharmaceutical products. At the time of Disodium sulphate JDMF registration, PMDA checks if the format is accurate, if the necessary items have been included (application), and if data has been attached.
click here to find a list of Disodium sulphate suppliers with JDMF on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a Disodium sulphate Drug Master File in Korea (Disodium sulphate KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of Disodium sulphate. The MFDS reviews the Disodium sulphate KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the Disodium sulphate KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a Disodium sulphate KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their Disodium sulphate API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of Disodium sulphate suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Disodium sulphate CEP of the European Pharmacopoeia monograph is often referred to as a Disodium sulphate Certificate of Suitability (COS). The purpose of a Disodium sulphate CEP is to show that the European Pharmacopoeia monograph adequately controls the purity of Disodium sulphate EP produced by a given manufacturer. Suppliers of raw materials can prove the suitability of Disodium sulphate to their clients by showing that a Disodium sulphate CEP has been issued for it. The manufacturer submits a Disodium sulphate CEP (COS) as part of the market authorization procedure, and it takes on the role of a Disodium sulphate CEP holder for the record. Additionally, the data presented in the Disodium sulphate CEP (COS) is managed confidentially and offers a centralized system acknowledged by numerous nations, exactly like the Disodium sulphate DMF.
A Disodium sulphate CEP (COS) is recognised by all 36 nations that make up the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. Disodium sulphate CEPs may be accepted in nations that are not members of the Ph. Eur. at the discretion of the authorities there.
click here to find a list of Disodium sulphate suppliers with CEP (COS) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Disodium sulphate as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Disodium sulphate API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Disodium sulphate as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Disodium sulphate and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Disodium sulphate NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Disodium sulphate suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Disodium sulphate Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Disodium sulphate GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Disodium sulphate GMP manufacturer or Disodium sulphate GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Disodium sulphate CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Disodium sulphate's compliance with Disodium sulphate specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Disodium sulphate CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Disodium sulphate CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Disodium sulphate may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Disodium sulphate EP), Disodium sulphate JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Disodium sulphate USP).

