


API Suppliers
0

US DMFs Filed
0

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
0
Other Suppliers
0
0
0

USA (Orange Book)
0

Europe
0

Canada
0

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
0
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
0
USFDA Orange Book Patents
0
USFDA Exclusivities
0
Blog #PharmaFlow
0
News
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Other Listed Suppliers
0
0
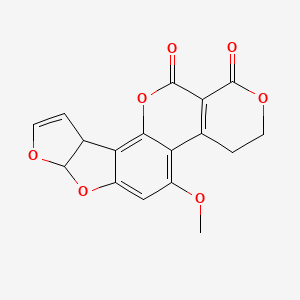

1. Aflatoxin G(1)
1. Aflatoxin
2. 1165-39-5
3. Aflatoxin G
4. Aflatoxin, Crude
5. 1402-68-2
6. 11-methoxy-6,8,16,20-tetraoxapentacyclo[10.8.0.02,9.03,7.013,18]icosa-1,4,9,11,13(18)-pentaene-17,19-dione
7. 5-(methyloxy)-3,4,7a,10a-tetrahydro-1h,12h-furo[3',2':4,5]furo[2,3-h]pyrano[3,4-c]chromene-1,12-dione
8. Aflatoxing
9. Hsdb 3411
10. 1h,12h-furo[3',2':4,5]furo[2,3-h]pyrano[3,4-c][1]benzopyran-1,12-dione, 3,4,7a,10a-tetrahydro-5-methoxy-, (7ar-cis)-
11. Aflatoxin G1 2 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
12. Schembl50772
13. Aflatoxin G1 In Acetonitrile
14. Aflatoxin G1-13c17 Solution
15. Aflatoxin G1, Reference Material
16. Chebi:190729
17. Mfcd28143303
18. Aflatoxin G1, From Aspergillus Flavus
19. Akos015896946
20. Ft-0621934
21. A937071
22. Q59260340
23. Aflatoxin G1 Solution, 2 Mug/ml In Acetonitrile, Analytical Standard
24. Aflatoxin G1 Solution, 3.78 Mug/g In Acetonitrile, Erm(r) Certified Reference Material
25. (7ar,10as)-5-methoxy-3,4,7a,10a-tetrahydro-1h,12h-furo[3',2':4,5]furo[2,3-h]pyrano[3,4-c]chromene-1,12-dione
26. 11-methoxy-6,8,16,20-tetraoxapentacyclo[10.8.0.0^{2,9}.0^{3,7}.0^{13,18}]icosa-1,4,9,11,13(18)-pentaene-17,19-dione
27. 1h,12h-furo[3',2':4,5]furo[2,3-h]pyrano[3,4-c][1]benzopyran-1,12-dione,3,4,7a,10a-tetrahydro-5-methoxy-, (7ar,10as)-
28. Aflatoxin G1 Solution, Certified Reference Material, 3 Mug/ml In Benzene:acetonitrile (98:2), Ampule Of 1 Ml
| Molecular Weight | 328.27 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H12O7 |
| XLogP3 | 1.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 328.05830272 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 328.05830272 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 80.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 666 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Aflatoxins B1 & G1 & their metabolites exist in systemic blood as protein conjugates. This conjugation is specific to plasma albumin & proceeds enzymatically by liver & kidney cells. The albumin-aflatoxin conjugate is permanent & conjugation is an irreversible one.
PMID:6811900 Nassar AY et al; Mycopathologia 79 (1): 35 (1982)
Three groups of four Large White sows were fed diets containing either 800 ppb purified aflatoxin B1 (group 1), 800 ppb purified aflatoxin G1 (group 2) or 400 ppb B1 and 400 ppb G1 (group 3) throughout gestation and lactation. A control group of four sows was fed a diet free of aflatoxins. Aflatoxins B1 and M1 were found in milk samples taken five and 25 days after parturition from the sows of group 1, aflatoxin G1 was present in the milk of the sows of group 2 and all three aflatoxins were present in samples from the sows of group 3. The concentration of aflatoxin in the milk was about 1000-fold lower than that in the feed, but increased over the 25 days after parturition.
PMID:9392065 Silvotti L et al; Vet Rec 141(18): 469-472 (1997)
Yields aflatoxin B3 in rhizopus ... yields aflatoxin gm1 in rat. From table/
Goodwin, B.L. Handbook of Intermediary Metabolism of Aromatic Compounds. New York: Wiley, 1976., p. A-27
Aflatoxin B1, aflatoxin B2, & aflatoxin G1 admin iv to rats were rapidly metabolized to 7 groups of metabolites each, 6 of which were excreted in the bile. All 3 toxins were hydroxylated at the 2- & 4-positions. Bile from the rats that had received aflatoxin G1 contained glucuronide.
PMID:5034521 Dann RE et al; Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 3 (3): 667 (1972)
...The incubation of human liver microsomes with aflatoxin B1 /or/ aflatoxin G1 ...yielded genotoxic metabolites that induced umuC gene expression in Salmonella typhimurium (TA-1535/psK1002). The rank order of genotoxic potency was ...aflatoxin B1>aflatoxin G1. Microsomal activation of the ...aflatoxins was completely inhibited upon incubation with polyclonal antibodies against p450NF, and immunochemical determinations of p450NF /(nifedipine oxidase)/ in the liver microsomal preparations were correlated with the microsomal activation of ...aflatoxin G1 and aflatoxin B1. P450NF converted the ...aflatoxins to genotoxic metabolites in a reconstituted monooxygenase system containing the purified enzyme and an NADPH generating system. ...
PMID:2492107 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC286490 Shimada T, Guengerich FP; Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 86 (2): 462-5 (1989)
Ability of aflatoxin B1, aflatoxin B2, & aflatoxin G1 to inhibit RNA polymerase activity & decr RNA content in rat hepatocyte nuclei was qualitatively similar to the carcinogenic & acute & subacute toxic actions of these compounds. Aflatoxin g1 induced a rapid macrosegregation of the fibrillar & granular portions of the hepatocyte nucleolus.
PMID:5120291 Edwards GS et al; Cancer Res 31 (12): 1943 (1971)
In vitro studies with human liver indicate that the major catalyst involved in the bioactivation of the hepato-carcinogen aflatoxin B1 to its genotoxic 2,3-epoxide derivative is cytochrome P-450NF, a previously characterized protein that also catalyzes the oxidation of nifedipine and other dihydropyridines, quinidine, macrolide antibiotics, various steroids, and other compounds. ...Cytochrome p-450NF or a closely related protein also appears to be the major catalyst involved in the activation of aflatoxin G1 and sterigmatocystin, the latter compound being more genotoxic than aflatoxin B1 in these systems. Several drugs and conditions are known to influence the levels and activity of cytochrome p-450NF in human liver, and the activity of the enzyme can be estimated by noninvasive assays. These findings provide a test system for the hypothesis that a specific human disease state (liver cancer) is linked to the level of oxidative metabolism in populations in which aflatoxin ingestion is high.
PMID:2492107 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC286490 Shimada T, Guengerich FP; Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 86 (2): 462-5 (1989)
Aflatoxin B1, aflatoxin G1 & aflatoxin G2 inhibited incorporation of (14)carbon labeled orotic acid into the RNA of rat liver slices at toxin concentrations of 100 umole/3 mL. Respective percent inhibitions were approx 90, 40, & 20. Aflatoxin B1, 20 umole/3 mL, aflatoxin G1, 150 umole/3 mL, & aflatoxin G2, 230 umole/3 mL inhibited the incorporation of (14)carbon labeled dl-leucine into proteins of rat liver slices by 32%, 35%, & 38%, respectively.
PMID:6033768 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1270395 Clifford JI et al; Biochem J 103: 258 (1967)
Phagocytosis, intracellular killing of Candida albicans, and superoxide production by rat peritoneal macrophages exposed to aflatoxins B1, B2, G1, G2, B2a, and M1 at several times and concn were analyzed to evaluate the intensity of a depressive effect for each mycotoxin. All aflatoxins used at very low concn had a depressive effect on the functions of macrophages. The biggest impairment of phagocytosis, intracellular killing, and spontaneous superoxide production was observed in macrophages exposed to aflatoxins B1 and M1.
PMID:2176448 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC184993 Cusumano V et al; Appl Environ Microbiol 56 (11): 3482-4 (1990)
Among the toxic aflatoxins, aflatoxins B1 and G1 are the most biologically active, but other derivatives also exhibit carcinogenicity. Aflatoxin B1 requires metabolic activation by the cytochrome p450 dependent mixed-function oxidase to be converted to the reactive 2,3-epoxide, the ultimate carcinogen. The aflatoxins, eg, aflatoxin B1, are genotoxic carcinogens and the reactive metabolites react with DNA. The major adduct formed with DNA in intracellular reactions is formed from the 2-position of aflatoxin B1 and the N-7 position of guanine in DNA.
Haddad, L.M., Clinical Management of Poisoning and Drug Overdose. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: W.B. Saunders Co., 1990., p. 515


