In 2019, concerns over quality of medicines continued to dominate news headlines. The ‘sartan’ recall saga, which was triggered in July 2018 after
the European Medicines Agency (EMA) began reviewing medicines containing valsartan, for the presence of the carcinogenic impurity N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA),
continued well through the year and had a major impact on the global
pharmaceutical industry.
View our Interactive 2019 cGMP Compliance Recap Dashboard (Free Excel Available)
In 2019, French drugmaker Sanofi announced
it would recall popular heartburn medicine Zantac in the United States and Canada, after medicines containing the active ingredient ranitidine were also linked with the presence of NDMA.
Several generic drugmakers followed suit
and as concerns mounted over cancer-causing impurities in commonly used antacid, diabetes and blood pressure medicines, the EMA’s human medicines committee (CHMP) requested that marketing authorization holders (MAHs) for human medicines containing chemically synthesized active substances review their medicines for the possible presence of nitrosamines and test all
products at risk. The review will include all generics and over-the counter
(OTC) products.
View our Interactive 2019 cGMP Compliance Recap Dashboard (Free Excel Available)
In Spain, a drug mixup caused children to develop a form of werewolf
syndrome (a rare and curious condition that causes excessive hair growth) after
they were given a wrong medication to treat heartburn.
Swiss drugmaker Novartis battled data manipulation allegations involving
its US$ 2.1 million gene therapy Zolgensma and a new book titled ‘Bottle of Lies’,
by investigative journalist Katherine Eban revealed how quality and efficacy of
generic drugs is being compromised by companies in India and China, the two
main countries that produce these drugs for the US consumer.
The book release sent the FDA in damage control mode, with senior officials issuing statements supporting the agency’s generic drug framework.
Inspection statistics
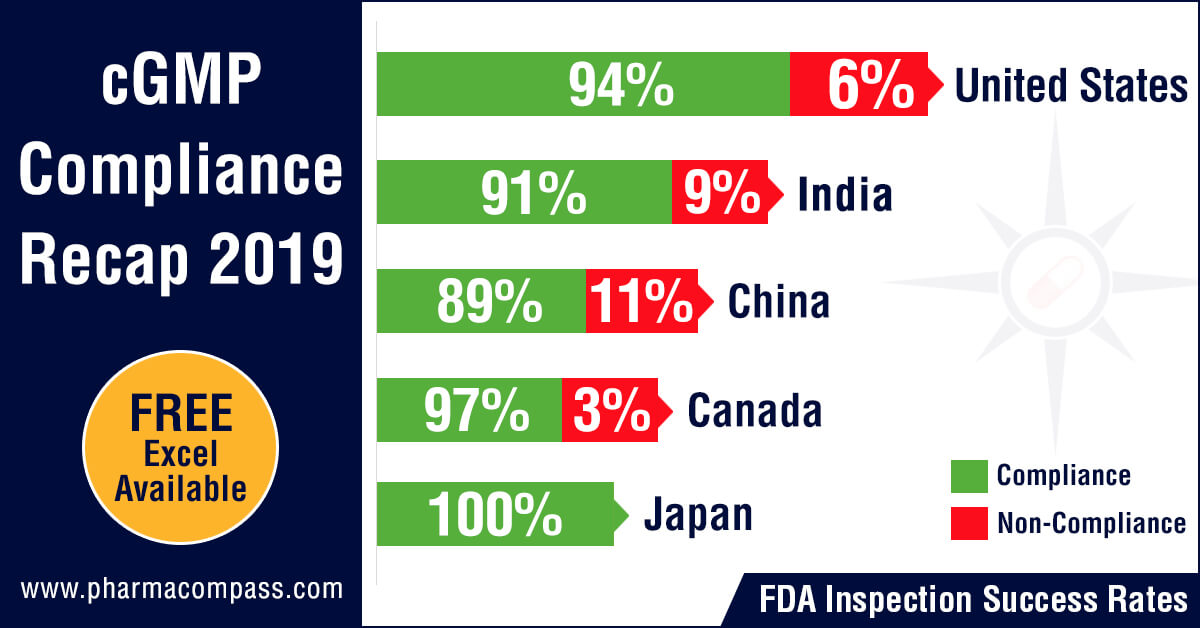
PharmaCompass reviewed the FDA and EDQM’s inspection statistics for the calendar year 2019 and found that the FDA’s Drug Quality Assurance division conducted 1,138 inspections with 2,280 inspections being performed by the member states of the EDQM.
The FDA was the most active in the United
States with 478 inspections followed by India where the inspection count was
193 and then in China where the count stood at 117.
With regard to non-compliance, there were 73 inspections which were classified as OAI (6.4 percent of the total number of inspections) by the FDA while the EDQM issued 20 non-compliance reports (0.87 percent of all inspections).
The highest number of facilities which failed to meet FDA’s standards were in the United States (29), followed by India (18) and then China (13). From an inspection success rate perspective, firms in the United States passed 94 percent of their inspections while the success rates in India and China were 91 percent and 89 percent respectively.
View our Interactive 2019 cGMP Compliance Recap Dashboard (Free Excel Available)
FDA investigators have identified persistent challenges while conducting foreign inspections, raising questions about the equivalence of foreign to domestic inspections. For example, while domestic inspections are almost always unannounced, FDA’s practice of pre-announcing foreign inspections up to 12 weeks in advance gives manufacturers the opportunity to fix problems.
A US Government Accountability Office preliminary analysis of FDA data revealed that from fiscal year 2012 through 2016, the number of foreign drug manufacturing establishment inspections increased. However, from fiscal year 2016 through 2018, both foreign and domestic inspections decreased—by about 10 percent and 13 percent, respectively. FDA officials attributed the decline, in part, to difficulty
in filling jobs abroad and on
the paucity of inspectors.
View our Interactive 2019 cGMP Compliance Recap Dashboard (Free Excel Available)
While the FDA is
actively working on increasing the number of inspectors, according to FDA
officials, it could take two to three years before the new staff is experienced
enough to conduct foreign inspections.
Concerns over
manufacturing quality in India re-emerge
In 2019, there was a surge of OAI
classifications and FDA warning letters issued to the manufacturing sites of
many major Indian pharmaceutical companies. The FDA issued warning letters to Aurobindo Pharma, Cadila Healthcare, Emcure Pharmaceuticals, Glenmark, Indoco Remedies, Jubilant, Lupin, Mylan, Strides and Torrent Pharmaceuticals.
There are more warning letters expected
as Form 483s issued after inspections at the facilities of Sun Pharma, Cipla and Lupin continue to reveal problems.
View our Interactive 2019 cGMP Compliance Recap Dashboard (Free Excel Available)
The Form 483 issued by the FDA, following the inspection at Sun Pharma’s Halol facility, highlighted that
Sun “failed to establish and implement controls which ensure data integrity” while Cipla’s finished
pharmaceuticals manufacturing facility in Goa got classified as Official Action Indicated (OAI) by the FDA following a September
2019 inspection in which the FDA investigators had issued a 38-page Form 483.
Regulatory actions lead to potential supply disruptions into
US
These regulatory actions have now begun to impact the supplies of
generic pharmaceuticals into the United
States. Injectable drugs, which constantly feature on the drug shortage list,
had Cadila and Pfizer announce the discontinuation of their supplies to the United States. Following FDA’s warning letter to Cadila, the firm informed the FDA that it would permanently cease production of injectable drug products for the United States.
In
2019, Pfizer announced that two manufacturing sites in India, which
it had acquired
through its US$ 17 billion acquisition of Hospira, will cease manufacturing operations.
The sites located near Chennai (Irungattukottai) and Aurangabad employed 1,700
people.
View our Interactive 2019 cGMP Compliance Recap Dashboard (Free Excel Available)
The
Irungattukottai site received an FDA warning letter in 2013
and in 2016, Pfizer halted production at the plant after a PIC/S (short for Pharmaceutical Inspection Convention and Pharmaceutical Inspection Co-operation Scheme) joint inspection with regulators from four international agencies — MHRA (Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency of the UK), USFDA (United States Food and Drug Administration), TGA (Therapeutic Goods Administration of Australia) and Health Canada — found various quality control problems.
Firms like Vital Laboratories and Alchymars ICM SM Private Limited, which had been issued warning letters in the past, were placed on import alert
by the FDA.
Concerns over
operations at firms responsible for valsartan recalls
The FDA
and EDQM both raised concerns over the operations at Lantech Pharmaceuticals Limited, a firm which undertakes contract solvent recovery for valsartan API manufacturing operations. Solvents recovered by Lantech and samples collected from Lantech’s equipment were found to contain mutagenic impurities.
Inspections at Lantech revealed that the firm failed to implement a procedure for investigating unknown peaks in recovered solvent chromatograms observed during analytical testing — an oversight which had led to the cancer-causing impurities not being detected in the ‘sartan’ APIs.
View our Interactive 2019 cGMP Compliance Recap Dashboard (Free Excel Available)
The FDA also raised data-integrity concerns at the facility as it was “routinely deleting recovered solvents gas chromatography (GC) data older than three months permanently, without any backup” and adequate controls.
As a fallout of the “sartan” recall, warning letters were issued to Mylan and Jubilant over their valsartan manufacturing operations.
Novartis’ data manipulation scandal
In a shocking announcement, the US Food
and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a press release on data accuracy issues with Novartis’ gene therapy — Zolgensma.
Zolgensma was acquired by Novartis in April 2018 when in a bid to secure its
leadership position in gene therapy, Novartis struck a deal to acquire Illinois-based AveXis Inc for US$ 8.7 billion.
The gene therapy, intended to treat children less than two years of age
with the most severe form of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), is priced at
US$ 2.1 million, making it the world’s most expensive drug.
View our Interactive 2019 cGMP Compliance Recap Dashboard (Free Excel Available)
On May 24,
2019, the FDA approved Zolgensma and a month later, on June 28,
the agency was informed by AveXis (the product's manufacturer) that its personnel had manipulated data from an in-vivo
murine potency assay.
The FDA used this information to evaluate
product comparability and nonclinical (animal) pharmacology as part of the
biologics license application (BLA), which was submitted and reviewed by the
FDA.
According
to information shared by the FDA, the product that was administered in the
Phase 1 clinical trial was manufactured by a different process than the product
that was administered in the Phase 3 clinical trial and the animal toxicology studies.
Because
the manufacturing processes were different, interpretation of the overall
clinical trial and nonclinical study results depends on understanding the
characteristics of the Phase 1 version of the product in relationship to the
characteristics of the Phase 3 version of the product.
View our Interactive 2019 cGMP Compliance Recap Dashboard (Free Excel Available)
AveXis’ investigation report revealed that the firm became aware of
the data manipulation as early as on March 14, 2019, more than two months prior
to the BLA approval. However, AveXis did not inform the FDA of the issue until
over a month after the BLA approval. If AveXis had informed FDA of this issue
prior to the BLA approval, there was a possibility that the approval would have been delayed beyond the PDUFA goal date
of May 31, 2019.
The FDA
assessment, however, stated that although the BLA would have eventually been
approved, it is carefully assessing this situation and remains confident
that Zolgensma should remain on the market.
While managing the crisis, Novartis CEO Vas
Narasimhan acknowledged that the company could have handled the furor surrounding Zolgensma better.
Novartis’ AveXis fired its former chief scientific officer Brian Kaspar in connection with the data manipulation scandal, although Kaspar’s lawyer said he did nothing wrong and is ready to
defend his name as needed.
The Swiss
drugmaker could face possible civil or criminal penalties, the FDA has said.
Our view
Over the past years, PharmaCompass has
provided on-time coverage of quality concerns that have emerged at
manufacturing operations around the world. With the widespread use of generic
drugs and the majority of them being manufactured in India and China,
data-integrity within manufacturing operations and assurance of product quality
continue to remain key concerns.
View our Interactive 2019 cGMP Compliance Recap Dashboard (Free Excel Available)
While streamlined, compliant operations still seem like a
distant dream, in 2019, the former promoters of Ranbaxy, the Singh brothers
were finally arrested for misappropriating funds. The legal action was in
connection with their
stake sale in the Indian drug behemoth to Japanese drugmaker Daiichi Sankyo for US$ 2.4 billion.
The sale took place in 2008, months before the US Food and Drug Administration
(FDA) banned imports from two of Ranbaxy’s Indian plants as a result of widespread
data falsification by the firm. That was the start of troubles for the duo, as
Daiichi later took them to court for allegedly suppressing
and misrepresenting facts at the time of sale.
We hope there is a lesson in this for the industry so that
companies improve their practices of falsifying data and the focus shifts
towards patient safety rather than minimizing cost and maximizing profit.
View our Interactive 2019 cGMP Compliance Recap Dashboard (Free Excel Available)
Impressions: 12573
In case you thought the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and EU’s actions against China’s Zhejiang Huahai Pharmaceutical (ZHP) for
supplying commonly used blood pressure medicine valsartan with
cancer-causing impurities, were over, you may want to think again.
Regulators in both US and Europe have stepped up action
against ZHP. Last week, Phispers had reported how the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had posted an
11-observation, highly redacted Form 483 issued to
ZHP (post an inspection of its active pharmaceutical ingredient facility) on
its website on September 21, 2018.
Post that, on September 28, 2018, the agency placed the firm
on import alert to “protect US patients while the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) manufacturer fully determines how impurities were introduced into its API and remediates its quality systems.”
Similarly,
European regulatory authorities issued Zhejiang
Huahai a non-compliance certificate that prohibits the
supply of valsartan and its intermediates to the EU market.
Import alert at Huahai to impact global API landscape
In 2007, Huahai became the first Chinese pharmaceutical
manufacturer to receive FDA approval for a finished drug product (nevirapine).
It continues to rank amongst the top Chinese drug
master file (DMF) filers
with the FDA.
As you are aware, in July this year, valsartan produced by
ZHP was found to contain traces of N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA), a
probable human carcinogen, due to a production change in 2012. The findings
have prompted recalls in more than 50 countries.
Last month, FDA’s testing of products showed an additional unexpected impurity in three lots of Torrent Pharmaceuticals’ recalled valsartan drug products. This second impurity — N-Nitrosodiethylamine (NDEA) — is a known animal and suspected human carcinogen. These Torrent products were included in the company’s recall. NDEA too was detected in valsartan made by ZHP using its previous
manufacturing process, before changes were introduced in 2012.
The FDA announcement issued last week said: “The import alert stops all API made by ZHP and finished drug products made using ZHP’s API from legally entering the United States.”
An import alert at ZHP’s facility is likely to have a significant impact on the global API supply landscape.
The FDA site shows 60 API DMFs of Huahai are Available for Reference for Generic Drug Applications in the United States. With each DMF assessment now requiring the applicant to submit a fee of US$ 55,013, the level of activity ZHP’s APIs generate in the US market and around the globe is significant.
EU issues non-compliance report
The FDA’s actions against ZHP weren’t isolated as an inspection by EU authorities in collaboration with European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines
(EDQM) found that
ZHP did not comply with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) in the manufacturing
of valsartan at the site in Linhai, China.
The European inspection came after the suspension of the company’s CEP (a certificate of compliance with European standards for quality testing) for valsartan in July 2018. The inspection continued to focus on the manufacturing of valsartan.
The September 2018 inspection by investigators from the Italian Ministry of Health found nine “major” and eight “other” deviations at ZHP.
The European authorities found that the investigation
conducted in the context of the NDMA/NDEA contamination of valsartan showed
significant flaws. Moreover, the risk assessment performed in the context of
the development/implementation of the optimized valsartan process, conducted in
July/August 2018 (post the announcement of the recall) was also not
satisfactory.
The regulator also raised data-integrity concerns in relation
to GC-FID (gas chromatograph-flame ionization detector) analysis and found that the company conducted inadequate investigation of unknown peaks detected in GC-MS (gas chromatography–mass spectrometry) analysis of batches of valsartan manufactured with the new process.
While the company has already been prohibited to supply
valsartan API to the EU market, the non-compliance report mentions that the
EDQM should consider actions related to other valsartan CEPs in which Huahai is
mentioned as an intermediate manufacturer.
The non-compliance certificate also prohibits the supply
of valsartan intermediates to the EU market.
‘The responsibility is on the manufacturer’
In addition to the FDA’s change control guidance document, which was published last month, the FDA highlighted that manufacturers must recognize “that it is their responsibility to develop and use suitable methods to detect impurities, including when they make changes to their manufacturing processes. If a manufacturer detects new or higher levels of impurities, they should fully evaluate the impurities and take action to ensure the product is safe.”
While the FDA has not announced additional product recalls other than
those already in place for valsartan medicines (and same is the case in the
EU), it remains to be seen if the problems at Huahai create significant
disruptions to the global API supply chain.
Impressions: 4537