
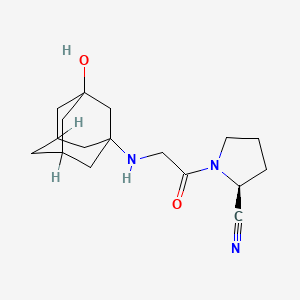

1. (2s)-(((3-hydroxyadamantan-1-yl)amino)acetyl)pyrrolidine-2-carbonitrile
2. Galvus
3. Nvp Laf237
4. Nvp-laf237
1. 274901-16-5
2. Galvus
3. Xiliarx
4. Jalra
5. Nvp-laf237
6. Equa
7. Laf237
8. Laf-237
9. Laf 237
10. Vitagliptin
11. Nvp-laf 237
12. Vildagliptine
13. Vidagliptin (see Vildagliptin)
14. Vildagliptina
15. Unii-i6b4b2u96p
16. I6b4b2u96p
17. (2s)-(((3-hydroxyadamantan-1-yl)amino)acetyl)pyrrolidine-2-carbonitrile
18. 2-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile, 1-(((3-hydroxytricyclo(3.3.1.13,7)dec-1-yl)amino)acetyl)-, (2s)-
19. Vildagliptin (mart.)
20. Vildagliptin [mart.]
21. (-)-(2s)-1-(((3-hydroxytricyclo(3.3.1.1(sup(3,7))dec-1-yl)amino)acetyl)pyrrolidine-2-carbonitrile
22. (2s)-1-(((3-hydroxytricyclo(3.3.1.1(sup 3,7))dec-1-yl)amino)acetyl)pyrrolidine-2-carbonitrile
23. 2-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile, 1-(((3-hydroxytricyclo(3.3.1.1(sup 3,7))dec-1-yl)amino)acetyl)-, (2s)-
24. Dtxsid80881091
25. Vildagliptinum
26. (2s)-{((3-hydroxyadamantan-1-yl)amino)acetyl}pyrrolidine-2-carbonitrile
27. (2s)-1-(((3-hydroxytricyclo(3.3.1.13,7)dec-1-yl)amino)acetyl)pyrrolidine-2-carbonitrile
28. (2s)-1-{[(3-hydroxytricyclo[3.3.1.13,7]dec-1-yl)amino]acetyl}pyrrolidine-2-carbonitrile
29. Dtxcid201022401
30. Vildagliptin (laf-237)
31. Nvp-laf-237
32. (2s)-1-[2-[(3-hydroxy-1-adamantyl)amino]acetyl]pyrrolidine-2-carbonitrile
33. 2-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile, 1-[2-[(3-hydroxytricyclo[3.3.1.13,7]dec-1-yl)amino]acetyl]-, (2s)-
34. Chembl142703
35. (2s)-1-{2-[(3-hydroxyadamantan-1-yl)amino]acetyl}pyrrolidine-2-carbonitrile
36. Galvus (tn)
37. Vildagliptin [usan]
38. Zomelis
39. Vildagliptin (jan/usan/inn)
40. Vildagliptin [usan:inn:ban:jan]
41. Equa (tn)
42. Vildagliptin [mi]
43. Vildagliptin [inn]
44. Vildagliptin [jan]
45. Schembl16579
46. Vildagliptin [who-dd]
47. Gtpl6310
48. Vildagliptin [ema Epar]
49. Bdbm11695
50. Vildagliptin - Bio-x Trade Mark
51. A10bd08
52. A10bh02
53. (s)-1-(2-(((1r,3r,5r,7s)-3-hydroxyadamantan-1-yl)amino)acetyl)pyrrolidine-2-carbonitrile
54. Chebi:135285
55. Syokidbdqmkndq-xwtibiiysa-n
56. S3033
57. Akos015898120
58. Ac-1273
59. Ccg-267505
60. Cs-1465
61. Db04876
62. Fv29102
63. Ncgc00386200-01
64. Ncgc00386200-02
65. 1st11066
66. Bv164521
67. Hy-14291
68. Ns00010516
69. Sw220049-1
70. D07080
71. Ab01566863_01
72. En300-18527744
73. Q421042
74. Brd-a94993966-001-04-4
75. Brd-a94993966-001-05-1
76. (2s)-1-[n-(3-hydroxyadamantan-1-yl)glycyl]pyrrolidine-2-carbonitrile
77. (2s)-1-{[(3-hydroxyadamant-1-yl)amino]acetyl}pyrrolidine-2-carbonitrile
78. (2s)-1-{2-[(3-hydroxyadamant-1-yl)amino]acetyl}pyrrolidine-2-carbonitrile
79. (2s)-1-[[(3-hydroxytricyclo[3.3.1.13,7]dec-1-yl)amino]acetyl]-pyrrolidine-2-carbonitrile
80. 1-[2-[(3-hydroxytricyclo[3.3.1.13,7]dec-1-yl)amino]acetyl]-2s-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile
81. 2s)-1-[[(3-hydroxytricyclo[3.3.1.13,7]decane-1-yl)amino]acetyl]-2-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile
| Molecular Weight | 303.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H25N3O2 |
| XLogP3 | 0.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | Da |
| Monoisotopic Mass | Da |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 76.4 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 523 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Vildagliptin is indicated in the treatment of type II diabetes mellitus in adults. As monotherapy, vildagliptin is indicated in adults inadequately controlled by diet and exercise alone and for whom metformin is inappropriate due to contraindications or intolerance. It is also indicated as dual therapy in combination with metformin, a sulphonylurea, or a thiazolidinedione in adults patients with insufficient glycemic control despite maximal tolerated dose of monotherapy. Vildagliptin is also marketed in a combination product with [metformin] for the treatment of adults with type II diabetes mellitus who inadequately respond to either monotherapy of vildagliptin or metformin. This fixed-dose formulation can be used in combination with a sulphonylurea or insulin (i.e., triple therapy) as an adjunct to diet and exercise in adults who do not achieve adequate glycemic control with monotherapy or dual therapy.
Vildagliptin is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycaemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: as monotherapy in patients in whom metformin is inappropriate due to contraindications or intolerance. in combination with other medicinal products for the treatment of diabetes, including insulin, when these do not provide adequate glycaemic control (see sections 4. 4, 4. 5 and 5. 1 for available data on different combinations).
Vildagliptin is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycaemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: as monotherapy in patients in whom metformin is inappropriate due to contraindications or intolerance. in combination with other medicinal products for the treatment of diabetes, including insulin, when these do not provide adequate glycaemic control
Vildagliptin is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycaemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: as monotherapy in patients in whom metformin is inappropriate due to contraindications or intolerance. in combination with other medicinal products for the treatment of diabetes, including insulin, when these do not provide adequate glycaemic control (see sections 4. 4, 4. 5 and 5. 1 for available data on different combinations).
Treatment of type II diabetes mellitus
Hypoglycemic Agents
Substances which lower blood glucose levels. (See all compounds classified as Hypoglycemic Agents.)
Dipeptidyl-Peptidase IV Inhibitors
Compounds that suppress the degradation of INCRETINS by blocking the action of DIPEPTIDYL-PEPTIDASE IV. This helps to correct the defective INSULIN and GLUCAGON secretion characteristic of TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS by stimulating insulin secretion and suppressing glucagon release. (See all compounds classified as Dipeptidyl-Peptidase IV Inhibitors.)
A10BH02
A10BH02
A10BH02
A10BH02
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A10 - Drugs used in diabetes
A10B - Blood glucose lowering drugs, excl. insulins
A10BH - Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (dpp-4) inhibitors
A10BH02 - Vildagliptin
Absorption
In a fasting state, vildagliptin is rapidly absorbed following oral administration. Peak plasma concentrations are observed at 1.7 hours following administration. Plasma concentrations of vildagliptin increase in an approximately dose-proportional manner. Food delays Tmax to 2.5 hours and decreases Cmax by 19%, but has no effects on the overall exposure to the drug (AUC). Absolute bioavailability of vildagliptin is 85%.
Route of Elimination
Vildagliptin is eliminated via metabolism. Following oral administration, approximately 85% of the radiolabelled vildagliptin dose was excreted in urine and about 15% of the dose was recovered in feces. Of the recovered dose in urine, about 23% accounted for the unchanged parent compound.
Volume of Distribution
The mean volume of distribution of vildagliptin at steady-state after intravenous administration is 71 L, suggesting extravascular distribution.
Clearance
After intravenous administration to healthy subjects, the total plasma and renal clearance of vildagliptin were 41 and 13 L/h, respectively.
About 69% of orally administered vildagpliptin is eliminated via metabolism not mediated by cytochrome P450 enzymes. Based on the findings of a rat study, DPP-4 contributes partially to the hydrolysis of vildagliptin. Vildagliptin is metabolized to pharmacologically inactive cyano (57%) and amide (4%) hydrolysis products in the kidney. LAY 151 (M20.7) is a major inactive metabolite and a carboxylic acid that is formed via hydrolysis of the cyano moiety: it accounts for 57% of the dose. Other circulating metabolites reported are an N-glucuronide (M20.2), an N-amide hydrolysis product (M15.3), two oxidation products, M21.6 and M20.9.
The mean elimination half-life following intravenous administration is approximately two hours. The elimination half-life after oral administration is approximately three hours.
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIP) are incretin hormones that regulate blood glucose levels and maintain glucose homeostasis. It is estimated that the activity of GLP-1 and GIP contribute more than 70% to the insulin response to an oral glucose challenge. They stimulate insulin secretion in a glucose-dependent manner via G-protein-coupled GIP and GLP-1 receptor signalling. In addition to their effects on insulin secretion, GLP-1 is also involved in promoting islet neogenesis and differentiation, as well as attenuating pancreatic beta-cell apoptosis. Incretin hormones also exert extra-pancreatic effects, such as lipogenesis and myocardial function. In type II diabetes mellitus, GLP-1 secretion is impaired, and the insulinotropic effect of GIP is significantly diminished. Vildagliptin exerts its blood glucose-lowering effects by selectively inhibiting dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4), an enzyme that rapidly truncates and inactivates GLP-1 and GIP upon their release from the intestinal cells. DPP-4 cleaves oligopeptides after the second amino acid from the N-terminal end. Inhibition of DPP-4 substantially prolongs the half-life of GLP-1 and GIP, increasing the levels of active circulating incretin hormones. The duration of DPP-4 inhibition by vildagliptin is dose-dependent. Vildagliptin reduces fasting and prandial glucose and HbA1c. It enhances the glucose sensitivity of alpha- and beta-cells and augments glucose-dependent insulin secretion. Fasting and postprandial glucose levels are decreased, and postprandial lipid and lipoprotein metabolism are also improved.
BUILDING BLOCK


