
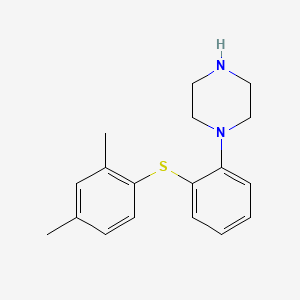

1. 1-(2-(2,4-dimethylphenylsulfanyl)phenyl)piperazine
2. Brintellix
3. Lu Aa21004
4. Lu-aa21004
5. Luaa21004
6. Vortioxetine Hydrobromide
1. 508233-74-7
2. Vortioxetina
3. Vortioxetinum
4. Unii-3o2k1s3wqv
5. 3o2k1s3wqv
6. Chebi:76016
7. Piperazine, 1-[2-[(2,4-dimethylphenyl)thio]phenyl]-
8. Hsdb 8250
9. Piperazine, 1-(2-((2,4-dimethylphenyl)thio)phenyl)-
10. 1-(2-(2,4-dimethylphenylsulfanyl)phenyl)piperazine
11. 1-[2-(2,4-dimethylphenylsulfanyl)phenyl]piperazine
12. N06ax26
13. 1-(2-((2,4-dimethylphenyl)thio)phenyl)piperazine
14. Lu Aa21004
15. 1-{2-[(2,4-dimethylphenyl)sulfanyl]phenyl}piperazine
16. Vortioxetine Free Base
17. Luaa21004
18. Lu-aa21004
19. Vortioxetine [usan]
20. 1-[2-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)sulfanylphenyl]piperazine
21. 508233-74-7 (free Base)
22. Vortioxetine (usan)
23. Brintellix (tn)
24. 1-[2-(2,4-dimethyl-phenylsulfanyl)-phenyl]-piperazine
25. Chembl2204360
26. 1-(2-((2,4-dimethylphenyl)sulfanyl)phenyl}piperazine
27. Vortioxetine [usan:inn]
28. Piperazine, 1-[2-[(2,4-dimethylphenyl)thio]phenyl]-; 1-[2-(2,4-dimethylphenylsulfanyl)phenyl]piperazine; Lu Aa 21004; Vortioxetine
29. Vtx
30. Ps37 - Vortioxetine
31. Vortioxetine (standard)
32. Vortioxetine [mi]
33. Vortioxetine [inn]
34. Vortioxetine [vandf]
35. Vortioxetine, Lu Aa21004
36. Schembl236115
37. Vortioxetine [who-dd]
38. Gtpl7351
39. Vortioxetine (lu Aa21004)
40. Chembl2104993
41. Vortioxetine (lu Aa21004)?
42. Dtxsid80965062
43. Yqnwzwmkldqsac-uhfffaoysa-n
44. Glxc-15242
45. Hms3886m08
46. Bcp05996
47. Qkd31662
48. Bdbm50400902
49. Hy-15414r
50. S5506
51. Stl483777
52. Akos016008748
53. Ccg-229998
54. Cs-1471
55. Db09068
56. Fd58721
57. Gg-0052
58. Sb16506
59. Compound 5m [pmid: 21486038]
60. Ncgc00386237-08
61. Ac-27648
62. Da-42264
63. Hy-15414
64. Ns00068019
65. D10184
66. En300-746942
67. Ar-270/43507985
68. Q3563148
69. 1-[2-(2,4-dimethylphenylsulfanyl)-phenyl]piperazine
70. Brd-k53963539-001-01-8
71. Brd-k53963539-004-02-0
72. 1-[2-[(2,4-dimethylphenyl)thio]phenyl]-piperazine; Vortioxetine; 1-(2-((2,4-dimethylphenyl)thio)phenyl)piperazine
73. Lu Aa 21004 Pound>>luaa21004 Pound>> Lu-aa21004 Pound>> Lu Aa21004 Pound>> Aa21004
| Molecular Weight | 298.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H22N2S |
| XLogP3 | 4.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | Da |
| Monoisotopic Mass | Da |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 40.6 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 316 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Anti-Anxiety Agents; Serotonin 5-HT1 Receptor Agonists; Serotonin 5-HT1 Receptor Antagonists; Serotonin 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonists; Serotonin Uptake Inhibitors
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Voritioxetine. Online file (MeSH, 2015). Available from, as of May 1, 2015: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/2014/mesh_browser/MBrowser.html
/CLINICAL TRIALS/ ClinicalTrials.gov is a registry and results database of publicly and privately supported clinical studies of human participants conducted around the world. The Web site is maintained by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and the National Institutes of Health(NIH). Each ClinicalTrials.gov record presents summary information about a study protocol and includes the following: Disease or condition; Intervention (for example, the medical product, behavior, or procedure being studied); Title, description, and design of the study; Requirements for participation (eligibility criteria); Locations where the study is being conducted; Contact information for the study locations; and Links to relevant information on other health Web sites, such as NLM's MedlinePlus for patient health information and PubMed for citations and abstracts for scholarly articles in the field of medicine. Vortioxetine is included in the database.
NIH/NLM; ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available from, as of July 18, 2015: https://clinicaltrials.gov/search/intervention=Lu+AA21004+OR+Vortioxetine
Brintellix is indicated for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD). The efficacy of Brintellix was established in six 6 to 8 week studies (including one study in the elderly) and one maintenance study in adults. /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Brintellix (Vortioxetine Hydrobromide) Tablet, Film Coated (Updated: July 2014). Available from, as of June 30, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=4b0700c9-b417-4c3a-b36f-de461e125bd3
/BOX WARNING/ WARNING: SUICIDAL THOUGHTS AND BEHAVIORS. Antidepressants increased the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior in children, adolescents, and young adults in short-term studies. These studies did not show an increase in the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior with antidepressant use in patients over age 24; there was a trend toward reduced risk with antidepressant use in patients aged 65 and older. In patients of all ages who are started on antidepressant therapy, monitor closely for worsening, and for emergence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors. Advise families and caregivers of the need for close observation and communication with the prescriber. Brintellix has not been evaluated for use in pediatric patients.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Brintellix (Vortioxetine Hydrobromide) Tablet, Film Coated (Updated: July 2014). Available from, as of June 30, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=4b0700c9-b417-4c3a-b36f-de461e125bd3
Potentially life-threatening serotonin syndrome has been reported with serotonergic antidepressants, including vortioxetine, when used alone, but particularly with concurrent use of other serotonergic drugs (including serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT) type 1 receptor agonists ("triptans"), tricyclic antidepressants, buspirone, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, and St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum)) and with drugs that impair the metabolism of serotonin (particularly monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors, both those used to treat psychiatric disorders and others, such as linezolid and methylene blue). Manifestations of serotonin syndrome may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, hyperthermia), neuromuscular symptoms (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, incoordination), seizures, and/or GI symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea). Patients receiving vortioxetine should be monitored for the development of serotonin syndrome. Concurrent or recent (i.e., within 2 weeks) therapy with MAO inhibitors intended to treat psychiatric disorders is contraindicated. Use of an MAO inhibitor intended to treat psychiatric disorders within 3 weeks of vortioxetine discontinuance also is contraindicated. Vortioxetine also should not be initiated in patients who are being treated with other MAO inhibitors such as linezolid or IV methylene blue. If concurrent therapy with vortioxetine and other serotonergic drugs is clinically warranted, the patient should be made aware of the potential increased risk for serotonin syndrome, particularly during initiation of therapy or when dosage is increased. If manifestations of serotonin syndrome occur, treatment with vortioxetine and any concurrently administered serotonergic agents should be immediately discontinued and supportive and symptomatic treatment initiated.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2015; Drug Information 2015. Bethesda, MD. 2015, p. 2386-7
Serotonergic antidepressants, including vortioxetine, may increase the risk of bleeding events. Concomitant use of aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents (NSAIAs), warfarin, and other anticoagulants may add to this risk. Case reports and epidemiologic studies have demonstrated an association between use of drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake and the occurrence of GI bleeding. Bleeding events related to drugs that inhibit serotonin reuptake have ranged from ecchymoses, hematomas, epistaxis, and petechiae to life-threatening hemorrhages. The manufacturer recommends that patients be advised of the increased risk of bleeding associated with concomitant use of vortioxetine and aspirin or other NSAIAs, warfarin, or other drugs that affect coagulation or bleeding.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2015; Drug Information 2015. Bethesda, MD. 2015, p. 2387
Treatment with serotonergic drugs, including vortioxetine, may result in hyponatremia. In many cases, hyponatremia appears to be due to the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH). One case of hyponatremia with a serum sodium concentration lower than 110 mmol/L has been reported with vortioxetine in a premarketing study. Geriatric individuals and patients receiving diuretics or who are otherwise volume depleted may be at greater risk of developing hyponatremia with serotonergic antidepressants. Signs and symptoms of hyponatremia include headache, difficulty concentrating, memory impairment, confusion, weakness, and unsteadiness, which may lead to falls; more severe and/or acute cases have been associated with hallucinations, syncope, seizures, coma, respiratory arrest, and death. Vortioxetine should be discontinued and appropriate medical intervention should be instituted in patients with symptomatic hyponatremia.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2015; Drug Information 2015. Bethesda, MD. 2015, p. 2387
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for VORTIOXETINE (18 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Vortioxetine is indicated for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD).
FDA Label
Treatment of major depressive episodes in adults.
Treatment of major depressive disorder
Anti-Anxiety Agents
Agents that alleviate ANXIETY, tension, and ANXIETY DISORDERS, promote sedation, and have a calming effect without affecting clarity of consciousness or neurologic conditions. ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS are commonly used in the symptomatic treatment of anxiety but are not included here. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Anxiety Agents.)
Antidepressive Agents
Mood-stimulating drugs used primarily in the treatment of affective disorders and related conditions. Several MONOAMINE OXIDASE INHIBITORS are useful as antidepressants apparently as a long-term consequence of their modulation of catecholamine levels. The tricyclic compounds useful as antidepressive agents (ANTIDEPRESSIVE AGENTS, TRICYCLIC) also appear to act through brain catecholamine systems. A third group (ANTIDEPRESSIVE AGENTS, SECOND-GENERATION) is a diverse group of drugs including some that act specifically on serotonergic systems. (See all compounds classified as Antidepressive Agents.)
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors
Compounds that specifically inhibit the reuptake of serotonin in the brain. (See all compounds classified as Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors.)
Serotonin 5-HT1 Receptor Agonists
Endogenous compounds and drugs that specifically stimulate SEROTONIN 5-HT1 RECEPTORS. Included under this heading are agonists for one or more of the specific 5-HT1 receptor subtypes. (See all compounds classified as Serotonin 5-HT1 Receptor Agonists.)
Serotonin 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate SEROTONIN 5-HT3 RECEPTORS, thereby blocking the actions of SEROTONIN or SEROTONIN 5-HT3 RECEPTOR AGONISTS. (See all compounds classified as Serotonin 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonists.)
N06AX26
N - Nervous system
N06 - Psychoanaleptics
N06A - Antidepressants
N06AX - Other antidepressants
N06AX26 - Vortioxetine
Absorption
The maximal plasma vortioxetine concentration (Cmax) after dosing is reached within 7 to 11 hours postdose. Absolute bioavailability is 75%. No effect of food on the pharmacokinetics was observed.
Route of Elimination
Following a single oral dose of [14C]labeled vortioxetine, approximately 59% and 26% of the administered radioactivity was recovered in the urine and feces, respectively as metabolites. Negligible amounts of unchanged vortioxetine were excreted in the urine up to 48 hours.
Volume of Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution of vortioxetine is approximately 2600 L, indicating extensive extravascular distribution.
/MILK/ It is not known whether vortioxetine is present in human milk. Vortioxetine is present in the milk of lactating rats.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Brintellix (Vortioxetine Hydrobromide) Tablet, Film Coated (Updated: July 2014). Available from, as of June 30, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=4b0700c9-b417-4c3a-b36f-de461e125bd3
Vortioxetine is a new multi-modal drug against major depressive disorder with high affinity for a range of different serotonergic targets in the CNS. We report the (11)C-labeling of vortioxetine with (11)C-MeI using a Suzuki-protocol that allows for the presence of an unprotected amine. Preliminary evaluation of (11)C-vortioxetine in a Danish Landrace pig showed rapid brain uptake and brain distribution in accordance with the pharmacological profile, all though an unexpected high binding in cerebellum was also observed. (11)C-vortioxetine displayed slow tracer kinetics with peak uptake after 60 min and with limited wash-out from the brain. Further studies are needed but this radioligand may prove to be a valuable tool in unraveling the clinical effects of vortioxetine.
PMID:24786133 Andersen VL et al; Bioorg Med Chem Lett 24 (11): 2408-11 (2014)
Vortioxetine and related material was mainly excreted by faeces in mice (84%), rats (69%) and dogs (59-65% in two separate studies), whereas humans showed prominent urinary excretion (59%) compared to faeces (26%). In excretion studies, the recovery of (14)C-Vortioxetine and related material was close to 100% in rodents. Dogs and humans exhibited a protracted excretion and the recovery was approximately 90% and 85% after 168 hours and 360 hours, respectively.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Brintellix (Vortioxetine) p.20 (2013). Available from, as of July 6, 2015: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/002717/WC500159447.pdf
The objective was to describe the pharmacokinetics of vortioxetine and evaluate the effect of intrinsic and extrinsic factors in the healthy population. Data from 26 clinical pharmacology studies were pooled. A total of 21,758 vortioxetine quantifiable plasma concentrations were collected from 887 subjects with corresponding demography. The doses ranged from 2.5 to 75 mg (single dose) and 2.5-60 mg (multiple QD doses). The pharmacokinetics of vortioxetine was best characterised by a two-compartment model with first-order absorption, lag-time and linear elimination, with interindividual error terms for absorption rate constant, oral clearance and central volume of distribution. The population mean was 32.7 L/hr for oral clearance and 1.97*10(3) L for the central volume of distribution. The average elimination half-life was 65.8 hr. CYP2D6 inferred metabolic status (ultra, extensive, intermediate or poor metabolisers) and age on oral clearance and height on central volume of distribution were identified as statistically significant covariate-parameter relationships. For CYP2D6 poor metabolizers, CL/F was approximately 50% to that seen in CYP2D6 extensive metabolizers. The impact of height on V2/F and age on CL/F was low and not considered to be clinically relevant. The final model was found to be reliable, stable and predictive. A reliable, stable and predictive pharmacokinetic model was developed to characterize pharmacokinetics of vortioxetine in the healthy population.
PMID:24766668 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4257570 Areberg J et al; Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 115 (6): 552-9 (2014)
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for VORTIOXETINE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Vortioxetine is extensively metabolized primarily through oxidation via cytochrome P450 isozymes CYP2D6, CYP3A4/5, CYP2C19, CYP2C9, CYP2A6, CYP2C8 and CYP2B6 and subsequent glucuronic acid conjugation. CYP2D6 is the primary enzyme catalyzing the metabolism of vortioxetine to its major, pharmacologically inactive, carboxylic acid metabolite, and poor metabolizers of CYP2D6 have approximately twice the vortioxetine plasma concentration of extensive metabolizers.
Vortioxetine is extensively metabolized primarily through oxidation via cytochrome P450 isozymes CYP2D6, CYP3A4/5, CYP2C19, CYP2C9, CYP2A6, CYP2C8 and CYP2B6 and subsequent glucuronic acid conjugation. CYP2D6 is the primary enzyme catalyzing the metabolism of vortioxetine to its major, pharmacologically inactive, carboxylic acid metabolite, and poor metabolizers of CYP2D6 have approximately twice the vortioxetine plasma concentration of extensive metabolizers.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Brintellix (Vortioxetine Hydrobromide) Tablet, Film Coated (Updated: July 2014). Available from, as of June 30, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=4b0700c9-b417-4c3a-b36f-de461e125bd3
All metabolites detected in human hepatocytes were also present in dogs, mice and rats (plasma and/or urine) in vivo, except for a glucuronide conjugate of monohydroxy-Vortioxetine which was not found in mice or rats. Among all species tested, rabbit hepatocytes appeared to have the metabolite profile closer to human hepatocyte metabolite profile.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Brintellix (Vortioxetine) p.20 (2013). Available from, as of July 6, 2015: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/002717/WC500159447.pdf
Mean terminal halflife is approximately 66 hours
The oral absolute bioavailability was approximately 10% in the rat, 48% in the dog and 75% in patients, with terminal elimination half-life values of 3.0, 7.9 and 66 hours, respectively.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Brintellix (Vortioxetine) p.19 (2013). Available from, as of July 6, 2015: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/002717/WC500159447.pdf
... Data from 26 clinical pharmacology studies were pooled. A total of 21,758 vortioxetine quantifiable plasma concentrations were collected from 887 subjects with corresponding demography. The doses ranged from 2.5 to 75 mg (single dose) and 2.5-60 mg (multiple QD doses). ... The average elimination half-life was 65.8 hr. ...
PMID:24766668 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4257570 Areberg J et al; Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 115 (6): 552-9 (2014)
The mean elimination half-life and oral clearance are 66 hours and 33 L/hr, respectively.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Brintellix (Vortioxetine Hydrobromide) Tablet, Film Coated (Updated: July 2014). Available from, as of June 30, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=4b0700c9-b417-4c3a-b36f-de461e125bd3
Vortioxetine is classified as a serotonin modulator and simulator (SMS) as it has a multimodal mechanism of action towards the serotonin neurotransmitter system whereby it simultaneously modulates one or more serotonin receptors and inhibits the reuptake of serotonin. More specifically, vortioxetine acts via the following biological mechanisms: as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SRI) through inhibition of the serotonin transporter, while also acting as a partial agonist of the 5-HT1B receptor, an agonist of 5-HT1A, and antagonist of the 5-HT3, 5-HT1D, and 5-HT7 receptors.
1-(2-(2,4-Dimethylphenyl-sulfanyl)-phenyl)-piperazine (Lu AA21004) is a human (h) serotonin (5-HT)(3A) receptor antagonist (K(i) = 3.7 nM), h5-HT(7) receptor antagonist (K(i) = 19 nM), h5-HT(1B) receptor partial agonist (K(i) = 33 nM), h5-HT(1A) receptor agonist (K(i) = 15 nM), and a human 5-HT transporter (SERT) inhibitor (K(i) = 1.6 nM) (J Med Chem 54:3206-3221, 2011). Here, we confirm that Lu AA21004 is a partial h5-HT(1B) receptor agonist [EC(50) = 460 nM, intrinsic activity = 22%] using a whole-cell cAMP-based assay and demonstrate that Lu AA21004 is a rat (r) 5-HT(7) receptor antagonist (K(i) = 200 nM and IC(50) = 2080 nM). In vivo, Lu AA21004 occupies the r5-HT(1B) receptor and rSERT (ED(50) = 3.2 and 0.4 mg/kg, respectively) after subcutaneous administration and is a 5-HT(3) receptor antagonist in the Bezold-Jarisch reflex assay (ED(50) = 0.11 mg/kg s.c.). In rat microdialysis experiments, Lu AA21004 (2.5-10.0 mg/kg s.c.) increased extracellular 5-HT, dopamine, and noradrenaline in the medial prefrontal cortex and ventral hippocampus. Lu AA21004 (5 mg/kg per day for 3 days; minipump subcutaneously), corresponding to 41% rSERT occupancy, significantly increased extracellular 5-HT in the ventral hippocampus. Furthermore, the 5-HT(3) receptor antagonist, ondansetron, potentiated the increase in extracellular levels of 5-HT induced by citalopram. Lu AA21004 has antidepressant- and anxiolytic-like effects in the rat forced swim (Flinders Sensitive Line) and social interaction and conditioned fear tests (minimal effective doses: 7.8, 2.0, and 3.9 mg/kg). In conclusion, Lu AA21004 mediates its pharmacological effects via two pharmacological modalities: SERT inhibition and 5-HT receptor modulation. In vivo, this results in enhanced release of several neurotransmitters and antidepressant- and anxiolytic-like profiles at doses for which targets in addition to the SERT are occupied. The multimodal activity profile of Lu AA21004 is distinct from that of current antidepressants.
PMID:22171087 Mork A et al; J Pharmacol Exp Ther 340 (3): 666-75 (2012)
The mechanism of the antidepressant effect of vortioxetine is not fully understood, but is thought to be related to its enhancement of serotonergic activity in the CNS through inhibition of the reuptake of serotonin (5-HT). It also has several other activities including 5-HT3 receptor antagonism and 5-HT1A receptor agonism. The contribution of these activities to vortioxetine's antidepressant effect has not been established.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Brintellix (Vortioxetine Hydrobromide) Tablet, Film Coated (Updated: July 2014). Available from, as of June 30, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=4b0700c9-b417-4c3a-b36f-de461e125bd3
The monoaminergic network, including serotonin (5-HT), norepinephrine (NE), and dopamine (DA) pathways, is highly interconnected and has a well-established role in mood disorders. Preclinical research suggests that 5-HT receptor subtypes, including 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT3, and 5-HT7 receptors as well as the 5-HT transporter (SERT), may have important roles in treating depression. This study evaluated the neuropharmacological profile of Lu AA21004, a novel multimodal antidepressant combining 5-HT3 and 5-HT7 receptor antagonism, 5-HT1B receptor partial agonism, 5-HT1A receptor agonism, and SERT inhibition in recombinant cell lines. Extracellular 5-HT, NE and DA levels were evaluated in the ventral hippocampus (vHC), medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) and nucleus accumbens (NAc) after acute and subchronic treatment with Lu AA21004 or escitalopram. The acute effects of LuAA21004 on NE and DA neuronal firing were also evaluated in the locus coeruleus (LC) and ventral tegmental area (VTA), respectively. Acute Lu AA21004 dose-dependently increased 5-HT in the vHC, mPFC and NAc. Maximal 5-HT levels in the vHC were higher than those in the mPFC. Furthermore, mPFC 5-HT levels were increased at low SERT occupancy levels. In the vHC and mPFC, but not the NAc, high Lu AA21004 doses increased NE and DA levels. Lu AA21004 slightly decreased LC NE neuronal firing and had no effect on VTA DA firing. Results are discussed in context of occupancy at 5-HT3, 5-HT1B and 5-HT1A receptors and SERT. In conclusion, Lu AA21004, acting via two pharmacological modalities, 5-HT receptor modulation and SERT inhibition, results in a brain region-dependent increase of multiple neurotransmitter concentrations. and ECNP. All rights reserved. PMID:22612991
PMID:22612991 Pehrson AL et al; Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 23 (2): 133-45 (2013)
Vortioxetine, a novel antidepressant with multimodal action, is a serotonin (5-HT)3, 5-HT7 and 5-HT1D receptor antagonist, a 5-HT1B receptor partial agonist, a 5-HT1A receptor agonist and a 5-HT transporter (SERT) inhibitor. Vortioxetine has been shown to improve cognitive performance in several preclinical rat models and in patients with major depressive disorder. Here we investigated the mechanistic basis for these effects by studying the effect of vortioxetine on synaptic transmission, long-term potentiation (LTP), a cellular correlate of learning and memory, and theta oscillations in the rat hippocampus and frontal cortex. Vortioxetine was found to prevent the 5-HT-induced increase in inhibitory post-synaptic potentials recorded from CA1 pyramidal cells, most likely by 5-HT3 receptor antagonism. Vortioxetine also enhanced LTP in the CA1 region of the hippocampus. Finally, vortioxetine increased fronto-cortical theta power during active wake in whole animal electroencephalographic recordings. In comparison, the selective SERT inhibitor escitalopram showed no effect on any of these measures. Taken together, our results indicate that vortioxetine can increase pyramidal cell output, which leads to enhanced synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus. Given the central role of the hippocampus in cognition, these findings may provide a cellular correlate to the observed preclinical and clinical cognition-enhancing effects of vortioxetine.
PMID:25122043 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4230848 Dale E et al; J Psychopharmacol 28 (10): 891-902 (2014)
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for VORTIOXETINE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
BUILDING BLOCK

CAS Number : 508233-74-7
End Use API :
End Use API : Vortioxetine Hydrobromide
About the Company : Established in May 2012, Shandong Loncom Pharmaceutical is a wholly owned subsidiary of Shandong Bestcomm Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Located in the Qihe Economic Development Zone, Shandon...

