


1. Phosphate, Pyridoxal
2. Pyridoxal 5 Phosphate
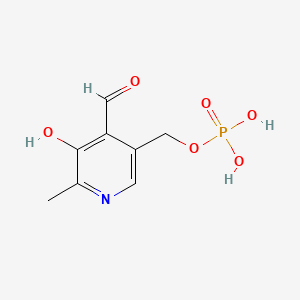
3. Pyridoxal 5-phosphate
4. Pyridoxal P
5. Pyridoxal-p
1. 54-47-7
2. Codecarboxylase
3. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
4. Pyridoxal 5-phosphate
5. Pyridoxyl Phosphate
6. (4-formyl-5-hydroxy-6-methylpyridin-3-yl)methyl Dihydrogen Phosphate
7. Pyridoxal P
8. Biosechs
9. Hairoxal
10. Pyromijin
11. Vitazechs
12. Pyridoxal-5'-phosphate
13. Hiadelon
14. Pidopidon
15. Himitan
16. Phosphopyridoxal
17. Pyridoxal-5-phosphate
18. 853645-22-4
19. Pal-p
20. Sechvitan
21. Pydoxal
22. Piodel
23. Apolon B6
24. Hi-pyridoxin
25. Pyridoxal-p
26. Phosphopyridoxal Coenzyme
27. Vitahexin P
28. Hexermin P
29. Coenzyme B6
30. Pyridoxal Monophosphate
31. Pyridoxaldehyde Phosphate
32. Apolon B(sub 6)
33. Plp
34. Phosphoridoxal Coenzyme
35. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate Hydrate
36. Vitamin B6 Phosphate
37. Pyridoxal 5'-(dihydrogen Phosphate)
38. Pyridoxal-5p
39. Pyridoxal 5-monophosphoric Acid Ester
40. Vitahexin-p
41. Hexermin-p
42. Pyridoxal Phosphate [jan]
43. 3-hydroxy-2-methyl-5-((phosphonooxy)methyl)-4-pyridinecarboxaldehyde
44. 4-pyridinecarboxaldehyde, 3-hydroxy-2-methyl-5-((phosphonooxy)methyl)-
45. Pyridoxal 5/'-phosphate (hydrate)
46. Pyridoxal, 5-(dihydrogen Phosphate)
47. 3-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylisonicotinaldehyde 5-phosphate
48. 3-hydroxy-2-methyl-5-[(phosphonooxy)methyl]-4-pyridinecarboxaldehyde
49. Pyridoxal Phosphate Anhydrous
50. 2-methyl-3-hydroxy-4-formyl-5-hydroxymethylpyridine-5-calcium Phosphate
51. 4-pyridinecarboxaldehyde, 3-hydroxy-2-methyl-5-[(phosphonooxy)methyl]-
52. Chembl82202
53. F06sge49m6
54. Chebi:18405
55. Pyridoxal-phosphate
56. Nsc82388
57. Nsc-82388
58. Mc-1
59. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate;pyridoxyl Phosphate
60. 3-hydroxy-2-methyl-5-([phosphonooxy]methyl)-4-pyridinecarboxaldehyde
61. 2-methyl-3-hydroxy-4-formyl-5-hydroxymethylpyridine-5-calcium Phosphate Trihydrate
62. (4-formyl-5-hydroxy-6-methyl-3-pyridyl)methyl Dihydrogen Phosphate
63. [(4-formyl-5-hydroxy-6-methylpyridin-3-yl)methoxy]phosphonic Acid
64. Pyridoxalphosphate
65. Sechvitan, Vitahexin P
66. Ncgc00166300-01
67. Pyridoxal-5-monophosphate
68. Einecs 200-208-3
69. Nsc 82388
70. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate 5
71. Pyridoxal Phosphate (6ci)
72. Unii-f06sge49m6
73. Vitamin B6 Phosphate (ester)
74. Pyridoxal, 5-(dihydrogenphosphate)
75. Sri 2392
76. Pyridoxal Phosphate
77. P-5'-p
78. Pridoxal-5-phosphate
79. Pyridoxal 5 Inverted Exclamation Marka-phosphate Hydrate
80. Pyridoxal 5''-phosphate
81. P5p
82. Pyridoxal, 5-(dihydrogen Phosphate) (8ci)
83. (4-formyl-5-hydroxy-6-methyl(3-pyridyl))methyl Dihydrogen Phosphate
84. Bmse000111
85. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate Monohydrate, Vitamin B6
86. Schembl23158
87. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphoric Acid
88. Gtpl5249
89. Sgcut00188
90. Dtxsid4048351
91. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate Anhydrous
92. 2-methyl-3-hydroxy-4-formyl-5-pyridylmethylphosphoric Acid
93. Ex-a980
94. 4-formyl-5-hydroxy-6-methyl-pyridin-3-yl)methoxyphosphonic Acid
95. Act03489
96. Bcp34576
97. Hy-b1744
98. Pyridoxal 5-phosphate [mi]
99. Pyridoxal Phosphate Treated .beta.-lactoglobulin From Bovine Whey
100. To_000077
101. Zinc1532514
102. (4-formyl-5-hydroxy-6-methyl-3-pyridinyl)methyl Dihydrogen Phosphate
103. Bdbm50118216
104. Mfcd00006333
105. Pyridoxal Phosphate [who-dd]
106. S5311
107. Stl185213
108. Pyridoxal 5''-(dihydrogen Phosphate)
109. Pyridoxal 5-phosphate [inci]
110. Akos015891654
111. Phosphoric Acid Mono-(4-formyl-5-hydroxy-6-methyl-pyridin-3-ylmethyl) Ester
112. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate;codecarboxylase
113. Ccg-266929
114. Cs-7767
115. Db00114
116. Sb18794
117. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate [vandf]
118. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate Hydrate, >=98%
119. As-19314
120. Db-052584
121. Vitamin B6 (pyridoxal 5-phosphate)
122. Ft-0631236
123. Ft-0655876
124. Isonicotinaldehyde, 5-(dihydrogen Phosphate)
125. C00018
126. F17391
127. Pyridoxal 5 Inverted Exclamation Marka-phosphate
128. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate Monohydrate - Vitamin B6
129. 468c251
130. A841303
131. Q418957
132. Sr-01000944534
133. Q-201645
134. Sr-01000944534-1
135. A26bdb6a-282a-4d13-a916-7b2b215b0fd6
136. (4-formyl-5-hydroxy-6-methylpyridin-3-yl)methyldihydrogenphosphate
137. 3-hydroxy-2-methyl-5-([phosphonooxy]methyl)-4-pyridinecarbaldehyde
138. (4-methanoyl-6-methyl-5-oxidanyl-pyridin-3-yl)methyl Dihydrogen Phosphate
139. 4-pyridinecarboxaldehyde,3-hydroxy-2-methyl-5-[(phosphonooxy)methyl]-
140. 4-pyridinecarboxaldehyde, 3-hydroxy-2-methyl-5-[(phosphonooxy)methyl]- (9ci)
141. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate Hydrate, Powder, Bioreagent, Suitable For Cell Culture
| Molecular Weight | 247.14 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C8H10NO6P |
| XLogP3 | -1.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 247.02457404 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 247.02457404 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 117 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 16 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 292 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For nutritional supplementation and for treating dietary shortage or imbalance.
Investigated for use/treatment in coronary artery disease.
The two major forms of vitamin B6 are pyridoxine and pyridoxamine. In the liver they are converted to pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) which is a cofactor in many reactions of amino acid metabolism. PLP also is necessary for the enzymatic reaction governing the release of glucose from glycogen. Pyroluria is one potential cause of vitamin B6 deficiency.
Vitamin B Complex
A group of water-soluble vitamins, some of which are COENZYMES. (See all compounds classified as Vitamin B Complex.)
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A11 - Vitamins
A11H - Other plain vitamin preparations
A11HA - Other plain vitamin preparations
A11HA06 - Pyridoxal phosphate
Pyridoxal Phosphate is a coenzyme of many enzymatic reactions. It is the active form of vitamin B6 which comprises three natural organic compounds, pyridoxal, pyridoxamine and pyridoxine. Pyridoxal phosphate acts as a coenzyme in all transamination reactions, and in some oxylation and deamination reactions of amino acids. The aldehyde group of pyridoxal phosphate forms a Schiff-base linkage with the epsilon-amino group of a specific lysine group of the aminotransferase enzyme. The alpha-amino group of the amino acid substrate displaces the epsilon-amino group of the active-site lysine residue. The resulting aldimine becomes deprotonated to become a quinoid intermediate, which in turn accepts a proton at a different position to become a ketimine. Ketimine becomes hydrolyzed so that the amino group remains on the protein complex.
MC-1 is a biologically active natural product which can be regarded as a chemical entity that has been evolutionarily selected and validated for binding to particular protein domains. Thus, its underlying structural architecture, or scaffold, has already been biologically established as safe and active, providing a powerful guiding principle for novel drug and library development.
