

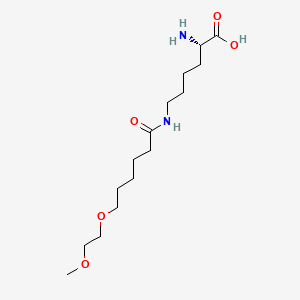

1. Bmn-165
2. Palynziq
3. Pegvaliase-pqpz
1. Ravpal-peg
2. Peg-pal
3. Pegvaliase-pqpz
4. 1585984-95-7
5. Pegvaliase [inn]
6. Unii-n6uah27euv
7. Phenylase
8. Bmn 165
9. N6uah27euv
10. Dtxsid501336362
11. Db12839
| Molecular Weight | 318.41 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H30N2O5 |
| XLogP3 | -2.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 15 |
| Exact Mass | 318.21547206 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 318.21547206 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 111 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 300 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Pegvaliase is indicated for the management of phenylketonuria (PKU) in adult patients who have uncontrolled blood phenylalanine concentrations greater than 600 micromol/L on existing management.
FDA Label
Palynziq is indicated for the treatment of patients with phenylketonuria (PKU) aged 16 years and older who have inadequate blood phenylalanine control (blood phenylalanine levels greater than 600 micromol/l) despite prior management with available treatment options.
Treatment of hyperphenylalaninaemia
In a phase 3 clinical trial of adult patients with phenylketonuria and blood phenylalanine concentrations greater than 600 mol/L on existing management therapies, subcutaneous administration of pegvaliase resulted in significantly reduced blood phenylalanine concentrations in most patients compared to their pre-treatment baseline levels within 24 months in addition to improved neuropsychiatric symptoms.
A16AB19
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A16 - Other alimentary tract and metabolism products
A16A - Other alimentary tract and metabolism products
A16AB - Enzymes
A16AB19 - Pegvaliase
Absorption
At steady state during maintenance treatment with pegvaliase 20 mg and 40 mg subcutaneously once daily, the mean SD (range) peak plasma concentration (Cmax) was 14.0 16.3 (0.26 to 68.5) mg/L and 16.7 19.5 (0.24 to 63.8) mg/L, respectively. The time to reach Cmax (Tmax) was approximately 8 hours.
Route of Elimination
Human elimination pathway of pegvaliase has not been studied.
Volume of Distribution
The mean SD (range) apparent volume of distribution at steady state was 26.4 64.8 (1.8 to 241) L and 22.2 19.7 (3.1 to 49.5) L after once-daily subcutaneous administration of 20 mg and 40 mg pegvaliase, respectively.
Clearance
At steady state following once-daily subcutaneous administration of 20 mg and 40 mg pegvaliase, the mean SD (range) apparent clearance was 0.39 0.87 L/h and 1.25 2.46 L/h, respectively.
It is expected that pegvaliase undergoes the catabolic pathway to be degraded into small peptides and amino acids.
Following once-daily subcutaneous administration of 20 mg and 40 mg pegvaliase, the mean SD (range) half-life at steady state was 47 42 (14 to 132) hours and 60 45 (14 to 127) hours, respectively.
Pegvaliase is a phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL) enzyme that temporarily restores the levels of deficient enzyme and reduces blood phenylalanine concentrations by converting phenylalanine to ammonia and _trans_-cinnamic acid. Formed conversion products are metabolized in the liver and later excreted in the urine.
