

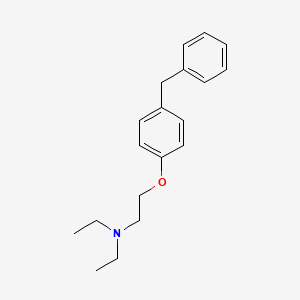

1. (2-(4-benzylphenoxy)ethyl)diethylamine
2. Bzphoet-diethylammonium Chloride
3. Depmpe
4. Dppe
5. Dppe Hydrochloride
6. Ethanamine, N,n-diethyl-2-(4-(phenylmethyl)phenoxy)-, (2ar-(2aalpha,4beta,4abeta,6beta,9alpha(alphar*,betas*),11alpha,12alpha,12aalpha,12balpha))-
7. N,n-diethyl-2-((4-phenylmethyl)phenoxy)-ethanamine Hydrochloride
8. N,n-diethyl-2-((4-phenylmethyl)phenoxy)ethanamine
9. N,n-diethyl-2-((4-phenylmethyl)phenoxy)ethanamine Hydrochloride
10. N,n-diethyl-2-(4-(phenylmethyl)phenoxy)ethanamine
11. N,n-diethyl-2-(4-(phenylmethyl)phenoxy)ethanamine Hydrochloride
12. Tesmilifene Hydrochloride
1. 98774-23-3
2. 2-(4-benzylphenoxy)-n,n-diethylethanamine
3. Tesmilifene [inn]
4. N,n-diethyl-2-((4-phenylmethyl)phenoxy)ethanamine
5. Depmpe
6. Chembl26424
7. I43t3id6g2
8. N,n-diethyl-2-[4-(phenylmethyl)phenoxy]ethanamine
9. N,n-diethyl-2-[4-benzylphenoxy]ethanamine
10. Ethanamine, N,n-diethyl-2-(4-(phenylmethyl)phenoxy)-
11. Ncgc00024762-02
12. N,n-diethyl-2-(4-benzylphenoxy)ethanamine
13. Dsstox_cid_25661
14. Dsstox_rid_81038
15. Dsstox_gsid_45661
16. Unii-i43t3id6g2
17. Cas-98774-23-3
18. Ethanamine, N,n-diethyl-2-[4-(phenylmethyl)phenoxy]-
19. Ymb1002
20. Tocris-0743
21. Tesmilifene [mi]
22. 2-((alpha-phenyl-p-tolyl)oxy)triethylamine
23. Tesmilifene [who-dd]
24. Schembl112525
25. Zinc2139
26. Dtxsid1045661
27. Chebi:93414
28. Bcp09123
29. Tox21 110924
30. Tox21_110924
31. Bdbm50085260
32. Tox21_110924_1
33. Db04905
34. [2-(4-benzylphenoxy)ethyl]diethylamine
35. Ncgc00024762-01
36. Ncgc00024762-03
37. Ncgc00024762-04
38. Ncgc00024762-05
39. N,n-diethyl-2-(p-benzylphenoxy)ethylamine
40. Db-103604
41. [2-(4-benzyl-phenoxy)-ethyl]-diethyl-amine
42. Triethylamine, 2-(.alpha.-phenyl-p-tolyloxy)-
43. Brd-k80315159-051-01-2
44. Q27095558
| Molecular Weight | 283.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C19H25NO |
| XLogP3 | 4.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 283.193614421 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 283.193614421 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 12.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 250 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Intended for the treatment of various forms of cancer.
Histamine Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate histamine receptors, thereby blocking the actions of histamine or histamine agonists. Classical antihistaminics block the histamine H1 receptors only. (See all compounds classified as Histamine Antagonists.)
Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors
Drugs or agents which antagonize or impair any mechanism leading to blood platelet aggregation, whether during the phases of activation and shape change or following the dense-granule release reaction and stimulation of the prostaglandin-thromboxane system. (See all compounds classified as Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors.)
Hepatic
Although the exact mechanism of action is not known, one study (PMID: 16413681) proposes that tesmilifene may be an activating p-gp substrate, which enables the p-gp pump to extrude typical p-gp substrates (such as anthracyclines or taxanes) more efficiently. This process consumes ATP, since the p-gp is absolutely, and highly dependent on ATP hydrolysis. The mechanism of cell death is likely to result not from the presence of chemotherapy inside the cell (in fact the chemotherapy is extruded) but, directly or indirectly, from the enhanced consumption of ATP. The ATP may be consumed below a threshold necessary for survival, or, (more likely) the enhanced ATP production required to maintain ATP levels may result in the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) to an extent that overwhelms the cells ability to inactivate them. The result would be additional cell death, but only in the mdr+ population. The doxorubicin would continue to act on the drug sensitive remainder of the cell population, but without the help of tesmilifene.
