
1. Apo Baclofen
2. Apo-baclofen
3. Apobaclofen
4. Atrofen
5. Awd, Baclofen
6. Ba-34,647
7. Ba-34647
8. Ba34,647
9. Ba34647
10. Baclofne Irex
11. Baclofne-irex
12. Baclofneirex
13. Baclofen Awd
14. Baclophen
15. Baclospas
16. Beta-(aminomethyl)-4-chlorobenzenepropanoic Acid
17. Beta-(p-chlorophenyl)-gamma-aminobutyric Acid
18. Chlorophenyl Gaba
19. Ciba-34,647-ba
20. Ciba34,647ba
21. Clofen
22. Gaba, Chlorophenyl
23. Gen Baclofen
24. Gen-baclofen
25. Genbaclofen
26. Genpharm
27. Lebic
28. Liorsal
29. Lioresal
30. Nu Baclo
31. Nu-baclo
32. Nubaclo
33. Pcp-gaba
34. Pms Baclofen
35. Pms-baclofen
36. Pmsbaclofen
1. 1134-47-0
2. Lioresal
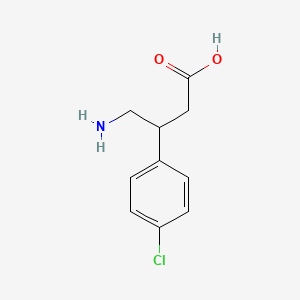
3. 4-amino-3-(4-chlorophenyl)butanoic Acid
4. Kemstro
5. Baclon
6. Dl-baclofen
7. Gabalon
8. (+-)-baclofen
9. Baclofene
10. Baclofeno
11. Baclofenum
12. (rs)-baclofen
13. Beta-(4-chlorophenyl)gaba
14. 4-amino-3-(4-chlorophenyl)butyric Acid
15. Ba-34647
16. Gablofen
17. Ciba 34,647-ba
18. (+/-)-baclofen
19. Dl-4-amino-3-p-chlorophenylbutanoic Acid
20. Beta-(aminomethyl)-4-chlorobenzenepropanoic Acid
21. Ba-34,647
22. Beta-(p-chlorophenyl)-gamma-aminobutyric Acid
23. Baclofen (r,s)
24. C 34647ba
25. Ba 34647
26. Beta-(aminomethyl)-p-chlorohydrocinnamic Acid
27. Gamma-amino-beta-(p-chlorophenyl)butyric Acid
28. Butanoic Acid, 4-amino-3-(4-chlorophenyl)-
29. Mfcd00055143
30. Chembl701
31. Nsc-755906
32. Benzenepropanoic Acid, Beta-(aminomethyl)-4-chloro-
33. Chebi:2972
34. H789n3fke8
35. (+)-baclofen; (l)-baclofen
36. Atrofen
37. Baclophen
38. Lioresal Intrathecal
39. Apo-baclofen
40. Ncgc00015156-11
41. (rs)-amino-3-(4-chlorophenyl)butyric Acid
42. Dsstox_cid_2641
43. 4-amino-3(4-chlorophenyl)butyric Acid
44. Baclofene [inn-french]
45. Baclofenum [inn-latin]
46. .beta.-(aminomethyl)-p-chlorohydrocinnamic Acid
47. Dsstox_rid_76670
48. Baclofeno [inn-spanish]
49. Dsstox_gsid_22641
50. .beta.-(aminomethyl)-4-chlorobenzenepropanoic Acid
51. Lioresal (tn)
52. Kemstro (tn)
53. Ccris 3722
54. Sr-01000000107
55. Einecs 214-486-9
56. Brn 2104494
57. Unii-h789n3fke8
58. Baclofen O
59. Ipx056
60. Mfcd01321057
61. Ipx 056
62. (y)-baclofen
63. Prestwick_85
64. Cas-1134-47-0
65. (?)-baclofen
66. Fleqsuvy
67. Lyvispah
68. Ozobax
69. Baclofen [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
70. (a+/-)-baclofen
71. Spectrum_000066
72. Baclofen [usan]
73. Baclofen [inn]
74. Baclofen [jan]
75. Baclofen [mi]
76. Baclofen [vandf]
77. (.+/-.)-baclofen
78. (.+/-.)-baklofen
79. Prestwick0_000085
80. Prestwick1_000085
81. Prestwick2_000085
82. Prestwick3_000085
83. Spectrum2_000092
84. Spectrum3_000310
85. Spectrum4_000245
86. Spectrum5_000852
87. Baclofen-[d4] (major)
88. Baclofen [mart.]
89. Baclofen [usp-rs]
90. Baclofen [who-dd]
91. Biomol-nt_000251
92. Upcmld-dp142
93. (±)-baclofen
94. B 5399
95. Lopac0_000163
96. Oprea1_440627
97. Schembl19333
98. Bspbio_000010
99. Bspbio_001880
100. Kbiogr_000650
101. Kbioss_000466
102. Mls000028480
103. .beta.-(4-chlorophenyl)gaba
104. Divk1c_000001
105. Spectrum1500135
106. Baclofen (jp17/usp/inn)
107. Hydrocinnamic Acid, .beta.-(aminomethyl)-p-chloro-
108. Spbio_000044
109. Spbio_001949
110. Baclofen [orange Book]
111. Benzenepropanoic Acid, .beta.-(aminomethyl)-4-chloro-
112. Bpbio1_000012
113. Bpbio1_000750
114. Gtpl1084
115. Baclofen [ep Monograph]
116. Baclofen [usp Monograph]
117. Dtxsid5022641
118. Hydrocinnamic Acid, Beta-(aminomethyl)-p-chloro-
119. Upcmld-dp142:001
120. Bdbm24182
121. Hms500a03
122. Kbio1_000001
123. Kbio2_000466
124. Kbio2_003034
125. Kbio2_005602
126. Kbio3_001380
127. Baclofen 0.5 Mg/ml In Methanol
128. Ninds_000001
129. Hms1568a12
130. Hms1920e21
131. Hms2091m03
132. Hms2095a12
133. Hms3260b07
134. Hms3712a12
135. Pharmakon1600-01500135
136. ( Inverted Question Mark)-baclofen
137. Albb-014712
138. Bcp11844
139. Bcp32777
140. Ex-a1378
141. Hy-b0007
142. Tox21_110090
143. Tox21_500163
144. Bbl010735
145. Ccg-38910
146. Cx1358
147. Nsc329137
148. Nsc755906
149. S4840
150. Stk535284
151. Akos005174692
152. Tox21_110090_1
153. Ac-4530
154. Db00181
155. Hs-1001
156. Lp00163
157. Mb00475
158. Nsc 755906
159. Nsc-329137
160. Sb67382
161. Sdccgsbi-0050151.p005
162. 4-amino-3-(4-chlorophenyl)butanoicacid
163. 4-amino-3-(p-chlorophenyl)butyric Acid
164. Idi1_000001
165. Smp1_000036
166. Ncgc00015156-04
167. Ncgc00015156-05
168. Ncgc00015156-06
169. Ncgc00015156-07
170. Ncgc00015156-08
171. Ncgc00015156-12
172. Ncgc00015156-13
173. Ncgc00015156-15
174. Ncgc00015156-26
175. Ncgc00015156-28
176. Ncgc00023843-03
177. Ncgc00024579-03
178. Ncgc00024579-04
179. Ncgc00024579-05
180. Ncgc00024579-06
181. Ncgc00260848-01
182. Bb166152
183. Smr000058294
184. Sy023865
185. Sy052300
186. Sbi-0050151.p004
187. (+/-)-baclofen, >=98% (tlc), Solid
188. 4-amino-3-(4-chlorophenyl)butanoic Acid #
189. Ab00051921
190. Eu-0100163
191. Ft-0622547
192. Ft-0662468
193. Ft-0662469
194. (rs)-4-amino-3-(4-chlorophenyl)butanoic Acid
195. D00241
196. Ab00051921_16
197. .beta.-(p-chlorophenyl)-.gamma.-aminobutyric Acid
198. .gamma.-amino-.beta.-(p-chlorophenyl)butyric Acid
199. 134b470
200. L000002
201. Q413717
202. J-002965
203. Sr-01000000107-2
204. Sr-01000000107-4
205. Sr-01000000107-6
206. Sr-01000000107-8
207. Brd-a84174873-001-05-2
208. (+/- )-beta-(aminomethyl)-4-chlorobenzenepropanoic Acid
209. Baclofen, British Pharmacopoeia (bp) Reference Standard
210. Baclofen, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
211. F2173-1127
212. Stx209; Stx-209; Stx 209; D-baclofen; Arbaclofen
213. Baclofen Lioresal 4-amino-3-(4-chlorophenyl)butyric Acid
214. Baclofen, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
215. N-boc-(2s,3s)-2-hydroxy-3-amino-5-methylhexanoicacid
216. Baclofen, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
217. Baclofen Solution, 500 Mug/ml In Methanol, Ampule Of 1 Ml, Certified Reference Material
218. Baclofen Solution, 500 Mug/ml (90:10 Meoh:dmso), Certified Reference Material, Ampule Of 1 Ml
219. Brivaracetam-d3 Solution, 100 Mug/ml In Methanol, Certified Reference Material, Ampule Of 1 Ml
| Molecular Weight | 213.66 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H12ClNO2 |
| XLogP3 | -1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 213.0556563 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 213.0556563 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 63.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 14 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 191 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Baclofen |
| PubMed Health | Baclofen |
| Drug Classes | Analgesic, Skeletal Muscle Relaxant, Centrally Acting |
| Drug Label | LIORESAL INTRATHECAL (baclofen injection) is a muscle relaxant and antispastic. Its chemical name is 4-amino-3-(4-chlorophenyl) butanoic acid, and its structural formula is: Baclofen is a white to off-white, odorless or practically odorless crystal... |
| Active Ingredient | Baclofen |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | 10mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Watson Labs; Vintage Pharms; Mylan Pharms; Ivax Sub Teva Pharms; Caraco; Lannett; Usl Pharma; Sun Pharm Inds; Northstar Hlthcare; Prosam Labs; Mylan; Impax Labs |
| 2 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Gablofen |
| PubMed Health | Baclofen |
| Drug Classes | Analgesic, Skeletal Muscle Relaxant, Centrally Acting |
| Drug Label | Gablofen (baclofen injection) is a muscle relaxant and antispastic. Baclofen's pharmacological class is a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) ergic agonist. Baclofen's chemical name is 4-amino- 3-(4-chlorophenyl) butanoic acid, and its structural for |
| Active Ingredient | Baclofen |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Intrathecal |
| Strength | 2mg/ml; 1mg/ml; 0.05mg/ml; 0.5mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mallinckrodt |
| 3 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lioresal |
| PubMed Health | Baclofen (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Skeletal Muscle Relaxant, Centrally Acting |
| Drug Label | LIORESAL INTRATHECAL (baclofen injection) is a muscle relaxant and antispastic. Its chemical name is 4-amino-3-(4-chlorophenyl) butanoic acid, and its structural formula is: Baclofen is a white to off-white, odorless or practically odorless crystal... |
| Active Ingredient | Baclofen |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Intrathecal |
| Strength | 2mg/ml; 0.05mg/ml; 0.5mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Medtronic Neuro |
| 4 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Baclofen |
| PubMed Health | Baclofen |
| Drug Classes | Analgesic, Skeletal Muscle Relaxant, Centrally Acting |
| Drug Label | LIORESAL INTRATHECAL (baclofen injection) is a muscle relaxant and antispastic. Its chemical name is 4-amino-3-(4-chlorophenyl) butanoic acid, and its structural formula is: Baclofen is a white to off-white, odorless or practically odorless crystal... |
| Active Ingredient | Baclofen |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | 10mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Watson Labs; Vintage Pharms; Mylan Pharms; Ivax Sub Teva Pharms; Caraco; Lannett; Usl Pharma; Sun Pharm Inds; Northstar Hlthcare; Prosam Labs; Mylan; Impax Labs |
| 5 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Gablofen |
| PubMed Health | Baclofen |
| Drug Classes | Analgesic, Skeletal Muscle Relaxant, Centrally Acting |
| Drug Label | Gablofen (baclofen injection) is a muscle relaxant and antispastic. Baclofen's pharmacological class is a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) ergic agonist. Baclofen's chemical name is 4-amino- 3-(4-chlorophenyl) butanoic acid, and its structural for |
| Active Ingredient | Baclofen |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Intrathecal |
| Strength | 2mg/ml; 1mg/ml; 0.05mg/ml; 0.5mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mallinckrodt |
| 6 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lioresal |
| PubMed Health | Baclofen (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Skeletal Muscle Relaxant, Centrally Acting |
| Drug Label | LIORESAL INTRATHECAL (baclofen injection) is a muscle relaxant and antispastic. Its chemical name is 4-amino-3-(4-chlorophenyl) butanoic acid, and its structural formula is: Baclofen is a white to off-white, odorless or practically odorless crystal... |
| Active Ingredient | Baclofen |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Intrathecal |
| Strength | 2mg/ml; 0.05mg/ml; 0.5mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Medtronic Neuro |
Baclofen is indicated for the treatment of spasticity resulting from multiple sclerosis and is particularly useful for the relief of flexor spasms and concomitant pain, clonus, and muscular rigidity. It may also be of value in the treatment of patients with spinal cord injuries or diseases. Baclofen is also indicated as an intrathecal injection for the management of severe spasticity of cerebral or spinal original in patients 4 years of age and older. Patients who respond to bolus intrathecal doses of baclofen, and who require chronic therapy, can use an implantable intrathecal pump to administer baclofen via long-term infusion.
FDA Label
Treatment of alcohol dependence
In neurological diseases associated with spasm of the skeletal muscles, the clinical effects of baclofen occur due to baclofen action on reflex muscle contractions and of significant relief from painful spasm, automatism, as well as clonus. Baclofen, when used as indicated, improves mobility, increasing levels of independence, and facilitates both passive and active physiotherapy. Baclofen also stimulates gastric acid secretion. GABA-B receptor activation by baclofen may produce protective neurological effects. Baclofen also possesses anti-inflammatory properties that may be of interest in the study of addiction treatment. Preclinical studies have shown that GABA-B receptors have roles in memory storage and retrieval, reward, motivation, mood, as well as anxiety. Neuroimaging studies in humans indicate that baclofen produces region-specific alterations in brain activity.
GABA-B Receptor Agonists
Endogenous compounds and drugs that bind to and activate GABA-B RECEPTORS. (See all compounds classified as GABA-B Receptor Agonists.)
Muscle Relaxants, Central
A heterogeneous group of drugs used to produce muscle relaxation, excepting the neuromuscular blocking agents. They have their primary clinical and therapeutic uses in the treatment of muscle spasm and immobility associated with strains, sprains, and injuries of the back and, to a lesser degree, injuries to the neck. They have been used also for the treatment of a variety of clinical conditions that have in common only the presence of skeletal muscle hyperactivity, for example, the muscle spasms that can occur in MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS. (From Smith and Reynard, Textbook of Pharmacology, 1991, p358) (See all compounds classified as Muscle Relaxants, Central.)
M03BX01
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
M - Musculo-skeletal system
M03 - Muscle relaxants
M03B - Muscle relaxants, centrally acting agents
M03BX - Other centrally acting agents
M03BX01 - Baclofen
Absorption
Rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Absorption may be dose-dependent, being reduced with increased doses. Baclofen, when introduced directly into the intrathecal space, allows for effective CSF concentrations to be achieved with resulting plasma concentrations 100 times less than concentrations occurring with oral administration,.
Route of Elimination
Baclofen is rapidly and extensively eliminated from the body. There is significant intersubject variation in elimination rates. Baclofen is excreted mainly by the kidney as unchanged drug. Seventy to eighty (70 - 80%) of a dose is measured in the urine as unchanged drug. The remainder of the dose is excreted as unchanged drug in the feces or as metabolites in the urine and feces. Excretion is complete within 72 hours after administration.
Volume of Distribution
**Apparent volume of distribution**: 59 liters. Baclofen does not readily cross the blood-brain barrier.
Clearance
**Total systemic clearance**: 180 mL/min **Renal clearance**: 103 mL/min Baclofen is primarily excreted unchanged by the kidneys. It should be administered cautiously, and it may be necessary to reduce the dosage in patients with reduced renal function.
Approximately 15% of the dose is metabolized in the liver, mainly by deamination. In a clinical study with radiolabeled baclofen, approximately 85% of the dose was excreted unchanged in the urine and feces. The -hydroxy metabolite, 3-(p-chlorophenyl)-4-hydroxybutyric acid, is formed by the deamination of baclofen. Because baclofen is partially metabolized in the liver, patients with impaired liver function should be regularly monitored with liver function tests.
Elimination half-life: Approximately 5.5 hours.
The exact mechanism of action of baclofen is not fully understood at this time,. Many studies indicate that baclofen is a GABA-B receptor agonist,,,,. Despite this, there is no conclusive evidence that the effects of baclofen on GABA systems are involved in the production of its clinical effects. Baclofen is an effective and widely used antispastic agent with a spinal site of action. Its mechanism of action and pharmacological properties are different from the effects of other antispastic agents. In addition, baclofen has central sites of action, shown by its adverse event profile and general CNS depressant properties. GABA-B receptors interact with signal transduction pathways and neurotransmitter systems. Baclofen exerts an antinociceptive effect. The clinical significance of this warrants further research data for clarification. Baclofen depresses monosynaptic and polysynaptic reflex transmission, by various actions, and possibly including the stimulation of GABA-receptors. This stimulation results in the inhibition of excitatory neurotransmitter (glutamate and aspartate) release, which may normally contribute to pain and spasticity. Although baclofen is an analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-amino-butyric acid (GABA), there are no conclusive data indicating GABA systems are involved in its clinical effects.