
1. Ametycine
2. Mitocin C
3. Mitocin-c
4. Mitocinc
5. Mitomycin
6. Mitomycin-c
7. Mutamycin
8. Nsc 26980
9. Nsc-26980
10. Nsc26980
1. Mitomycin
2. 50-07-7
3. Ametycine
4. Mutamycin
5. Mitomycin-c
6. Mitocin-c
7. Mytozytrex
8. Ametycin
9. Mitomycinum
10. Mytomycin
11. Mitozytrex
12. Mitamycin
13. Mitosol
14. Mmc
15. Nsc-26980
16. Muamycin
17. 7-amino-9alpha-methoxymitosane
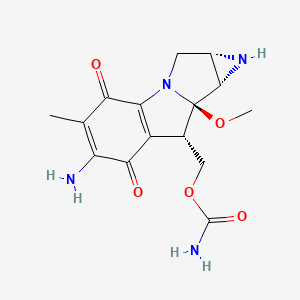
18. C15h18n4o5
19. Nsc 26980
20. Mitomycyna C
21. Nci-c04706
22. Mito-c
23. Nsc26980
24. Mit-c
25. Mitomycinum C
26. Mitocin C
27. Chebi:27504
28. Rcra Waste Number U010
29. Ugn-101
30. Ugn-102
31. 50sg953sk6
32. Mitomycyna C [polish]
33. 6-amino-1,1a,2,8,8a,8b-hexahydro-8-(hydroxymethyl)-8a-methoxy-5-methylazirino(2',3':3,4)pyrrolo(1,2-a)indole-4,7-dione Carbamate (ester)
34. Dsstox_cid_898
35. Dsstox_rid_75853
36. Dsstox_gsid_20898
37. Mitomycin (tn)
38. [(1as,8s,8ar,8bs)-6-amino-8a-methoxy-5-methyl-4,7-dioxo-1,1a,2,4,7,8,8a,8b-octahydroazireno[2',3':3,4]pyrrolo[1,2-a]indol-8-yl]methyl Carbamate
39. [(4s,6s,7r,8s)-11-amino-7-methoxy-12-methyl-10,13-dioxo-2,5-diazatetracyclo[7.4.0.0^{2,7}.0^{4,6}]trideca-1(9),11-dien-8-yl]methyl Carbamate
40. Azirino[2',3':3,4]pyrrolo[1,2-a]indole-4,7-dione, 6-amino-8-[[(aminocarbonyl)oxy]methyl]-1,1a,2,8,8a,8b-hexahydro-8a-methoxy-5-methyl-, (1as,8s,8ar,8bs)-
41. Cas-50-07-7
42. Muamycin (tn)
43. ((1as,8s,8ar,8bs)-6-amino-8a-methoxy-5-methyl-4,7-dioxo-1,1a,2,4,7,8,8a,8b-octahydroazirino[2',3':3,4]pyrrolo[1,2-a]indol-8-yl)methyl Carbamate
44. [1as-(1a?,8?,8a?,8b?)]-6-amino-8-[[(aminocarbonyl)oxy]methyl]-1,1a,2,8,8a,8b-hexahydro-8a-methoxy-5-methylazirino[2',3':3,4]pyrrolo[1,2-a]indole-4,7-dione
45. Azirino(2',3':3,4)pyrrolo(1,2-a)indole-4,7-dione, 6-amino-8-(((aminocarbonyl)oxy)methyl)-1,1a,2,8,8a,8b-hexahydro-8a-methoxy-5-methyl-, (1as,8s,8ar,8bs)-
46. Ccris 414
47. Hsdb 3239
48. Mitomycin (usp/inn)
49. Mls002702984
50. (amino-methoxy-methyl-dioxo-[?]yl)methyl Carbamate
51. Einecs 200-008-6
52. Rcra Waste No. U010
53. 7-amino-9.alpha.-methoxymitosane
54. Mitonco
55. Mitoplus
56. Mitoextra
57. Unii-50sg953sk6
58. Ai3-26199
59. Mitomycin [usan:usp:inn:ban]
60. Ncgc00095258-01
61. [(1as,8s,8ar,8bs)-6-amino-8a-methoxy-5-methyl-4,7-dioxo-1,1a,2,4,7,8,8a,8b-octahydroazirino[2'',3'':3,4]pyrrolo[1,2-a]indol-8-yl]methyl Carbamate
62. [(1as,8s,8ar,8bs)-6-amino-8a-methoxy-5-methyl-4,7-dioxo-1,1a,2,4,7,8,8a,8b-octahydroazirino[2',3':3,4]pyrrolo[1,2-a]indol-8-yl]methyl Carbamate
63. Azirino(2',3':3,4)pyrrolo(1,2-a)indole-4,7-dione, 6-amino-1,1a,2,8,8a,8b-hexahydro-8-(hydroxymethyl)-8a-methoxy-5-methyl-, Carbamate (ester)
64. Jelmyto (tn)
65. Mfcd00078109
66. Jelmyto
67. Mitomycin C- Bio-x
68. Azirino(2',3':3,4)pyrrolo(1,2-a)indole-4,7-dione, 6-amino-8-(((aminocarbonyl)oxy)methyl)-1,1a,2,8,8a,8b-hexahydro-8a-methoxy-5-methyl-, (1as-(1aalpha,8beta,8aalpha,8balpha))-
69. Mitomycin C From Streptomyces Caespitosus
70. Mitomycin [inn]
71. Mitomycin C (jp17)
72. Mitomycin [hsdb]
73. Mitomycin [usan]
74. Mitomycin [vandf]
75. Mitomycin C [mi]
76. Chembl105
77. Mitomycin [mart.]
78. Mitomycin C [jan]
79. Mitomycin [usp-rs]
80. Mitomycin [who-dd]
81. Mitomycin C [iarc]
82. Schembl3760
83. Cbiol_001927
84. Bspbio_001267
85. Kbiogr_000607
86. Kbioss_000607
87. Mitomycin C (4% In Nacl)
88. Mls001332654
89. Mitozytrex (tn) (supergene)
90. 50-07-7 (non-salt)
91. Ametycin Pound Notmitomycin C
92. Gtpl7089
93. Mitomycin [orange Book]
94. Dtxsid2020898
95. Mitomycin [ep Monograph]
96. Kbio2_000607
97. Kbio2_003175
98. Kbio2_005743
99. Kbio3_001073
100. Kbio3_001074
101. Ex-a501
102. Mitomycin [usp Monograph]
103. Bcpp000410
104. Bio1_000213
105. Bio1_000702
106. Bio1_001191
107. Bio2_000464
108. Bio2_000944
109. Hms1362o09
110. Hms1792o09
111. Hms1990o09
112. Hms2089f16
113. Hms3403o09
114. Amy10316
115. Azirino(2',3':3,4)pyrrolo(1,2-a)indole-4,7-dione, 6-amino-8-(((aminocarbonyl)oxy)methyl)-1,1a,2,8,8a,8b-hexahydro-8a-methoxy-5-methyl-, (1as-(1a.alpha.,8.beta.,8a.alpha.,8b.alpha.))-
116. Tox21_111493
117. Ac-918
118. Bdbm50428658
119. Gr-311
120. S8146
121. Zinc30726187
122. Akos015895703
123. Tox21_111493_1
124. Bcp9000285
125. Ccg-208564
126. Cs-0564
127. Db00305
128. Ks-5148
129. Idi1_002219
130. Smp1_000307
131. Mitomycin 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
132. Ncgc00163468-02
133. Ncgc00163468-03
134. Ncgc00163468-05
135. Ncgc00163468-06
136. 1404-00-8
137. Bm164668
138. Hy-13316
139. Smr000058401
140. Bcp0726000181
141. M2320
142. C06681
143. D00208
144. D91590
145. Ab00918689-03
146. Ab00918689-04
147. 078m109
148. Mitomycin C, Antibiotic For Culture Media Use Only
149. Q-201410
150. Brd-k59670716-001-02-6
151. Brd-k59670716-001-06-7
152. Q19856779
153. Wln: T D3 B556 Bn Em Jv Mvttt&j Go1 H1ovz Kz L1
154. Mitomycin C From Streptomyces Caespitosus, >=970 Mug/mg (usp Xxiv)
155. Mitomycin C From Streptomyces Caespitosus, Powder, Bioreagent, Suitable For Cell Culture
156. Mitomycin C From Streptomyces Caespitosus, Powder, Contains Nacl As Solubilizer
157. Azirino[2',4]pyrrolo[1,2-a]indole-4,7-dione, 6-amino-1,1a,2,8,8a,8b-hexahydro-8-(hydroxymethyl)-8a- Methoxy-5-methyl-, Carbamate (ester)
158. Azirino[2',4]pyrrolo[1,2-a]indole-4,7-dione, 6-amino-8-[[(aminocarbonyl)oxy]methyl]-1,1a,2,8,8a,8b- Hexahydro-8a-methoxy-5-methyl-, [1ar-(1a.alpha.,8.beta.,8a.alpha.,8b.alpha.)]-
159. Mitomycin C From Streptomyces Caespitosus, >=98% (hplc), Potency: >=970 Mug Per Mg (usp Xxiv), Gamma-irradiated, Suitable For Cell Culture
| Molecular Weight | 334.33 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H18N4O5 |
| XLogP3 | -0.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 334.12771969 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 334.12771969 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 147 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 757 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Mitomycin |
| PubMed Health | Mitomycin |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic, Antineoplastic Agent |
| Drug Label | Mitomycin (also known as mitomycin and/or mitomycin-C) is an antibiotic isolated from the broth of Streptomyces caespitosus which has been shown to have antitumor activity. The compound is heat stable, has a high melting point, and is freely soluble... |
| Active Ingredient | Mitomycin |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 5mg/vial; 20mg/vial; 40mg/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Bedford; Accord Hlthcare; Hikma Maple |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Mitosol |
| Active Ingredient | Mitomycin |
| Dosage Form | For solution |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 0.2mg/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mobius Therap |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Mitomycin |
| PubMed Health | Mitomycin |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic, Antineoplastic Agent |
| Drug Label | Mitomycin (also known as mitomycin and/or mitomycin-C) is an antibiotic isolated from the broth of Streptomyces caespitosus which has been shown to have antitumor activity. The compound is heat stable, has a high melting point, and is freely soluble... |
| Active Ingredient | Mitomycin |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 5mg/vial; 20mg/vial; 40mg/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Bedford; Accord Hlthcare; Hikma Maple |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Mitosol |
| Active Ingredient | Mitomycin |
| Dosage Form | For solution |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 0.2mg/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mobius Therap |
Antibiotics, Antineoplastic; Nucleic Acid Synthesis Inhibitors
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Mitomycin is useful for the palliative treatment of gastric adenocarcinoma, in conjunction with fluorouracil and doxorubicin. It has produced temporary beneficial effects in carcinomas of the cervix, colon, rectum, pancreas, breast, bladder, head and neck, and lung, and in melanoma. It has also shown activity against lymphomas and leukemia, particularly chronic granulocytic leukemia, but not in myeloma.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1247
Thirty patients with advanced colorectal adenocarcinoma were treated by chemotherapy with an alternating regimen consisting of 5-fluorouracil mitomycin C and 5-fluorouracil dacarbazine at 3 wk intervals. ... The toxicity of this regimen was essentially digestive with 30% of grade 3 or 4 nausea and vomiting. In spite of the reported active and synergistic action of drug association in colorectal carcinoma, this treatment schedule is not better than 5-fluorouracil alone. Gastrointestinal toxicity was incr.
PMID:2496369 Herait P et al; Oncology 46 (2): 88-90 (1989)
Forty-two patients with metastatic breast cancer refractory to first line therapies were treated with combination chemotherapy with mitomycin-C and vinblastine. ... The toxicity was acceptable with 20 episodes of moderate myelosuppression (58.8%) and 2 cases with congestive heart failure that responded to medical treatment.
PMID:2497417 Navarro M et al; Oncology 46 (3): 137-42 (1989)
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for MITOMYCIN C (19 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Mitomycin is contraindicated in patients with pre-existing myelosupression & anemia.
Knoben, J.E. and P.O. Anderson (eds.) Handbook of Clinical Drug Data. 6th ed. Bethesda, MD: Drug Intelligence Publications, Inc. 1988., p. 417
Because normal defense mechanisms may be suppressed by mitomycin therapy, the patient's antibody response to the vaccine may be decreased. The interval between discontinuation of medications that cause immunosuppression and restoration of the patient's ability to respond to the vaccine depends on the intensity and type of immunosuppression-causing medication used, the underlying disease, and other factors; estimates vary from 3 months to 1 year.
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 16th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: U.S. Pharmaceutical Convention, Inc. 1996 (Plus updates)., p. 2088
cBecause normal defense mechanisms may be suppressed by mitomycin therapy, concurrent use with a live virus vaccine may potentiate the replication of the vaccine virus, may increase the side/adverse effects of the vaccine virus, and/or may decrease the patient's antibody response to the vaccine; immunization of these patients should be undertaken only with extreme caution after careful review of the patient's hematologic status and only with the knowledge and consent of the physician managing the cytarabine therapy. The interval between discontinuation of medication that cause immunosuppression and restoration of the patient's ability to respond to the vaccine depends on the intensity and type of immunosuppression-causing medications used, the underlying disease, and other factors; estimates vary from 3 months to 1 year. Patients with leukemia in remission should not receive live virus vaccine until at least 3 months after their last chemotherapy. In addition, immunization with oral polio-virus vaccine should be postponed in persons in close contact with the patient, especially family members.
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 16th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: U.S. Pharmaceutical Convention, Inc. 1996 (Plus updates)., p. 2088
Gonadal suppression, resulting in amenorrhea or azoospermia, may occur in patients taking antineoplastic therapy, especially with the alkylating agents. In general, these effects appear to be related to dose and length of therapy and may be irreversible. Prediction of the degree of testicular or ovarian function impairment is complicated by the common use of combinations of several antineoplastics, which makes it difficult to assess the effects of individual agents.
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 16th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: U.S. Pharmaceutical Convention, Inc. 1996 (Plus updates)., p. 2087
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for MITOMYCIN C (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For treatment of malignant neoplasm of lip, oral cavity, pharynx, digestive organs, peritoneum, female breast, and urinary bladder. Also used as an adjunct to ab externo glaucoma surgery. Mitomycin is also indicated as a pyelocalyceal solution for the treatment of adults with low-grade upper tract urothelial cancer (LG-UTUC).
FDA Label
Mitomycin is one of the older chemotherapy drugs, which has been around and in use for decades. It is an antibiotic which has been shown to have antitumor activity. Mitomycin selectively inhibits the synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). The guanine and cytosine content correlates with the degree of mitomycin-induced cross-linking. At high concentrations of the drug, cellular RNA and protein synthesis are also suppressed. Mitomycin has been shown in vitro to inhibit B cell, T cell, and macrophage proliferation and impair antigen presentation, as well as the secretion of interferon gamma, TNFa, and IL-2.
Alkylating Agents
Highly reactive chemicals that introduce alkyl radicals into biologically active molecules and thereby prevent their proper functioning. Many are used as antineoplastic agents, but most are very toxic, with carcinogenic, mutagenic, teratogenic, and immunosuppressant actions. They have also been used as components in poison gases. (See all compounds classified as Alkylating Agents.)
Antibiotics, Antineoplastic
Chemical substances, produced by microorganisms, inhibiting or preventing the proliferation of neoplasms. (See all compounds classified as Antibiotics, Antineoplastic.)
Nucleic Acid Synthesis Inhibitors
Compounds that inhibit cell production of DNA or RNA. (See all compounds classified as Nucleic Acid Synthesis Inhibitors.)
Cross-Linking Reagents
Reagents with two reactive groups, usually at opposite ends of the molecule, that are capable of reacting with and thereby forming bridges between side chains of amino acids in proteins; the locations of naturally reactive areas within proteins can thereby be identified; may also be used for other macromolecules, like glycoproteins, nucleic acids, or other. (See all compounds classified as Cross-Linking Reagents.)
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01D - Cytotoxic antibiotics and related substances
L01DC - Other cytotoxic antibiotics
L01DC03 - Mitomycin
Absorption
Erratic.
Route of Elimination
Approximately 10% of a dose of mitomycin is excreted unchanged in the urine.
FOLLOWING IV INJECTION OF 2 MG/KG BODY WT ... WISTAR RATS, 18% WAS RECOVERED UNCHANGED IN URINE WITHIN 24 HR AT ... 8 MG/KG ... 35% WAS RECOVERED IN URINE, BUT NONE IN FECES OR TISSUES.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V10 174 (1976)
THIRTY MIN AFTER IV INJECTION OF 8 MG/KG BODY WT TO MICE TRACES REMAINED IN BLOOD. IN GUINEA PIGS DRUG WAS CONCN IN KIDNEYS & NOT IN LIVER, SPLEEN OR BRAIN & WAS EXCRETED IN URINE.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V10 174 (1976)
Mitomycin is absorbed inconsistently from the gastrointestinal tract, and it is therefore administered intravenously. It disappears rapidly from the blood after injection. Peak concentrations in plasma are 0.4 ug/ml after doses of 20 mg/m sq ... The drug is widely distributed throughout the body but is not detected in the brain.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1247
In animals, highest mitomycin concentrations are found in the kidneys, followed by muscles, eyes, lung, intestines, and stomach. The drug is not detectable in the liver, spleen, or brain which rapidly inactivate mitomycin. Higher concentrations of the drug are generally present in cancer tissues than in normal tissues.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). AHFS Drug Information 90. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1990 (Plus Supplements 1990)., p. 537
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for MITOMYCIN C (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Primarily hepatic, some in various other tissues.
SUGGESTED ALKYLATING METABOLITES OF CARCINOGENS: MITOMYCIN C: REDUCTION PRODUCTS. /FROM TABLE/
Searle, C. E. (ed.). Chemical Carcinogens. ACS Monograph 173. Washington, DC: American Chemical Society, 1976., p. 95
Inactivation occurs by metabolism, but the products have not been identified. It is metabolized primarily in the liver, and less than 10% of the active drug is excreted in the urine or the bile.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1247
The drug is eliminated primarily by hepatic metabolism with about 20% hepatic extraction and 10-30% recovery of intact drug in the urine. Clearance is 0.3-0.4 l/hr/kg.
IATA. Dangerous Goods Regulations. 30th ed. Montreal, Canada: International Air Transport Association. Dangerous Goods Board, January 1, 1989., p. 416
Mitomycin disappears rapidly from the blood after intravenous injection. It is widely distributed but does not appear to cross the blood-brain barrier. Mitomycin is metabolized mainly in the liver; up to 10% of a dose is excreted unchanged in the urine.
Reynolds, J.E.F., Prasad, A.B. (eds.) Martindale-The Extra Pharmacopoeia. 28th ed. London: The Pharmaceutical Press, 1982., p. 221
MITOMYCIN C WAS PREFERENTIALLY ACTIVATED & METABOLIZED BY SONICATED CELL PREPARATIONS. BIOACTIVATION OF MITOMYCIN TO ALKYLATING AGENT BY EMT6 & SARCOMA 180 CELL SONICATES REQUIRED HYPOXIC CONDITIONS & NADPH-GENERATING SYSTEM.
PMID:7388797 KENNEDY KA ET AL; CANCER RES 40 (7): 2356 (1980)
8-48 min
After doses of 20 mg/m sq ... Mitomycin is cleared from plasma with a half-time of approximately 1 hour.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1247
/Mitomycin/ has an alpha half-life of 5-10 min after IV injection and beta half-life of 46 min.
Knoben, J.E. and P.O. Anderson (eds.) Handbook of Clinical Drug Data. 6th ed. Bethesda, MD: Drug Intelligence Publications, Inc. 1988., p. 416
Mitomycin is activated in vivo to a bifunctional and trifunctional alkylating agent. Binding to DNA leads to cross-linking and inhibition of DNA synthesis and function. Mitomycin is cell cycle phase-nonspecific.
... REACTS WITH BACTERIAL DNA BUT NOT WITH ISOLATED DNA, UNLESS ... REDUCING SYSTEM IS ADDED. CROSS LINKING EFFICIENCY ... INCR IN ISOLATED BACTERIAL DNA CONTAINING INCR AMT OF CYTOSINE & GUANOSINE.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V10 175 (1976)
ITS REDUCED FORM CONTAINS INDOLE GROUP EMBODYING ALLYLIC CARBAMATE RESIDUE. ANTIBIOTIC IS CYTOTOXIC & CARCINOGENIC BUT IS INACTIVE AS CYTOTOXIC AGENT UNLESS REDUCED ... IT ACTS AS DIFUNCTIONAL AGENT IN CROSS LINKING DNA.
Searle, C. E. (ed.). Chemical Carcinogens. ACS Monograph 173. Washington, DC: American Chemical Society, 1976., p. 96
The drug inhibits DNA synthesis and cross-links DNA at the N6 position of adenine and at the O6 and N2 positions of guanine. In addition, single-strand breakage of DNA is caused by reduced mitomycin; this can be prevented by free radical scavengers. Its action is most prominent during the late G1 and early S phases of the cell cycle.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1247
In high concentrations ... /mitomycin/ may ... inhibit RNA and protein synthesis.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). AHFS Drug Information 90. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1990 (Plus Supplements 1990)., p. 537
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for MITOMYCIN C (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.