

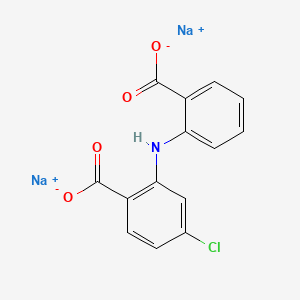

1. 2-((2-carboxyphenyl)amino)-4-chlorobenzoic Acid
2. 4-chloro-2,2'-iminodibenzoic Acid
3. Cca Lobenzarit
4. Disodium 4-chloro-2,2'-iminodibenzoate
5. Lobenzarit
6. Lobenzarit Disodium
7. Lobenzarit, Disodium Salt
8. Lobenzart
9. N-(2-carboxyphenyl)-4-chloroanthranilic Acid
1. Lobenzarit Disodium
2. 64808-48-6
3. Lobenzarit Disodium Salt
4. Carfenil
5. Lobenzarit Sodium [usan]
6. Disodium 4-chloro-2,2'-iminodibenzoate
7. Sodium 2-((2-carboxylatophenyl)amino)-4-chlorobenzoate
8. 7z9sp74bxf
9. 2-((2-carboxyphenyl)amino)-4-chlorobenzoic Acid Disodium Salt
10. Benzoic Acid, 2-((2-carboxyphenyl)amino)-4-chloro-, Disodium Salt
11. Cca
12. Disodium;2-(2-carboxylatoanilino)-4-chlorobenzoate
13. Benzoic Acid, 2-[(2-carboxyphenyl)amino]-4-chloro, Disodium Salt
14. Ncgc00181760-01
15. Unii-7z9sp74bxf
16. Disodium 4-chloro-2,2'-iminobenzoate
17. Ccris 8090
18. Carfenil (tn)
19. N-(2-carboxyphenyl)-4-chloroanthranilic Acid Disodium Salt
20. Disodium Lobenzarit
21. Dsstox_cid_28532
22. Dsstox_rid_82804
23. Dsstox_gsid_48606
24. Schembl635305
25. Lobenzarit Sodium [jan]
26. Chembl2107179
27. Dtxsid8048606
28. Chebi:31778
29. Lobenzarit Sodium (jp17/usan)
30. Lobenzarit Sodium [mart.]
31. Lobenzarit Sodium [who-dd]
32. Tox21_112941
33. Mfcd00941422
34. Lobenzarit Disodium Salt [mi]
35. Akos025311428
36. Ac-26450
37. Cas-64808-48-6
38. L0278
39. D01808
40. H11986
41. A834889
42. Disodium N-(2-carboxyphenyl)-4-chloroanthranilate
43. Q27269066
44. Sodium 2-(2-carboxylatophenylamino)-4-chlorobenzoate
| Molecular Weight | 335.65 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H8ClNNa2O4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 334.9937240 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 334.9937240 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 92.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 365 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 3 |
Adjuvants, Immunologic
Substances that augment, stimulate, activate, potentiate, or modulate the immune response at either the cellular or humoral level. The classical agents (Freund's adjuvant, BCG, Corynebacterium parvum, et al.) contain bacterial antigens. Some are endogenous (e.g., histamine, interferon, transfer factor, tuftsin, interleukin-1). Their mode of action is either non-specific, resulting in increased immune responsiveness to a wide variety of antigens, or antigen-specific, i.e., affecting a restricted type of immune response to a narrow group of antigens. The therapeutic efficacy of many biological response modifiers is related to their antigen-specific immunoadjuvanticity. (See all compounds classified as Adjuvants, Immunologic.)
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal
Anti-inflammatory agents that are non-steroidal in nature. In addition to anti-inflammatory actions, they have analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions. They act by blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, which converts arachidonic acid to cyclic endoperoxides, precursors of prostaglandins. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis accounts for their analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions; other mechanisms may contribute to their anti-inflammatory effects. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal.)
Immunosuppressive Agents
Agents that suppress immune function by one of several mechanisms of action. Classical cytotoxic immunosuppressants act by inhibiting DNA synthesis. Others may act through activation of T-CELLS or by inhibiting the activation of HELPER CELLS. While immunosuppression has been brought about in the past primarily to prevent rejection of transplanted organs, new applications involving mediation of the effects of INTERLEUKINS and other CYTOKINES are emerging. (See all compounds classified as Immunosuppressive Agents.)
