


1. Dihydrochloride, Flunarizine
2. Flunarizin
3. Flunarizine Dihydrochloride
4. Flunarizine Hydrochloride
5. Hydrochloride, Flunarizine
6. R 14950
7. R-14950
8. R14950
9. Sibelium
1. 52468-60-7
2. Sibelium
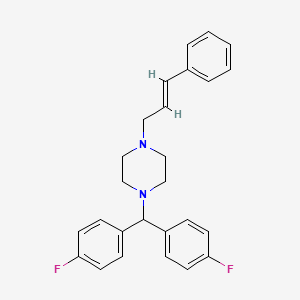
3. 1-(bis(4-fluorophenyl)methyl)-4-cinnamylpiperazine
4. Flunarizinum [inn-latin]
5. Flunarizina [inn-spanish]
6. 40218-96-0
7. Flunarizine (inn)
8. (e)-1-(bis(4-fluorophenyl)methyl)-4-(3-phenyl-2-propenyl)piperazine
9. R7pla2dm0j
10. 1-[bis(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]-4-[(e)-3-phenylprop-2-enyl]piperazine
11. Chembl30008
12. (e)-1-[bis-(p-fluorophenyl)methyl]-4-cinnamylpiperazine
13. Piperazine, 1-(bis(4-fluorophenyl)methyl)-4-(3-phenyl-2-propenyl)-, (e)-
14. Flunarizine [inn]
15. 1-[bis(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]-4-[(2e)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-yl]piperazine
16. Piperazine, 1-[bis(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]-4-(3-phenyl-2-propenyl)-, (e)-
17. Flunarizine [inn:ban]
18. Dsstox_cid_25616
19. Dsstox_rid_81005
20. Dsstox_gsid_45616
21. Flunarazine
22. Narzine
23. Sibelium (tn)
24. Cas-52468-60-7
25. Einecs 257-937-5
26. Unii-r7pla2dm0j
27. 1-[bis(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]-4-(3-phenylprop-2-enyl)piperazine
28. (e)-1-(bis-(p-fluorophenyl)methyl)-4-cinnamylpiperazine
29. Flunarizine2hcl
30. Ncgc00018102-06
31. Einecs 254-842-0
32. Flunarizine [mi]
33. Prestwick2_000312
34. Prestwick3_000312
35. Spectrum5_001570
36. Lopac0_000527
37. Schembl43440
38. Schembl43441
39. Bspbio_000304
40. Bspbio_001341
41. Bspbio_003096
42. Flunarizine [who-dd]
43. Bpbio1_000336
44. Dtxsid6045616
45. Bcbcmap01_000120
46. Chebi:92209
47. Cid_6365505
48. 1-[bis(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]-4-[(e)-cinnamyl]piperazine
49. Chebi:135652
50. Hms1361d03
51. Hms1791d03
52. Hms1989d03
53. Hms2089h21
54. Hy-b0358
55. Tox21_110825
56. Bdbm50017702
57. Piperazine, 1-(bis(4-fluorophenyl)methyl)-4-(3-phenyl-2-propenyl)-
58. Stl477617
59. Zinc19360739
60. 1-[bis(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]-4-[(2e)-3-phenyl-2-propenyl]piperazine
61. 4-((2e)-3-phenylprop-2-enyl)-1-[bis(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]piperazine
62. Akos015960783
63. Tox21_110825_1
64. Ac-1283
65. Ccg-204617
66. Db04841
67. Sdccgsbi-0050510.p004
68. Idi1_000043
69. Idi1_033811
70. Ncgc00018102-04
71. Ncgc00018102-05
72. Ncgc00018102-07
73. Ncgc00018102-08
74. Ncgc00018102-09
75. Ncgc00018102-10
76. Ncgc00018102-12
77. Ncgc00018102-24
78. Ncgc00024308-04
79. Ncgc00024308-05
80. Ncgc00024308-06
81. Ncgc00024308-07
82. As-75845
83. Sbi-0050510.p003
84. Cs-0013608
85. D07971
86. D93478
87. Ab00053586-15
88. Ab00053586_16
89. Ab00053586_17
90. A899896
91. Q416237
92. 1-[bis-(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]-4-cinnamylpiperazine
93. Brd-k12184470-300-01-8
94. Brd-k29582677-001-02-7
95. Brd-k29582677-300-05-6
96. Brd-k29582677-300-06-4
97. 1-[bis-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-methyl]-4-(3-phenyl-allyl)-piperazine
98. 1-[bis(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]-4-[(2z)-3-phenyl-2-propen-1-yl]piperazine
99. 1-[bis-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-methyl]-4-((e)-3-phenyl-allyl)-piperazine
100. Piperazine, 1-[bis(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]-4-[(2e)-3-phenyl-2-propenyl]-
101. 1-[bis-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-methyl]-4-(3-phenyl-allyl)-piperazine(flunarizine)
| Molecular Weight | 404.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C26H26F2N2 |
| XLogP3 | 6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 404.20640516 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 404.20640516 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 6.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 487 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Used in the prophylaxis of migraine, occlusive peripheral vascular disease, vertigo of central and peripheral origin, and as an adjuvant in the therapy of epilepsy.
Flunarizine is a selective calcium entry blocker with calmodulin binding properties and histamine H1 blocking activity.
Anticonvulsants
Drugs used to prevent SEIZURES or reduce their severity. (See all compounds classified as Anticonvulsants.)
Calcium Channel Blockers
A class of drugs that act by selective inhibition of calcium influx through cellular membranes. (See all compounds classified as Calcium Channel Blockers.)
Histamine H1 Antagonists
Drugs that selectively bind to but do not activate histamine H1 receptors, thereby blocking the actions of endogenous histamine. Included here are the classical antihistaminics that antagonize or prevent the action of histamine mainly in immediate hypersensitivity. They act in the bronchi, capillaries, and some other smooth muscles, and are used to prevent or allay motion sickness, seasonal rhinitis, and allergic dermatitis and to induce somnolence. The effects of blocking central nervous system H1 receptors are not as well understood. (See all compounds classified as Histamine H1 Antagonists.)
Vasodilator Agents
Drugs used to cause dilation of the blood vessels. (See all compounds classified as Vasodilator Agents.)
N - Nervous system
N07 - Other nervous system drugs
N07C - Antivertigo preparations
N07CA - Antivertigo preparations
N07CA03 - Flunarizine
Absorption
85% following oral administration.
Hepatic, to two metabolites via N-dealylation and hydroxylation.
Flunarizine has known human metabolites that include 1-[bis(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]piperazine, bis(4-fluorophenyl)methanone, and p-Hydroxyflunarizine.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
18 days
Flunarizine inhibits the influx of extracellular calcium through myocardial and vascular membrane pores by physically plugging the channel. The decrease in intracellular calcium inhibits the contractile processes of smooth muscle cells, causing dilation of the coronary and systemic arteries, increased oxygen delivery to the myocardial tissue, decreased total peripheral resistance, decreased systemic blood pressure, and decreased afterload.
