
1. Estorra
2. Lunesta
1. 138729-47-2
2. Lunesta
3. (s)-zopiclone
4. Estorra
5. Esopiclone
6. (+)-zopiclone
7. Eszopiclon
8. Eszopiclone Civ
9. Sep-190
10. Zopiclone S-form
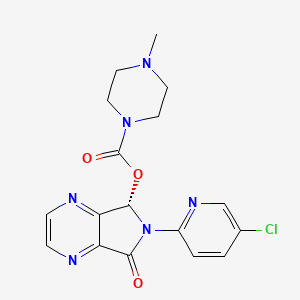
11. [(7s)-6-(5-chloropyridin-2-yl)-5-oxo-7h-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyrazin-7-yl] 4-methylpiperazine-1-carboxylate
12. Chebi:53760
13. (+)-(5s)-6-(5-chloropyridin-2-yl)-7-oxo-6,7-dihydro-5h-pyrrolo(3,4-b)pyrazin-5-yl 4-methylpiperazine-1-carboxylate
14. Sep-225441
15. Uzx80k71oe
16. (5s)-6-(5-chloropyrid-2-yl)-5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)carbonyloxy-7-oxo-6,7-dihydro-5h-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyrazine
17. 1-piperazinecarboxylic Acid, 4-methyl-, (5s)-6-(5-chloro-2-pyridinyl)-6,7-dihydro-7-oxo-5h-pyrrolo(3,4-b)pyrazin-5-yl Ester
18. Gsk-1755165
19. Ncgc00159515-02
20. Dsstox_cid_26086
21. Dsstox_rid_81327
22. Dsstox_gsid_46086
23. Eszopiclone [usan:inn]
24. (5s)-6-(5-chloropyridin-2-yl)-7-oxo-6,7-dihydro-5h-pyrrolo(3,4-b)pyrazin-5-yl 4-methylpiperazine-1-carboxylate
25. (5s)-6-(5-chloropyridin-2-yl)-7-oxo-6,7-dihydro-5h-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyrazin-5-yl 4-methylpiperazine-1-carboxylate
26. Lunivia
27. (s)-eszopiclone
28. Estorra (tn)
29. Lunesta (tn)
30. Cas-138729-47-2
31. Hsdb 7472
32. Sr-05000001914
33. Dea No. 2784
34. Unii-uzx80k71oe
35. Zopiclon
36. Eszopiclone [usan]
37. Ks-1055
38. Sep-0227018
39. Sep-0227108
40. (s)-(+)-zopiclone
41. Eszopiclone [inn]
42. Eszopiclone [jan]
43. Eszopiclone [hsdb]
44. Eszopiclone [vandf]
45. Eszopiclone ( S-zopiclone)
46. Chembl1522
47. Eszopiclone [mart.]
48. Schembl28657
49. Eszopiclone [who-dd]
50. Mls001165744
51. Eszopiclone (jan/usp/inn)
52. Spectrum1505188
53. Zopiclone S-form [mi]
54. Gtpl7429
55. Dtxsid8046086
56. Eszopiclone [orange Book]
57. Eszopiclone Civ [usp-rs]
58. Hms2864o09
59. Hms3259b17
60. Hms3264f04
61. Eszopiclone [usp Monograph]
62. Bcp04910
63. Tox21_111733
64. Bdbm50247998
65. Mfcd03700720
66. Zinc19632834
67. Akos015895596
68. Tox21_111733_1
69. Ac-5546
70. Ac-5547
71. Ccg-213172
72. Db00402
73. Nc00663
74. Ncgc00159515-03
75. (s)-6-(5-chloropyridin-2-yl)-7-oxo-6,7-dihydro-5h-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyrazin-5-yl 4-methylpiperazine-1-carboxylate
76. [(7s)-6-(5-chloro-2-pyridyl)-5-oxo-7h-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyrazin-7-yl] 4-methylpiperazine-1-carboxylate
77. Smr000550478
78. En300-52506
79. D02624
80. Ab00828423_06
81. 729e472
82. A807426
83. Q413184
84. Sr-05000001914-1
85. Sr-05000001914-2
86. Eszopiclone, (+)-zopiclone, (s)-zopiclone, Estorra (r)-isomer
87. (+)-(5s)-6-(5-chloropyridin-2-yl)-7-oxo-6,7-dihydro-5h-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyrazin-5-yl-4-methylpiperazine-1-carboxylate
88. (s)-4-methylpiperazine-1-carboxylic Acid 6-(5-chloropyridin-2-yl)-7-oxo-6,7-dihydro-5h-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyrazin-5-yl Ester
89. (s)-6-(5-chloro-2-pyridinyl)- 7-oxo- 6,7-dihydro- 5h-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyrazin-5-yl- 4-methyl- 1-piperazinecarboxylate
90. 1-piperazinecarobxylic Acid,4-methyl-,(5s)-6-(5-chloro-2-pyridinyl)-6,7-dihydro-7-oxo-5h-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyrazin-5-yl Ester
91. 1140433-81-3
| Molecular Weight | 388.8 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H17ClN6O3 |
| XLogP3 | 0.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 388.1050661 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 388.1050661 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 91.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 573 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Eszopiclone |
| PubMed Health | Eszopiclone (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Nonbarbiturate Hypnotic |
| Drug Label | LUNESTA (eszopiclone) is a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic agent that is a pyrrolopyrazine derivative of the cyclopyrrolone class. The chemical name of eszopiclone is (+)-(5S)-6-(5-chloropyridin-2-yl)-7-oxo-6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b] pyrazin-5-yl 4-met... |
| Active Ingredient | Eszopiclone |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 2mg; 1mg; 3mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Glenmark Generics; Teva; Lupin; Dr Reddys Labs; Orchid Hlthcare; Sun Pharma Global; Roxane |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lunesta |
| PubMed Health | Eszopiclone (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Nonbarbiturate Hypnotic |
| Drug Label | LUNESTA (eszopiclone) is a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic agent that is a pyrrolopyrazine derivative of the cyclopyrrolone class. The chemical name of eszopiclone is (+)-(5S)-6-(5-chloropyridin-2-yl)-7-oxo-6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b] pyrazin-5-yl 4-met... |
| Active Ingredient | Eszopiclone |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 1mg; 2mg; 3mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Sunovion Pharms |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Eszopiclone |
| PubMed Health | Eszopiclone (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Nonbarbiturate Hypnotic |
| Drug Label | LUNESTA (eszopiclone) is a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic agent that is a pyrrolopyrazine derivative of the cyclopyrrolone class. The chemical name of eszopiclone is (+)-(5S)-6-(5-chloropyridin-2-yl)-7-oxo-6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b] pyrazin-5-yl 4-met... |
| Active Ingredient | Eszopiclone |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 2mg; 1mg; 3mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Glenmark Generics; Teva; Lupin; Dr Reddys Labs; Orchid Hlthcare; Sun Pharma Global; Roxane |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lunesta |
| PubMed Health | Eszopiclone (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Nonbarbiturate Hypnotic |
| Drug Label | LUNESTA (eszopiclone) is a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic agent that is a pyrrolopyrazine derivative of the cyclopyrrolone class. The chemical name of eszopiclone is (+)-(5S)-6-(5-chloropyridin-2-yl)-7-oxo-6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b] pyrazin-5-yl 4-met... |
| Active Ingredient | Eszopiclone |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 1mg; 2mg; 3mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Sunovion Pharms |
Hypnotics and Sedatives; Sedative-hypnotic
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 2006)
Eszopiclone is indicated for the treatment of insomnia. /Included in US product label/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 1411
Eszopiclone is a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic with a chemical structure unrelated to pyrazolopyrimidines, imidazopyridines, benzodiazepines, barbiturates,or other drugs with hypnotic properties.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 1411
Since sleep disturbances may be a manifestation of a physical and/or psychiatric disorder, symptomatic treatment of insomnia should be initiated only after careful evaluation of the patient. The failure of insomnia to remit after 7-10 days of therapy may indicate the presence of an underlying psychiatric and/or medical condition requiring evaluation.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 2501
Sedative and hypnotic agents are associated with numerous abnormal thought and behavioral processes (e.g., decreased inhibition, agitation, bizarre behavior, hallucinations, depersonalization, depression, suicidal ideation); many are similar to manifestations of alcohol intoxication or effects associated with other CNS depressants. Studies demonstrate short-term amnesic effects with eszopiclone. As with other sedative and hypnotic agents, emergence of new psychiatric abnormalities during eszopiclone therapy requires evaluation.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 2501
Studies using relatively high eszopiclone dosages (e.g., 2-4 times the recommended hypnotic dosage) in individuals with a history of benzodiazepine abuse suggest that the abuse potential of eszopiclone is similar to that of benzodiazepines (e.g., diazepam); caution is advised in patients with a history of drug or alcohol dependence or abuse.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 2501
Physical dependence results in the manifestation of withdrawal symptoms (e.g., anxiety) upon rapid dose decrease or abrupt discontinuance of many sedative and hypnotic drugs, including eszopiclone. Clinical trials of eszopiclone did not reveal evidence of a serious withdrawal syndrome; however, anxiety, abnormal dreams, nausea, and upset stomach were reported at an incidence of 2% or less after placebo substitution within 48 hours following the last dose of the drug.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 2501
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for ESZOPICLONE (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Considering the man's weakened physical condition, 90 mg could represent a minimum lethal zopiclone dose. /Steroisomer/
PMID:9068198 Meatherall RC et al; J Forensic Sci 42 (2): 340-3 (1997)
Eszopiclone is indicated for the treatment of insomnia.
Treatment of insomnia
Eszopiclone rapidly induces sleep and decreases sleep latency. It also aids in the maintenance of sleep, preventing frequent awakenings. This drug has shown anticonvulsant and muscle relaxant properties in animals but is used in humans for its sedating effects. Eszopiclone is a central nervous system depressant with various effects. These include changes in alertness and motor coordination and the risk of next morning impairment, increasing with the amount of eszopiclone administered. Exercise caution and advise against driving a motor vehicle or activities that require full mental alertness the next morning. Complex sleep behaviors may result from eszopiclone use. Eszopiclone should be discontinued in these cases. Avoid the use of alcohol and other CNS depressants when eszopiclone is administered. Advise patients to skip the eszopiclone dose if alcohol has been consumed before bed or during the evening. Use the smallest dose of eszopiclone as possible, especially in elderly patients, who may experience exaggerated drug effects. Though the potential for dependence and abuse with eszopiclone is lower than for other hypnotic drugs, this drug has been abused and is known to cause dependence.
Hypnotics and Sedatives
Drugs used to induce drowsiness or sleep or to reduce psychological excitement or anxiety. (See all compounds classified as Hypnotics and Sedatives.)
N - Nervous system
N05 - Psycholeptics
N05C - Hypnotics and sedatives
N05CF - Benzodiazepine related drugs
N05CF04 - Eszopiclone
Absorption
Eszopiclone is rapidly absorbed and the peak concentration is reached within about 1 hour after oral administration. The mean AUC after a 3 mg dose of eszopiclone was 278 ng/mL h. The consumption of a high-fat has been shown to slow absorption. Steady-state concentrations of eszopiclone are reached within 24-48 hours.
Route of Elimination
Only about 10% of an eszopiclone dose is found excreted in the urine as the parent drug. As much as 75% of an orally administered dose of racemic zopiclone as is found to be excreted in the urine in the form of metabolites. Eszopiclone, the S-isomer of racemic zopiclone, would likely show the same excretion pattern.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution of eszopiclone is estimated at 89.9L
Clearance
The mean clearance of eszopiclone in young, healthy volunteers was 184 mL/min in one pharmacokinetic study.
Eszopiclone is rapidly absorbed following oral administration. Peak plasma concentrations are achieved within approximately 1 hour after oral administration. Eszopiclone is weakly bound to plasma protein (52-59%). The large free fraction suggests that eszopiclone disposition should not be affected by drug-drug interactions caused by protein binding. The blood-to-plasma ratio for eszopiclone is less than one, indicating no selective uptake by red blood cells.
Physicians Desk Reference 60th ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2006., p. 3139
Onset of action may be reduced if taken with or immediately after a high-fat or heavy meal.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 1411
Up to 75% of an oral dose of racemic zopiclone is excreted in the urine, primarily as metabolites. A similar excretion profile would be expected for eszopiclone, the S-isomer of racemic zopiclone. Less than 10% of the orally administered eszopiclone dose is excreted in the urine as parent drug.
Physicians Desk Reference 60th ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2006., p. 3139
It is not known whether eszopiclone is distributed into milk; however, racemic zopiclone is distributed into milk. Use in nursing women is not recommended.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 2501
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for ESZOPICLONE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Following oral administration, eszopiclone is extensively biotransformed and the major metabolites are S-desmethylzopiclone and zopiclone-N-oxide, which are largely inactive.. The enzymes involved in the metabolism of eszopiclone are CYP3A (the primary metabolizing enzyme), CYP2C8, and CYP2E1. The N-oxide derivative shows weak pharmacological activity in animals. The N-desmethyl metabolite is pharmacologically active.
Extensively metabolized by CYP3A4 and CYP2E1 via oxidation and demethylation. The two primary metabolites are (S)-zopiclone-N-oxide (inactive) and (S)-N-demethylzopiclone which binds to GABA receptors with lower potency then eszopiclone.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 1411
Eszopiclone has known human metabolites that include N-desmethyl-zopiclone and N-oxide-zopiclone.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
The half-life is 6.1 hours in healthy patients but is prolonged in various patients, including those with hepatic impairment, elderly patients, in addition to those taking CYP3A enzyme inhibiting drugs.
Eszopiclone has an intermediate duration of action (i.e., possesses a half-life of approximately 5-7 hours).
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 2501
The exact mechanism of action of eszopiclone is unknown at this time but is thought to occur via binding with the GABA receptor complexes at binding sites located near benzodiazepine receptors, possibly explaining its hypnotic and sedative effects. It has particular affinity for GABA-A (or GABAA) receptor subunits 1, 3 and 5. Eszopiclone increases GABA-A channel currents significantly. GABA-A channels are major inhibitory channels that cause CNS depression when their receptors are activated.
Eszopiclone, the S-enantiomer of zopiclone (not commercially available in the US), is a sedative and hypnotic agent that is structurally unrelated to benzadiazepines and other sedative and hypnotic agents that are commercially available in the US, including barbiturates, imidazopyridines (e.g., zolpidem), and pyrazolopyrimidines (e.g., zaleplon). Eszopiclone is pharmacologically similar to zaleplon and zolpidem; all of these agents have been shown to interact with the CNS gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor complex at binding domains located close to or allosterically coupled to benzodiazepine receptors.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 2501
The precise mechanism of action of eszopiclone as a hypnotic is unknown. Its pharmalogic effect is believed to result from its interaction with GABA-receptor complexes at binding domains located close to or allosterically coupled to benzodiazepine receptors.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 1411