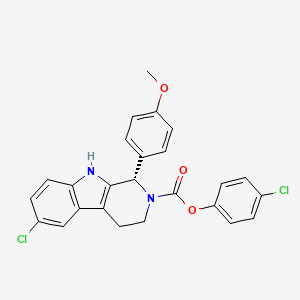

1. 6-chloro-1,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-, 4-chlorophenyl Ester, (1s)-2h-pyrido(3,4-b)indole-2-carboxylic Acid
2. Emvododstat
3. Ptc299
1. Emvododstat
2. Ptc299
3. Ptc-299
4. 1256565-36-2
5. Emvododstat [usan]
6. 053qd2i96a
7. Emvododstat [inn]
8. Emvododstat [who-dd]
9. Schembl8509210
10. Chembl4650336
11. Gtpl11421
12. 1219951-09-3
13. 2h-pyrido(3,4-b)indole-2-carboxylic Acid, 6-chloro-1,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-, 4-chlorophenyl Ester, (1s)-
14. Ex-a5798
15. At24059
16. Hy-124593
17. Cs-0087039
18. 4-chlorophenyl (1s)-6-chloro-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,3,4,9-tetrahydro-2h-pyrido(3,4-b)indole-2-carboxylate
19. 4-chlorophenyl (s)-6-chloro-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,3,4,9-tetrahydro-2h-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-2-carboxylate
| Molecular Weight | 467.3 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C25H20Cl2N2O3 |
| XLogP3 | 6.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 466.0850979 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 466.0850979 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 54.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 32 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 651 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Investigated for use/treatment in cancer/tumors (unspecified) and solid tumors.
PTC299 demonstrated a broad range of activity in blocking VEGF synthesis in multiple tumor types, including breast, cervical, colorectal, fibrosarcoma, gastric, lung, melanoma, neuroblastoma, ovarian, pancreatic, prostate and renal cell cancer lines. PTC299 as a monotherapy significantly reduced VEGF concentrations in tumors and plasma, reduced tumor blood vessel density, and substantially impeded tumor progression.
PTC299 was designed to inhibit VEGF production in tumors by targeting the post-transcriptional control processes that regulate VEGF formation. Because PTC299 inhibits VEGF production, its action occurs at a different point in the VEGF pathway than therapies, such as Avastin or Sutent. PTC299 may be active both as a single agent or when used in combination with other anti-angiogenic agents or with chemotherapy agents for the treatment of cancers.
