


1. Carbitol
2. Ethyl Carbitol
3. Ethylcarbitol
4. Transcutol
5. Transcutol Hp
6. Transcutol P
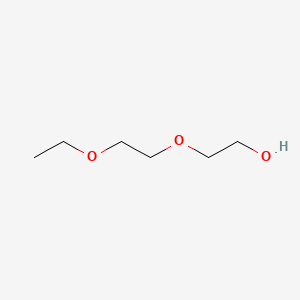
1. 2-(2-ethoxyethoxy)ethanol
2. 111-90-0
3. Carbitol
4. Transcutol
5. 2(2-ethoxyethoxy)ethanol
6. Ethoxy Diglycol
7. Ethyl Carbitol
8. Ethoxydiglycol
9. Dioxitol
10. Ethanol, 2-(2-ethoxyethoxy)-
11. Ethyl Digol
12. Carbitol Solvent
13. Transcutol P
14. Solvolsol
15. Losungsmittel Apv
16. Dowanol De
17. Carbitol Cellosolve
18. Poly-solv De
19. Diglycol Monoethyl Ether
20. Diethylene Glycol Ethyl Ether
21. Degmee
22. Ektasolve De
23. Ethyl Diethylene Glycol
24. 3,6-dioxa-1-octanol
25. Dowanol 17
26. Karbitol
27. Diethyleneglycol Monoethyl Ether
28. Ethylene Diglycol Monoethyl Ether
29. 2-(2-ethoxyethoxy) Ethanol
30. Monoethyl Ether Of Diethylene Glycol
31. 3,6-dioxa-1-oktanol
32. Ethanol, 2,2'-oxybis-, Monoethyl Ether
33. 2-(ethoxyethoxy)ethanol
34. A1a1i8x02b
35. Chebi:40572
36. Nsc-408451
37. Diethylene Glycol Monoethyl Ether [nf]
38. Dsstox_cid_1941
39. Aqualine™ Complete 1
40. Aqualine™ Complete 2
41. Aqualine™ Complete 5
42. Dsstox_rid_76417
43. Karbitol [czech]
44. Dsstox_gsid_21941
45. 149818-01-9
46. 2-(2-ethoxyethoxy)-ethanol
47. Diethylene Glycol Monoethyl Ether (nf)
48. Acetamide, N-5-(1,2-dihydroxyethyl)-4-hydroxy-3-pyrrolidinyl-, Monohydrochloride, 3s-3.alpha.,4.beta
49. Ae3
50. Cas-111-90-0
51. Hsdb 51
52. Aethyldiaethylenglycol
53. Aethyldiaethylenglycol [german]
54. 3,6-dioxa-1-oktanol [czech]
55. Einecs 203-919-7
56. Nsc 408451
57. Pm 1799
58. Brn 1736441
59. Unii-a1a1i8x02b
60. Diethoxol
61. Ai3-01740
62. O-ethyldigol
63. Eastman De
64. Ethyl Di-icinol
65. Glycol Ether De
66. Mfcd00002872
67. (ethoxyethoxy)ethanol
68. 3,6-dioxaoctan-1-ol
69. 2-(2ethoxyethoxy)ethanol
70. Ec 203-919-7
71. Diethyleneglycolmonoethylether
72. 1-hydroxy-3,6-dioxaoctane
73. Schembl16399
74. 2-(2-ethoxyethoxy);ethanol
75. Aqualine™ Complete 5k
76. Ethoxydiglycol [inci]
77. Diethyleneglycol Monoethylether
78. Wln: Q2o2o2
79. 2-(2-ethoxy-ethoxy)-ethanol
80. 2-(.beta.-ethoxyethoxy)ethanol
81. 3,6-dioxaoctane-1-ol
82. Chembl1230841
83. Diethylene Glycol-monoethyl Ether
84. Dtxsid2021941
85. Zinc1600621
86. Tox21_200413
87. Tox21_300080
88. Ethanol,2'-oxybis-, Monoethyl Ether
89. Nsc408451
90. Stl453580
91. Akos009031390
92. Ehanol, 2,2'-oxybis-, Monoethyl Ether
93. Ncgc00247898-01
94. Ncgc00247898-02
95. Ncgc00254003-01
96. Ncgc00257967-01
97. Di(ethylene Glycol) Ethyl Ether, >=99%
98. Diethylene Glycol Monoethyl Ether, >=99%
99. Cs-0015134
100. E0048
101. Ft-0624897
102. Ft-0693130
103. Diethylene Glycol Monoethyl Ether [ii]
104. Diethylene Glycol Monoethyl Ether [mi]
105. Glycol Ether De (low Gravity) Reagent Grade
106. D08904
107. D72502
108. Diethylene Glycol Monoethyl Ether [hsdb]
109. A802441
110. Diethylene Glycol Monoethyl Ether [usp-rs]
111. Diethylene Glycol Monoethyl Ether [who-dd]
112. Q416399
113. J-505606
114. Diethylene Glycol Monoethyl Ether [ep Monograph]
115. Diethylene Glycol Monoethyl Ether, Reagentplus(r), 99%
116. Diethylene Glycol Monoethyl Ether, Saj First Grade, >=98.0%
117. Diethylene Glycol Monoethyl Ether, Vetec(tm) Reagent Grade, 99%
118. Diethylene Glycol Monoethyl Ether, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
| Molecular Weight | 134.17 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C6H14O3 |
| XLogP3 | -0.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 134.094294304 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 134.094294304 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 38.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 9 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 47.6 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
It has been estimated that the single oral dose /of diethylene glycol/ lethal for humans is approximately 1 ml/kg. /Diethylene glycols/
Amdur, M.O., J. Doull, C.D. Klaasen (eds). Casarett and Doull's Toxicology. 4th ed. New York, NY: Pergamon Press, 1991., p. 704
To assist evaluation of the hazards of skin contact with selected undiluted glycol ethers, their absorption across isolated human abdominal epidermis was measured in vitro. Epidermal membranes were set up in glass diffusion cells and, following an initial determination of permeability to tritiated water, excess undiluted glycol ether was applied to the outer surface for 8 hr. The appearance of glycol ether in an aqueous receptor phase bathing the underside of the epidermis was quantified by a gas chromatographic technique. A final determination of tritiated water permeability was compared with initial values to establish any irreversible alterations in epidermal barrier function induced by contact with the glycol ethers. 2-methoxyethanol (EM) was most readily absorbed (mean steady rate 2.82 mg/sq cm/hr), and a relatively high absorption rate (1.17 mg/sq cm/hr) was also apparent for 1-methoxypropan-2-ol (PM). There was a trend of reducing absorption rate with increasing molecular weight or reducing volatility for monoethylene glycol ethers (EM, 2.82 mg/sq cm/hr; 2-ethoxyethanol, EE, 0.796 mg/sq cm/hr; 2-butoxyethanol, EB, 0.198 mg/sq cm/hr) and also within the diethylene glycol series: 2-(2-methoxyethoxy) ethanol (DM, 0.206 mg/sq cm/hr); 2-(2-ethoxyethoxy) ethanol (DE, 0.125 mg/sq cm/hr) and 2-(2-butoxyethoxy) ethanol (DB, 0.035 mg/sq cm/hr). The rate of absorption of 2-ethoxyethyl acetate (EEAc) was similar to that of the parent alcohol, EE. Absorption rates of diethylene glycol ethers were slower than their corresponding monoethylene glycol equivalents. Combination of intrinsic toxicity and ability to pass across skin contribute to assessment of hazards of contact with undiluted glycol ethers.
PMID:6499804 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1568269 Dugard PH et al; Environ Health Perspect 57: 193-7 (1984)
When a single /oral/ dose of diethylene glycol monoethyl ether (11.2 mmol) was given to an adult human volunteer (sex and age not specified) about 68% of the dose was excreted in the urine as (2-ethoxyethoxy)acetic acid within 12 hr.
FAO/WHO Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives; WHO Food Additives Series 30 Diethylene Glycol Monoethyl Ether. Available from, as of February 20, 2007: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
The quantitative urinary excretion of diethylene glycol monoethyl ether was investigated in the rabbit after oral, intravenous, subcutaneous and percutaneous administration. After oral dosing of two animals at a level of 5 mL/kg bw, both animals died during the first day and total excretion was only 0.8% and 0.33%. After intravenous administration to 15 rabbits at dose levels of 0.5-3.4 mL/kg most of the dose was excreted during the first day (for 13/15 rabbits), the percentage excreted tending to increase with dose. After a single parenteral dose of 1.0-3.0 mL/kg, urinary excretion was monitored for up to 4 consecutive days. Excretion was high in the first 24 hr and the total percentage of the dose excreted in urine increased with dose. After repeated daily parenteral doses of 0.16, 0.32 or 0.63 mL/kg bw, total urinary excretion increased with dose and equalled 4.7, 5.0 and 11.6%, respectively.
FAO/WHO Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives; WHO Food Additives Series 30 Diethylene Glycol Monoethyl Ether. Available from, as of February 20, 2007: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
The oral administration fo 1503 mg Diethylene glycol monoethyl ether to a normal man resulted in the excretion of 1140 mg of 2-ethoxyethoxyacetic acid, 69 % of the total dose, within 12 hr.
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. V7 197
...Carbitol is largely destroyed in body or conjugated with glucuronic acid and excreted as the glucuronate. ...This metabolic peculiarity may explain its lesser toxicity when compared with that of diethyl, methyl and butyl cellosolve.
Browning, E. Toxicity and Metabolism of Industrial Solvents. New York: American Elsevier, 1965., p. 630
