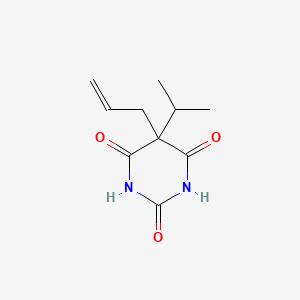

1. Allylpropymal
2. Allylpropymal, Monosodium Salt
3. Aprobarbitone
1. Allypropymal
2. Alurate
3. Allylpropymal
4. Aprobarbitone
5. Allonal
6. Allional
7. Aprobarbita
8. Aprozal
9. Numal
10. 77-02-1
11. Allylisopropylmalonylurea
12. 5-allyl-5-isopropylbarbituric Acid
13. Alurate Elixir Verdum
14. Allylisopropylbarbituric Acid
15. Isopropylallylbarbituric Acid
16. 5-isopropyl-5-allylbarbituric Acid
17. 5-allyl-5-isopropylbarbiturate
18. Barbituric Acid, 5-allyl-5-isopropyl-
19. Nsc 120769
20. Aprobarbital (inn)
21. 5-(1-methylethyl)-5-(2-propenyl)-2,4,6(1h,3h,5h)-pyrimidinetrione
22. Nsc120769
23. Q0ykg9l6rf
24. Nsc-120769
25. 2,4,6(1h,3h,5h)-pyrimidinetrione, 5-(1-methylethyl)-5-(2-propenyl)-
26. 5-allyl-5-isopropylpyrimidine-2,4,6(1h,3h,5h)-trione
27. Chebi:2791
28. Allypropymalum
29. Isonal (swedish)
30. Aprobarbitale
31. Aprobarbitalum
32. Aprobarbitale [dcit]
33. Aprobarbital [inn]
34. Aprobarbitalum [inn-latin]
35. 2,4,6(1h,3h,5h)-pyrimidinetrione, 5-(1-methylethyl)-5-(2-propenyl)- (9ci)
36. Alurate (tn)
37. Ccris 7088
38. Hsdb 3290
39. Einecs 200-997-4
40. Unii-q0ykg9l6rf
41. Brn 0180858
42. Aprobarbital [inn:dcf:nf]
43. 5-propan-2-yl-5-prop-2-enyl-1,3-diazinane-2,4,6-trione
44. Aprobarbital [mi]
45. Aprobarbital [hsdb]
46. Aprobarbital [vandf]
47. Chembl7863
48. Schembl78101
49. Aprobarbital [mart.]
50. Aprobarbital [who-dd]
51. Dtxsid8022616
52. Schembl15364625
53. Schembl22556213
54. 5-(prop-2-en-1-yl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1,3-diazinane-2,4,6-trione
55. Hy-u00166
56. 5-(1-methylethyl)-5-prop-2-en-1-ylpyrimidine-2,4,6(1h,3h,5h)-trione
57. 5-(propan-2-yl)-5-(prop-2-en-1-yl)pyrimidine-2,4,6(1h,3h,5h)-trione
58. Akos003404772
59. Aprobarbital (1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol)
60. Cs-7223
61. Db01352
62. Wln: T6vmvmv Fhj Fy1&1 F2u1
63. Ns00005163
64. C07826
65. D00698
66. Q411940
67. 5-allyl-5-isopropyl-2,4,6(1h,3h,5h)-pyrimidinetrione
68. 2,6(1h,3h,5h)-pyrimidinetrione, 5-(1-methylethyl)-5-(2-propenyl)-
| Molecular Weight | 210.23 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H14N2O3 |
| XLogP3 | 1.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 75.3 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 15 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 314 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
BARBITURATES MAY BE USED FOR PREANESTHETIC MEDICATION & TO PRODUCE BASAL ANESTHESIA. ... BARBITURATES ARE EMPLOYED AS DIAGNOSTIC & THERAPEUTIC AIDS IN PSYCHIATRY, IN NARCOANALYSIS & NARCOTHERAPY. /BARBITURATES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 119
ONE OF THE INTERMEDIATE-ACTING BARBITURATES ...
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 1003
Aprobartital has been used for the short-term treatment /2 weeks or less/ of insomnia; however, it generally has been replaced by benzodiazepines. ... Has also been used for routine sedation to relieve anxiety, tension, and apprehension; however, barbiturates generally have been replaced by benzodiazepines for daytime sedation. /Uses are included in the labeling approved by the US Food and Drug Administration/.
United States Pharmacopeial Convention; USP Dispensing Information 12th ed Vol IA p.574 (1992)
The primary Medication Classification of the Veterans Administrations is CN301: Barbituric Acid Derivatives, Sedatives/Hyponotics.
United States Pharmacopeial Covention; USP Dispensing Information 12th ed Vol IA p.573 (1992)
May be habit forming.
Budavari, S. (ed.). The Merck Index - Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals. Rahway, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 1989., p. 119
AS WITH ETHANOL ... SEDATIVE DOSES THAT EXERT NO EFFECTS OBVIOUS TO UNTRAINED OBSERVER OR PATIENTS CAN CAUSE IMPAIRMENT IN LEARNING, JUDGEMENT, SHORT-TERM MEMORY, DRIVING PERFORMANCE ... /BARBITURATES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 106
... IMPORTANT IN USE ... DURING LABOR IS ... POSSIBLE RESP DEPRESSANT EFFECT ON INFANT, SINCE PLACENTA OFFERS NO SIGNIFICANT BARRIER ... /BARBITURATES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 110
CAPACITY OF BARBITURATES TO INCR SYNTHESIS OF PORPHYRINS IS RESPONSIBLE FOR ONE ... BIZARRE & DANGEROUS SIDE EFFECT. IN PT SUFFERING FROM ACUTE INTERMITTENT PORPHYRIA, DRUGS MAY PPT SEVERE ATTACK, POSSIBLY ... PARALYSIS & DEATH. /BARBITURATES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 111
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for APROBARBITAL (15 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
N - Nervous system
N05 - Psycholeptics
N05C - Hypnotics and sedatives
N05CA - Barbiturates, plain
N05CA05 - Aprobarbital
RATE OF DECLINE OF BLOOD CONCN AFTER A LARGE DOSE FOR ... ALURATE ... IS 25-40% /PER 24 HR/ ... RATE OF DECLINE IS A FUNCTION OF ACCUMULATION IN LIVER, METAB OF DRUG & URINARY EXCRETION.
Thienes, C., and T.J. Haley. Clinical Toxicology. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lea and Febiger, 1972., p. 63
AS MUCH AS 50% OF HYPNOTIC DOSE OF ... APROBARBITAL MAY BE EXCRETED UNCHANGED BY KIDNEY. ... APROBARBITAL ... ELIMINATED SLOWLY, OVER A PERIOD OF SEVERAL DAYS.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 114
A FRACTION OF BARBITURATE IN BLOOD IS REVERSIBLY BOUND TO PLASMA PROTEIN, CHIEFLY ALBUMIN. ... THE CEREBROSPINAL FLUID IS VIRTUALLY PROTEIN FREE. ACCORDINGLY, THE MAXIMAL CONCN OF BARBITURATES ATTAINED IN CEREBROSPINAL FLUID IS LESS THAN THE PLASMA CONCN, BEING IN MOST CASES SLIGHTLY LESS THAN THE CONCN IN AN ULTRAFILTRATE OF PLASMA. THE CONCN IN OCULAR FLUID IS SIMILAR TO THAT OF CEREBROSPINAL FLUID. IN TISSUES, THE BARBITURATE CONCN IS GENERALLY AS HIGH AS OR SLIGHTLY HIGHER THAN IN PLASMA. /BARBITURATES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 113
... SODIUM SALTS ARE MORE RAPIDLY ABSORBED THAN FREE ACIDS ... FOOD IN STOMACH DECR RATE OF ABSORPTION BUT NOT AMT ABSORBED. THERE EXISTS NO IMPENETRABLE BARRIER TO ... BARBITURATES IN BODY ... IF SOJOURN OF DRUG IN PLASMA IS SUFFICIENTLY LONG, IT WILL BE DISTRIBUTED TO ALL TISSUES & FLUIDS. /BARBITURATES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 112
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for APROBARBITAL (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
PARTLY METABOLIZED IN LIVER BY OXIDN OF C-5 SUBSTITUENT(S) (ALLYL &/OR ISOPROPYL GROUPS) ... ALLYL GROUP ... MAY ALSO /BE REMOVED/. RESULTING /IN/ INACTIVE METABOLITES /HUMAN, ORAL/.
American Society of Hospital Pharmacists. Data supplied on contract from American Hospital Formulary Service and other current ASHP sources., p. 1975
Hepatic biotransformation, primarily by the hepatic microsomal enzyme system. /barbiturates/
United States Pharmacopeial Convention; USP Dispensing Information 12th ed Vol IA p.574 (1992)
Partially metabolized in the liver by oxidation of the C5 substituent(s) (allyl and/or isopropyl groups). Removal of the allyl group at C5 may also occur. The resulting inactive metbolites, which have not been identified are excreted in the urine.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 92. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1992 (Plus Supplements 1992)., p. 1322
With the exception of the less lipid-soluble aprobarbital and phenobarbital, nearly complete metabolism and/or conjugation of barbiturates in the liver precedes their renal excretion. The oxidation of radicals at C5 is the most important biotransformation responsible for termination of biological activity. Oxidation results in the formation of alcohols, ketones, phenols, or carboxylic acids, which may appear in the urine as such or as glucuronic acid conjugates. In some instances (eg, phenobarbital), N-glucosylation is an important metabolic pathway. Other biotransformations include N-hydroxylation, desulfuration of thiobarbiturates to oxybarbiturates, opening of the barbituric acid ring, and N-dealkylation of N-alkylbarbiturates to active metabolites (eg, mephobarbital to phenobarbital).
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 361
APROBARBITAL DOSE 0.75 G ORAL REACHED CONCN 2.3 MG% IN 3-9 HR; T/2 WAS 24-36 HR. /FROM TABLE/
Sunshine, I. (ed.). CRC Handbook of Analytical Toxicology. Cleveland: The Chemical Rubber Co., 1969., p. 336
Plasma half-life is about 14 fto 40 hours.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 92. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1992 (Plus Supplements 1992)., p. 1322
Aprobarbital (like all barbiturates) works by binding to the GABAA receptor at either the alpha or the beta sub unit. These are binding sites that are distinct from GABA itself and also distinct from the benzodiazepine binding site. Like benzodiazepines, barbiturates potentiate the effect of GABA at this receptor. This GABAA receptor binding decreases input resistance, depresses burst and tonic firing, especially in ventrobasal and intralaminar neurons, while at the same time increasing burst duration and mean conductance at individual chloride channels; this increases both the amplitude and decay time of inhibitory postsynaptic currents. In addition to this GABA-ergic effect, barbiturates also block the AMPA receptor, a subtype of glutamate receptor. Glutamate is the principal excitatory neurotransmitter in the mammalian CNS. Aprobarbital also appears to bind neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.
... REVERSIBLY DEPRESS ACTIVITY OF ALL EXCITABLE TISSUES. ... CNS IS ... SENSITIVE, SO ... IN SEDATIVE OR HYPNOTIC DOSES, VERY LITTLE EFFECT ON SKELETAL, CARDIAC, OR SMOOTH MUSCLE OCCURS. ... PROBABLE THAT EXCITABILITY IN EACH TISSUE IS DEPRESSED BY AN ACTION ON OR IN A MEMBRANE & THAT ... MECHANISMS ... ARE ... SIMILAR. /BARBITURATES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 104
AS DOSE ... INCR, HYPOXIC & CHEM DRIVES TO RESP ARE DIMINISHED ... HOWEVER, HYPOXIC DRIVE PERSISTS @ LEVELS OF INTOXICATION CAUSING ... INSENSITIVITY OF RESP CENTERS TO CO2. ... AS INTOXICATION /INCR/ ... THERE IS SHIFT IN CONTROL OF RESP FROM CO2-SENSITIVE AREAS OF MEDULLA TO MORE PRIMITIVE ... CAROTID & AORTIC ... /BARBITURATES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 109
WHATEVER ... THE EFFECTS OF BARBITURATES ELSEWHERE IN CNS, IT IS EFFECT ON RETICULAR SYSTEM ... RESPONSIBLE FOR INABILITY TO MAINTAIN WAKEFULNESS UNDER INFLUENCE OF A BARBITURATE. /BARBITURATES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 108
BARBITURATES DECR TURNOVER OF 5-HYDROXYTRYPTAMINE & CATECHOLAMINES IN BRAIN OF EXPTL ANIMALS, BUT WHETHER THIS IS CAUSE OR EFFECT OF ANESTHESIA IS CONJECTURAL. /BARBITURATES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 106
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for APROBARBITAL (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.