

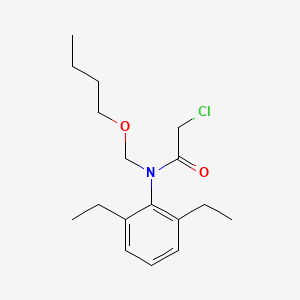

1. 2-chloro-2',6'-diethyl-n-(butoxymethyl)acetanilide
2. Machete
1. 23184-66-9
2. Machette
3. N-(butoxymethyl)-2-chloro-n-(2,6-diethylphenyl)acetamide
4. Bilchlor
5. Machete
6. Butaclor
7. Hiltachlor
8. Delchlor 5g
9. Rasayanchlor
10. Delchlor
11. Butanex
12. Machete (herbicide)
13. N-(butoxymethyl)-2-chloro-2',6'-diethylacetanilide
14. Acetamide, N-(butoxymethyl)-2-chloro-n-(2,6-diethylphenyl)-
15. 2-chloro-2',6'-diethyl-n-(butoxymethyl)acetanilide
16. Cp 53619
17. Nsc 221683
18. 2',6'-diethyl-n-butoxymethyl-2-chloroacetanilide
19. Sha 112301
20. Brn 2873811
21. 2',6'-diethyl-n-butoxymethyl-alpha-chloroacetanilide
22. N-butoxymethyl-alpha-chloro-2',6'-diethylacetanilide
23. Acetanilide, N-(butoxymethyl)-2-chloro-2',6'-diethyl-
24. 94nu90oo5k
25. Chebi:3230
26. Nsc-221683
27. Acetanilide, 2-chloro-2',6'-diethyl-n-(butoxymethyl)-
28. Amichlor
29. Pillarsete
30. Weedout
31. Mach-mach
32. Caswell No. 119b
33. Butachlor [ansi:bsi:iso]
34. Ccris 9107
35. Hsdb 6865
36. Einecs 245-477-8
37. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 112301
38. Unii-94nu90oo5k
39. Aimchlor
40. Butachlor [iso]
41. Butachlor [mi]
42. Butachlor [hsdb]
43. Acetanilide,6'-diethyl-
44. Dsstox_cid_14402
45. Dsstox_rid_79154
46. Dsstox_gsid_34402
47. Schembl65784
48. Butachlor, Analytical Standard
49. Chembl1399036
50. Dtxsid3034402
51. Hkphpirejkheco-uhfffaoysa-
52. Hy-b2042
53. Zinc1532059
54. Butachlor 100 Microg/ml In Hexane
55. Tox21_300940
56. Nsc221683
57. Butachlor 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
58. Akos015960716
59. Butachlor 10 Microg/ml In Cyclohexane
60. Butachlor 1000 Microg/ml In Methanol
61. Ncgc00163749-01
62. Ncgc00163749-02
63. Ncgc00163749-03
64. Ncgc00163749-04
65. Ncgc00254842-01
66. As-76784
67. Cas-23184-66-9
68. Db-046099
69. Cs-0014137
70. Ft-0630494
71. Butachlor, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
72. 184b669
73. A816615
74. N-butoxymethyl-2-chloro-2',6'-diethylacetanilide
75. Q411950
76. W-110560
77. N-n-butoxymethyl-n-(2,6-diethylphenyl)chloroacetamide
78. N-butoxymethyl-2-chloro-2',6'- Diethyltacetanilide
79. Acetamide, N-(butoxymethyl)-2-chloro-n-(2,6- Diethylphenyl)
| Molecular Weight | 311.8 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H26ClNO2 |
| XLogP3 | 4.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Exact Mass | 311.1652068 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 311.1652068 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 29.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 287 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Carcinogens
Substances that increase the risk of NEOPLASMS in humans or animals. Both genotoxic chemicals, which affect DNA directly, and nongenotoxic chemicals, which induce neoplasms by other mechanism, are included. (See all compounds classified as Carcinogens.)
Herbicides
Pesticides used to destroy unwanted vegetation, especially various types of weeds, grasses (POACEAE), and woody plants. Some plants develop HERBICIDE RESISTANCE. (See all compounds classified as Herbicides.)
In varying degrees, organochlorines are absorbed from the gut and also by the lung and across the skin. /Soild Organochlorines/
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency/Office of Prevention, Pesticides, and Toxic Substances. Reigart, J.R., Roberts, J.R. Recognition and Management of Pesticide Poisonings. 5th ed. 1999. EPA Document No. EPA 735-R-98-003, and available in electronic format at: https://www.epa.gov/pesticides/safety/healthcare, p. 55
The results of dermal penetration studies with rhesus monkeys indicate that butachlor is poorly absorbed through the skin. ... Employing a 6-hr topical exposure period, only 0.02 % of the dose was systemically absorbed during exposure to a granular formulation, and 5 % of the dose was absorbed when an EC (emulsifiable concentrate) formulation was applied.
Krieger, R. (ed.). Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology. Volume 2, 2nd ed. 2001. Academic Press, San Diego, California., p. 1550
Approximately 85 % of an orally administered dose is eliminated in 48 hr; 60 % of the excretedmaterial is found in the feces and 40 % in urine.
Krieger, R. (ed.). Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology. Volume 2, 2nd ed. 2001. Academic Press, San Diego, California., p. 1550
... Following a 24-hr exposure, an average butachlor quantity of approximately 5.00% of the applied dose (1.01 micrograms) was absorbed by the skin. The mean peak penetration rate was 0.7% of the applied dose per hour. The skin retained 1.40 to 8.10% of the applied butachlor.
PMID:8337702 Ademola JI et al; Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 121 (1): 78-86 (1993)
... Butachlor ... yielded 20-60 mol% formaldehyde on incubation with the mouse liver microsomal mixed function oxidase system under standard conditions.
Jacobsen NE et al; J Agric Food Chem 39 (7): 1342-50 (1991)
The metabolism of butachlor was studied in rat liver and kidney homogenates. In vitro incubation of butachlor with liver fractions (S9, microsome and cytosolic fractions) formed a considerable amount of butachlor glutathione conjugate, while the conjugating activity was not efficient for the kidney S9 fraction. There is a sex difference in the distribution of glutathione S-transferase in the liver. ... More enzyme activity was detected in the female liver microsome, while this is not the case in its cytosolic fraction. Further biotransformation of butachlor glutathione conjugate to mercapturate was not observed in the liver S9 fraction. This metabolite was further transformed to butachlor acetyl cysteine conjugate in the presence of acetyl CoA, but to butachlor cysteine conjugate in the absence of acetyl CoA.
PMID:1728663 Ou YH, Lin JK; J Toxicol Environ Health 35 (1): 19-28 (1992)
Butachlor metabolism in rats is complex due to extensive biliary excretion, intestinal microbial metabolism, and enterohepatic circulation of metabolites. Metabolism in rats follows three major pathways: initial conjugation with glutathione followed by mercapturic acid pathway metabolism; cytochrome P-450-mediated hydroxylation of the aromatic ring, its ethyl groups and the N- butoxymethylene group; and cleavage of the amide bonds via aryl amidase to form 2,6-diethyl aniline, which is further oxidized to 4-amino-3,5-diethylphenol.
Krieger, R. (ed.). Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology. Volume 2, 2nd ed. 2001. Academic Press, San Diego, California., p. 1550
... Butachlor is metabolized to CDEPA to a much greater extent by rat liver microsomes (0.045 nmol/min/mg) than by human liver microsomes (< 0.001 nmol/min/mg).
PMID:11133395 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1240196 Coleman S et al; Environ Health Perspect 108 (12): 1151-1157 (2000)
Butachlor has known human metabolites that include 2-Chloro-N-(2,6-diethylphenyl)acetamide.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
Biological half-lives after exposure to high and low concentrations were 11.6 and 23.1 days, respectively; [HSDB]
... The biological half-lives of the three herbicides on exposure at high and low concentrations were 11.6 and 23.1 days for butachlor,
Lin K-H et al; Pestic Sci 49 (2); 178-184 (1997)
