
1. (21r)-argatroban
2. (21r)-argatroban Anhydrous
3. (21s)-argatroban
4. (21s)-argatroban Anhydrous
5. (2r,4r)-1-((2s)-5-((aminoiminomethyl)amino)-1-oxo-2-((((3r)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-3-methyl-8-quinolinyl)sulfonyl)amino)pentyl)-4-methyl-2-piperidinecarboxylic Acid
6. (2r,4r)-1-((2s)-5-((aminoiminomethyl)amino)-1-oxo-2-((((3s)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-3-methyl-8-quinolinyl)sulfonyl)amino)pentyl)-4-methyl-2-piperidinecarboxylic Acid
7. (2r,4r)-1-(5-((aminoiminomethyl)amino)-1-oxo-2-(((1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-3-methyl-8-quinolinyl)sulfonyl)amino)pentyl)-4-methyl-2-piperidinecarboxylic Acid
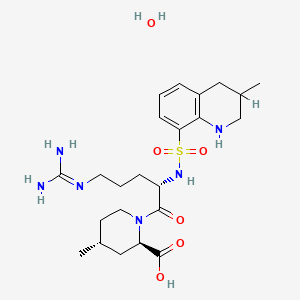
8. (2r,4r)-1-(5-((aminoiminomethyl)amino)-1-oxo-2-(((1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-3-methyl-8-quinolinyl)sulfonyl)amino)pentyl)-4-methyl-2-piperidinecarboxylic Acid Monohydrate
9. Acova
10. Argatroban
11. Argatroban Anhydrous
12. Argatroban Hydrate
13. Mci 9038
14. Mci-9038
15. Md 805
16. Md-805
17. Md805
18. Mmtqap
19. Mpqa
20. Novastan
1. Argatroban
2. 141396-28-3
3. Argatroban Hydrate
4. Argatroban (monohydrate)
5. Argipidine
6. Gn1600
7. Novastan
8. Acova
9. Dk-7419
10. Iy90u61z3s
11. Argatroban Injection
12. (2r,4r)-1-[(2s)-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)-2-[(3-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolin-8-yl)sulfonylamino]pentanoyl]-4-methylpiperidine-2-carboxylic Acid;hydrate
13. 2-piperidinecarboxylic Acid, 1-(5-((aminoiminomethyl)amino)-1-oxo-2-(((1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-3-methyl-8-quinolinyl)sulfonyl)amino)pentyl)-4-methyl-, Monohydrate
14. Argatroban [usan]
15. 74863-84-6
16. Argatroban In Sodium Chloride
17. (2r,4r)-4-methyl-1-(((3-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolin-8-yl)sulfonyl)-l-arginyl)piperidine-2-carboxylic Acid Hydrate
18. Unii-iy90u61z3s
19. Argatra
20. Exembol
21. Slonnon
22. Argatroban [usan:inn:ban:jan]
23. Novastan (tn)
24. Argatroban (usp)
25. Argatroban [vandf]
26. Argatroban [usp-rs]
27. Argatroban Hydrate (jp17)
28. Schembl3447908
29. Argatroban [orange Book]
30. Argatroban Hydrate [jan]
31. Hy-b0375a
32. Mdi-805
33. Argatroban [usp Monograph]
34. Argatroban Monohydrate [mi]
35. Bcp09304
36. Mfcd00895735
37. Om-805
38. S5074
39. Akos026673901
40. Argatroban Monohydrate [who-dd]
41. Ccg-269893
42. Cs-4257
43. (2r,4r)-4-methyl-1-(n(sup 2)-((1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-3-methyl-8-quinolyl)sulfonyl)-l-arginyl)pipecolic Acid, Monohydrate
44. 2-piperidinecarboxylic Acid, 1-(5-((aminoiminomethyl)amino)-1-oxo-2-(((1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-3-methyl-8-quinolinyl)sulfonyl)amino)pentyl)methyl-, Monohydrate, (2r-((2s*),2-alpha,4-beta))-
45. D00181
46. 748a846
47. Q-101034
48. (2r,4r)-1-((2s)-5-guanidino-2-(3-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline-8-sulfonamido)pentanoyl)-4-methylpiperidine-2-carboxylic Acid Hydrate
49. (2r,4r)-1-[(2s)-5-carbamimidamido-2-[(3-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolin-8-yl)sulfonylamino]pentanoyl]-4-methylpiperidine-2-carboxylic Acid;hydrate
50. (2r,4r)-1-[n2-3-(methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-8-quinolinesulfonyl)-l-arginyl]-4-methyl-2-piperidinecarboxylic Acid Monohydrate
51. (2r,4r)-4-methyl-1-(n (sup 2)-((1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-3-methyl-8-quinolyl)sulfonyl)-l-arginyl)pipecolic Acid, Monohydrate
52. 2-piperidinecarboxylic Acid, 1-[(2s)-5-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]-1-oxo-2-[[(1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-3-methyl-8-quinolinyl)sulfonyl]amino]pentyl]-4-methyl-, Hydrate (1:1), (2r,4r)-
| Molecular Weight | 526.7 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C23H38N6O6S |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Exact Mass | 526.25735413 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 526.25735413 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 190 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 36 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 887 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Antithrombins; Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Argatroban. Online file (MeSH, 2018). Available from, as of November 8, 2018: https://meshb.nlm.nih.gov/search
/CLINICAL TRIALS/ ClinicalTrials.gov is a registry and results database of publicly and privately supported clinical studies of human participants conducted around the world. The Web site is maintained by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Each ClinicalTrials.gov record presents summary information about a study protocol and includes the following: Disease or condition; Intervention (for example, the medical product, behavior, or procedure being studied); Title, description, and design of the study; Requirements for participation (eligibility criteria); Locations where the study is being conducted; Contact information for the study locations; and Links to relevant information on other health Web sites, such as NLM's MedlinePlus for patient health information and PubMed for citations and abstracts for scholarly articles in the field of medicine. Argatroban is included in the database.
NIH/NLM; ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available from, as of November 8, 2018: https://clinicaltrials.gov/
Argatroban injection is indicated as an anticoagulant in adult patients with or at risk for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Argatroban Injection (Updated: June 28, 2018). Available from, as of November 14, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=35db0a86-76af-4f5e-a5c6-0a664f53f6da
Argatroban injection is indicated for prophylaxis or treatment of thrombosis in adult patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT). /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Argatroban Injection (Updated: June 28, 2018). Available from, as of November 14, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=35db0a86-76af-4f5e-a5c6-0a664f53f6da
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Argatroban (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Other nonhemorrhagic adverse effects occurring in at least 2% of argatroban-treated patients with HIT/HITTS undergoing PCI include chest pain, back pain, headache, bradycardia, and myocardial infarction.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists; Drug Information 2018. Bethesda, MD. 2018, p. 1604
Adverse hemorrhagic effects reported in 2% or more of nonsurgical patients with HIT/HITSS receiving argatroban include major or minor GI bleeding, minor genitourinary bleeding or hematuria, minor decrease in hemoglobin/hematocrit, minor groin or brachial bleeding (e.g., catheter insertion site), and hemoptysis;9 nonhemorrhagic effects include dyspnea, hypotension, fever, diarrhea, sepsis, cardiac arrest, nausea, ventricular tachycardia, pain, urinary tract infection, vomiting, infection, pneumonia, atrial fibrillation, coughing, abnormal renal function, abdominal pain, and cerebrovascular disorder.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists; Drug Information 2018. Bethesda, MD. 2018, p. 1604
Safety and efficacy of argatroban not fully established in pediatric patients; however, the drug has been evaluated in a limited number of seriously ill pediatric patients younger than 16 years of age with HIT or HITTS. In a small, multicenter open-label study, 18 seriously ill pediatric patients with a clinical condition requiring alternative nonheparin anticoagulation received argatroban at an initial dosage of 1 ug/kg per minute titrated to maintain a target aPTT of 1.5-3 times the baseline value. During the 30-day study period, thrombotic events occurred in 5 patients and major bleeding (intracranial hemorrhage) was reported in 2 patients. All of the patients had serious comorbid conditions and were receiving multiple concomitant medications; most were diagnosed with documented or suspected HIT. Pharmacokinetic analysis of the data indicated that argatroban clearance was reduced by 50% in seriously ill pediatric patients compared with healthy adults and by approximately 80% in pediatric patients with elevated bilirubin concentrations compared to pediatric patients with normal bilirubin concentrations. Based on these results, reduced dosages of argatroban are recommended in pediatric patients.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists; Drug Information 2018. Bethesda, MD. 2018, p. 1604
There are no data on the presence of argatroban in human milk, or its effects on milk production. Argatroban is present in rat milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for Argatroban and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from Argatroban or from the underlying maternal condition.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Argatroban Injection (Updated: June 28, 2018). Available from, as of November 14, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=35db0a86-76af-4f5e-a5c6-0a664f53f6da
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Argatroban (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors
Drugs or agents which antagonize or impair any mechanism leading to blood platelet aggregation, whether during the phases of activation and shape change or following the dense-granule release reaction and stimulation of the prostaglandin-thromboxane system. (See all compounds classified as Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors.)
Antithrombins
Endogenous factors and drugs that directly inhibit the action of THROMBIN, usually by blocking its enzymatic activity. They are distinguished from INDIRECT THROMBIN INHIBITORS, such as HEPARIN, which act by enhancing the inhibitory effects of antithrombins. (See all compounds classified as Antithrombins.)
B - Blood and blood forming organs
B01 - Antithrombotic agents
B01A - Antithrombotic agents
B01AE - Direct thrombin inhibitors
B01AE03 - Argatroban
Argatroban is excreted primarily in the feces, presumably through biliary secretion. In a study in which (14)C-argatroban (5 ug/kg/min) was infused for 4 hours into healthy subjects, approximately 65% of the radioactivity was recovered in the feces within 6 days of the start of infusion with little or no radioactivity subsequently detected. Approximately 22% of the radioactivity appeared in the urine within 12 hours of the start of infusion. Little or no additional urinary radioactivity was subsequently detected. Average percent recovery of unchanged drug, relative to total dose, was 16% in urine and at least 14% in feces.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Argatroban Injection (Updated: June 28, 2018). Available from, as of November 14, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=35db0a86-76af-4f5e-a5c6-0a664f53f6da
It is not known if argatroban crosses the human placenta. the molecular weight (about 527 for the hydrated from), low metabolism, and moderate serum protein binding suggest that exposure of the embryo-fetus should be expected, especially sine the drug is given as a continuous infusion.
Briggs, G.G., Freeman, R.K., Yaffee, S.J.; Drugs in Pregancy and Lactation Tenth Edition. Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA. 2015, p. 83
Argatroban distributes mainly in the extra cellular fluid as evidenced by an apparent steady-state volume of distribution of 174 mL/kg (12.18 L in a 70 kg adult). Argatroban is 54% bound to human serum proteins, with binding to albumin and a1 - acid glycoprotein being 20% and 34%, respectively.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Argatroban Injection (Updated: June 28, 2018). Available from, as of November 14, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=35db0a86-76af-4f5e-a5c6-0a664f53f6da
/MILK/ Argatroban is detected in rat milk.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Argatroban Injection (Updated: June 28, 2018). Available from, as of November 14, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=35db0a86-76af-4f5e-a5c6-0a664f53f6da
The main route of argatroban metabolism is hydroxylation and aromatization of the 3-methyltetrahydroquinoline ring in the liver. The formation of each of the 4 known metabolites is catalyzed in vitro by the human liver microsomal cytochrome P450 enzymes CYP3A4/5. The primary metabolite (M1) exerts 3- to 5-fold weaker anticoagulant effects than argatroban. Unchanged argatroban is the major component in plasma. The plasma concentrations of M1 range between 0% and 20% of that of the parent drug. The other metabolites (M2 to M4) are found only in very low quantities in the urine and have not been detected in plasma or feces. These data, together with the lack of effect of erythromycin (a potent CYP3A4/5 inhibitor) on argatroban pharmacokinetics, suggest that CYP3A4/5-mediated metabolism is not an important elimination pathway in vivo.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Argatroban Injection (Updated: June 28, 2018). Available from, as of November 14, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=35db0a86-76af-4f5e-a5c6-0a664f53f6da
Argatroban is metabolized principally by the liver via hydroxylation and aromatization of the 3-methyltetrahydroquinoline ring.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists; Drug Information 2018. Bethesda, MD. 2018, p. 1604
The terminal elimination half life is 39-51 minutes.
Briggs, G.G., Freeman, R.K., Yaffee, S.J.; Drugs in Pregancy and Lactation Tenth Edition. Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA. 2015, p. 82