



API Suppliers

US DMFs Filed

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
EU WC
0
Listed Suppliers
0
0
0

USA (Orange Book)

Europe
0

Canada
0

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
0
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
0
USFDA Orange Book Patents
0
USFDA Exclusivities
0
Blog #PharmaFlow
0
News
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Other Listed Suppliers
0
0
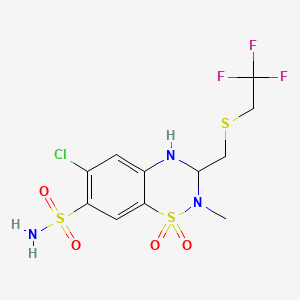

1. Renese
1. Renese
2. 346-18-9
3. Drenusil
4. Nephril
5. P-2525
6. P 2525
7. Nsc 108161
8. Polythiazide (200 Mg)
9. Polythiazide, (+)-
10. Nephril, (+)-
11. Swy93bd8rl
12. 2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-2-methyl-3-(((2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thio)methyl)-, 1,1-dioxide
13. 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-2-methyl-3-(((2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thio)methyl)-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
14. Nsc-108161
15. Chebi:8327
16. 2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-2-methyl-3-[[(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thio]methyl]-, 1,1-dioxide
17. 36780apv5n
18. Ncgc00182076-02
19. Politiazida
20. Polythiazidum
21. Dsstox_cid_5939
22. Dsstox_rid_77972
23. Dsstox_gsid_25939
24. Politiazida [inn-spanish]
25. Polythiazidum [inn-latin]
26. Drenusil; Nsc 108161; Nephril; P 2525; Renese
27. 2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-2-methyl-3-(((2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thio)methyl)-, 1,1-dioxide, (+)-
28. 6-chloro-2-methyl-3-(((2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thio)methyl)-3,4-dihydro-2h-benzo[e][1,2,4]thiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
29. 96783-10-7
30. Cas-346-18-9
31. Renese (tn)
32. Ccris 6094
33. Hsdb 850
34. Einecs 206-468-4
35. Brn 0770371
36. Unii-36780apv5n
37. Polythiazide (jan/usan/inn)
38. 2-methyl-3-(beta,beta,beta-trifluoroethylthiomethyl)-6-chloro-7-sulfamyl-3,4-dihydro-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide
39. 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-2-methyl-7-sulphamoyl-3-(2,2,2-trifluoroethylthiomethyl)-2h-benzo-1,2,4-thiadiazine 1,1-dioxide
40. Polythiazide [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
41. Unii-swy93bd8rl
42. Polythiazide [mi]
43. Polythiazide [inn]
44. Polythiazide [jan]
45. Polythiazide [hsdb]
46. Polythiazide [usan]
47. Chembl1587
48. Polythiazide [vandf]
49. Schembl27909
50. Polythiazide [mart.]
51. Polythiazide(200mg)
52. Polythiazide [who-dd]
53. Gtpl7274
54. Dtxsid6025939
55. Polythiazide [orange Book]
56. Tox21_113137
57. Nsc108161
58. Minizide Component Polythiazide
59. Akos037653999
60. Renese-r Component Polythiazide
61. Tox21_113137_1
62. Db01324
63. Ks-1466
64. Ncgc00182076-03
65. Polythiazide Component Of Minizide
66. 6-chloro-2-methyl-3-{[(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thio]methyl}-3,4-dihydro-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
67. Hy-16403
68. Polythiazide Component Of Renese-r
69. Cs-0006323
70. Ft-0673974
71. C07766
72. D00657
73. Sr-01000883970
74. Q7227099
75. Sr-01000883970-1
76. Wln: T66 Bswn Em Dhj C1 D1s1xfff Hg Iszw
77. 2h-1,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-2-methyl-3-[[(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thio]methyl]-, 1,1-dioxide
78. 6-chloro-2-methyl-1,1-dioxo-3-(2,2,2-trifluoroethylsulfanylmethyl)-3,4-dihydro-1?^{6},2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
79. 6-chloro-2-methyl-1,1-dioxo-3-(2,2,2-trifluoroethylsulfanylmethyl)-3,4-dihydro-1lambda6,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
80. 6-chloro-2-methyl-1,1-dioxo-3-(2,2,2-trifluoroethylsulfanylmethyl)-3,4-dihydrobenzo[e][1,2,4]thiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
81. 6-chloro-2-methyl-1,1-dioxo-3-{[(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)sulfanyl]methyl}-3,4-dihydro-2h-1$l^{6},2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
82. 6-chloro-2-methyl-3-([(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)sulfanyl]methyl)-3,4-dihydro-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide #
83. 6-chloro-2-methyl-3-[[(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)sulfanyl]methyl]-3,4-dihydro-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
84. 6-chloro-3,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thio]methyl]-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
| Molecular Weight | 439.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C11H13ClF3N3O4S3 |
| XLogP3 | 2.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 11 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 438.9708816 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 438.9708816 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 152 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 25 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 692 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Antihypertensive Agents; Diuretics, Thiazide
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
THIAZIDES ARE DIURETICS OF CHOICE IN MGMNT OF EDEMA DUE TO MILD-TO-MODERATE CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE. EDEMA DUE TO CHRONIC HEPATIC OR RENAL DISEASE MAY ALSO RESPOND FAVORABLY. ...HYPERTENSIVE DISEASE... /BENZOTHIADIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 902
ALTHOUGH THIAZIDE DIURETICS...REPORTED TO PRODUCE ELEVATION OF PLASMA RENIN ACTIVITY, CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF THIS HAS NOT BEEN ESTABLISHED. ...HAVE BEEN EFFECTIVE DIURETICS IN SOME PT WITH NEPHROSIS, BUT THEIR OVERALL THERAPEUTIC USEFULNESS...UNPREDICTABLE. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 832
MOST OF THIAZIDES ARE GIVEN IN DIVIDED DAILY DOSES FOR TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION & FOR DIURESIS. ...POLYTHIAZIDE COULD BE GIVEN LESS FREQUENTLY, SINCE...DURATION OF ACTION /IS/ LONGER THAN 24 HR.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 902
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for POLYTHIAZIDE (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
CLINICAL TOXICITY IS RELATIVELY RARE & USUALLY RESULTS FROM UNEXPECTED HYPERSENSITIVITY. /BENZOTHIADIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 902
...NUMBER OF HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS HAVE BEEN REPORTED /ONE OF SUCH IS/ PANCREATITIS...
Gosselin, R.E., H.C. Hodge, R.P. Smith, and M.N. Gleason. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 4th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1976., p. II-239
...IF PATIENTS DEVELOPS HYPOKALEMIA WHILE TAKING THIAZIDE FOR HYPERTENSION, CLINICIAN SHOULD CONSIDER DECR DOSAGE...RATHER THAN ADDING POTASSIUM SUPPLEMENT. SPECIAL CARE IS NECESSARY TO ENSURE ADEQUATE DIETARY INTAKE OF POTASSIUM BY PATIENTS RECEIVING THIAZIDE & DIGITALIS CONCURRENTLY. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 804
IN PATIENTS, PARTICULARLY THOSE WITH HYPOTENSIVE DISEASE & DECR RENAL RESERVE, MANIFESTATIONS OF RENAL INSUFFICIENCY MAY BE AGGRAVATED AFTER INTENSIVE OR PROLONGED COURSES OF THIAZIDES THAT LEAD TO EXCESSIVE DEPLETION OF FLUID & ELECTROLYTE. /BENZOTHIADIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 902
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for POLYTHIAZIDE (15 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
3. 3= MODERATELY TOXIC: PROBABLE ORAL LETHAL DOSE (HUMAN) 0.5-5 G/KG; BETWEEN 1 OZ & 1 PINT (OR 1 LB). /BENZOTHIADIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gosselin, R.E., H.C. Hodge, R.P. Smith, and M.N. Gleason. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 4th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1976., p. II-239
Polythiazide is a thiazide diuretic used to decrease edema and decrease blood pressure.
As a thiazide diuretic, Polythiazide inhibits the sodium-chloride symporter which decreases solute reabsorption leading to a retention of water in the urine, as water normally follows solutes. More frequent urination is due to the increased loss of water that has not been retained from the body as a result of a concomitant relationship with sodium loss from the convoluted tubule. The short-term anti-hypertensive action is based on the fact that thiazides decrease preload, decreasing blood pressure
Diuretics
Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. (See all compounds classified as Diuretics.)
Sodium Chloride Symporter Inhibitors
Agents that inhibit SODIUM CHLORIDE SYMPORTERS. They act as DIURETICS. Excess use is associated with HYPOKALEMIA. (See all compounds classified as Sodium Chloride Symporter Inhibitors.)
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
C - Cardiovascular system
C03 - Diuretics
C03A - Low-ceiling diuretics, thiazides
C03AA - Thiazides, plain
C03AA05 - Polythiazide
THIAZIDES ARE RAPIDLY ABSORBED FROM GI TRACT... IN GENERAL, THIAZIDES WITH RELATIVELY LONG DURATIONS OF ACTION SHOW...HIGH DEGREES OF BOTH BINDING TO PLASMA PROTEINS & ARE REABSORBED TO GREATER EXTENT BY RENAL TUBULES. ... POLYTHIAZIDE.../HAS/ LONGER DURATION OF ACTION THAT IS CORRELATED WITH SLOWER EXCRETION.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 902
IN DOGS...ABOUT 30% OF DRUG IS METABOLIZED & ITS METABOLITES ARE EXCRETED PRIMARILY IN URINE. ABOUT 60 TO 90% OF DRUG & METABOLITE ARE EXCRETED WITHIN 24 HR IN DOG; PRIMARILY IN URINE, BUT UP TO 20% MAY BE EXCRETED IN FECES.
American Hospital Formulary Service. Volumes I and II. Washington, DC: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, to 1984., p. 40:28
THIAZIDES CROSS PLACENTA & APPEAR IN CORD BLOOD. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
American Hospital Formulary Service. Volumes I and II. Washington, DC: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, to 1984., p. 40:28
THIAZIDES...APPEAR IN MILK OF NURSING MOTHER. /THIAZIDES/
American Hospital Formulary Service. Volumes I and II. Washington, DC: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, to 1984., p. 40:28
STUDY OF NORMAL HUMAN SUBJECTS RECEIVING SINGLE 1 MG ORAL DOSES REVEALED MEAN PLASMA T/2 FOR ABSORPTION & ELIMINATION OF 1.2 & 25.7 HR, RESPECTIVELY. APPROX 25% OF DRUG WAS EXCRETED UNCHANGED IN THE URINE.
HOBBS DC; CLIN PHARMACOL THER 23(2) 241 (1978)
YIELDS 5-CHLORO-2-METHYLSULFAMYL-4-SULFAMYLANILINE IN DOG. /FROM TABLE/
Goodwin, B.L. Handbook of Intermediary Metabolism of Aromatic Compounds. New York: Wiley, 1976., p. 36
Half-life is approx 25 hr. /From table/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996., p. 703
As a diuretic, polythiazide inhibits active chloride reabsorption at the early distal tubule via the thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter (TSC), resulting in an increase in the excretion of sodium, chloride, and water. Thiazides like polythiazide also inhibit sodium ion transport across the renal tubular epithelium through binding to the thiazide sensitive sodium-chloride transporter. This results in an increase in potassium excretion via the sodium-potassium exchange mechanism. The antihypertensive mechanism of polythiazide may be mediated through its action on carbonic anhydrases in the smooth muscle or through its action on the large-conductance calcium-activated potassium (KCa) channel, also found in the smooth muscle.
DOMINANT ACTION OF THIAZIDES IS TO INCR RENAL EXCRETION OF SODIUM & CHLORIDE & ACCOMPANYING VOL OF WATER. THIS EFFECT IS VIRTUALLY INDEPENDENT OF ACID-BASE BALANCE. /BENZOTHIADIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 899
RENAL ACTIONS OF THIAZIDE DIURETICS DECR EXTRACELLULAR FLUIDS & PLASMA VOL, CARDIAC OUTPUT, & TOTAL EXCHANGEABLE SODIUM IN INDIVIDUALS WITHOUT ANY EVIDENCE OF CARDIAC FAILURE. AT THIS STAGE, SODIUM & WATER DEPLETION APPEARS TO PROVIDE ADEQUATE BASIS FOR ANTIHYPERTENSIVE EFFECT... /BENZOTHIADIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 901
GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE MAY BE REDUCED BY THIAZIDES... THIS IS PRESUMABLY RESULT OF DIRECT ACTION ON RENAL VASCULATURE. ...THIAZIDES DECR RENAL EXCRETION OF CALCIUM RELATIVE TO THAT OF SODIUM, SINCE ITS REABSORPTION IS UNAFFECTED IN DISTAL NEPHRON WHEREAS THAT OF SODIUM IS BLOCKED. /BENZOTHIADIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 901
BECAUSE HEMODYNAMIC MEASUREMENTS INDICATE THAT PERIPHERAL VASCULAR RESISTANCE IS DECR BY THIAZIDES, DIRECT ACTION OF THESE DRUGS ON ARTERIOLAR SMOOTH MUSCLE HAS BEEN SUGGESTED. /BENZOTHIADIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 804
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for POLYTHIAZIDE (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.


