



API Suppliers

US DMFs Filed

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
Other Suppliers
0

USA (Orange Book)

Europe

Canada

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
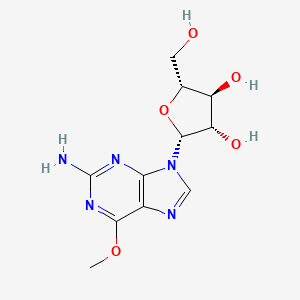

1. 2-amino-6-methoxypurine Arabinoside
2. 2-amino-9-beta-d-arabinofuranosyl-6-methoxy-9h-purine
3. 506u78
4. Arranon
5. Compound 506u78
6. Gw506u78
1. Nelzarabine
2. 121032-29-9
3. Arranon
4. Atriance
5. 506u78
6. Gw-506u78
7. 506u
8. Gw 506u78
9. Attriance
10. Nsc-686673
11. 2-amino-9-beta-d-arabinofuranosyl-6-methoxy-9h-purine
12. (2r,3s,4s,5r)-2-(2-amino-6-methoxy-9h-purin-9-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-3,4-diol
13. Nelarabine (arranon)
14. Chebi:63612
15. Nsc-755985
16. (2r,3s,4s,5r)-2-(2-amino-6-methoxy-9h-purin-9-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolane-3,4-diol
17. May
18. 2-amino-6-methoxypurine Arabinoside
19. Nsc-759876
20. Ncgc00181098-01
21. 60158cv180
22. S1213
23. Dsstox_cid_26842
24. Dsstox_rid_81952
25. Dsstox_gsid_46842
26. Nelarabine [usan]
27. Arranong
28. Gw506u78
29. Smr002544682
30. Arranon (tn)
31. Nelzarabine (usan)
32. Cas-121032-29-9
33. Compound 506u78
34. 9-beta-d-arabinofuranosyl-6-methoxy-9h-purin-2-amine
35. Nelarabine [usan:inn:ban]
36. Gw-506u
37. Unii-60158cv180
38. Nelarabine [inn]
39. 9beta-d-arabinofuranosyl-6-methoxy-9h-purin-2-amine
40. Nsc 686673
41. Nelarabine [mi]
42. Nelarabine [jan]
43. Nelarabine [vandf]
44. Nelarabine [mart.]
45. Nelarabine [who-dd]
46. Schembl18820
47. Mls003915614
48. Mls004774135
49. Mls006010906
50. Nelarabine (jan/usan/inn)
51. Nelarabine [ema Epar]
52. Gtpl7090
53. Chembl1201112
54. Dtxsid6046842
55. Nelarabine [orange Book]
56. Bcpp000392
57. Hms3715i16
58. Zinc3823492
59. Tox21_112714
60. Bdbm50247985
61. Mfcd00871078
62. Nsc755985
63. 2-(2-amino-6-methoxy-purin-9-yl)-5-hydroxymethyl-tetrahydro-furan-3,4-diol
64. Akos015852325
65. Akos015920191
66. Tox21_112714_1
67. Bcp9000318
68. Ccg-267441
69. Cs-1607
70. Db01280
71. Ncgc00274059-01
72. Ncgc00274059-02
73. As-47664
74. Hy-13701
75. N1144
76. Sw218086-2
77. D05134
78. F15095
79. Ab01274773-01
80. Ab01274773_02
81. 032n299
82. A804639
83. A935144
84. Sr-01000931847
85. 9-?-d-arabinofuranosyl-6-methoxy-9h-purin-2-amine
86. Q1216264
87. Sr-01000931847-3
88. 2-amino-6-methoxy-9-b-d-arabinofuranosyl-9 H-purine
89. 2-amino-6-methoxy-9-b-d-arabinofuranosyl-9h-purine
90. 9h-purin-2-amine, 9-b-d-arabinofuranosyl-6-methoxy-
91. Brd-k84466663-001-01-3
92. 2-amino-6-methoxy-9-beta-d-arabinofuranosyl-9h-purine
93. 9-(beta-d-arabinofuranosyl)-6-methoxy-9h-purin-2-amine
94. 9-beta -d-arabinofuranosyl-2-amino-6-methoxy-9h-purine
95. 9-beta-d-arabinofuranosyl-2-amino-6-methoxy-9 H-purine
96. 9h-purin-2-amine, 9beta-d-arabinofuranosyl-6-methyl-
97. 2-amino-6-methoxy-9-(beta-d-arabinofuranosyl)-9h-purine
98. 2-amino-9-.beta.-d-arabinofuranosyl-6-methoxy-9h-purine
99. 9-.beta.-d-arabinofuranosyl-6-methoxy-9h-purin-2-amine
100. 9h-purin-2-amine, 9-.beta.-d-arabinofuranosyl-6-methoxy-
101. (2r,3s,4s,5r)-2-(2-amino-6-methoxy-9-purinyl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolane-3,4-diol
102. (2r,3s,4s,5r)-2-(2-amino-6-methoxy-purin-9-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-3,4-diol
103. (2r,3s,4s,5r)-2-(2-azanyl-6-methoxy-purin-9-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolane-3,4-diol
104. (2r,3s,4s,5r)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-5-(2-imino-6-methoxy-3,9-dihydro-2h-purin-9-yl)oxolane-3,4-diol
| Molecular Weight | 297.27 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C11H15N5O5 |
| XLogP3 | -0.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 297.10731860 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 297.10731860 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 149 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 377 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Arranon |
| PubMed Health | Nelarabine (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent |
| Drug Label | ARRANON (nelarabine) is a pro-drug of the cytotoxic deoxyguanosine analogue, 9--D-arabinofuranosylguanine (ara-G). The chemical name for nelarabine is 2-amino-9--D-arabinofuranosyl-6-methoxy-9H-purine. It has the molecular formula C11H15N5O5 and... |
| Active Ingredient | Nelarabine |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Iv (infusion) |
| Strength | 250mg/50ml (5mg/ml) |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Smithkline Beecham |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Arranon |
| PubMed Health | Nelarabine (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent |
| Drug Label | ARRANON (nelarabine) is a pro-drug of the cytotoxic deoxyguanosine analogue, 9--D-arabinofuranosylguanine (ara-G). The chemical name for nelarabine is 2-amino-9--D-arabinofuranosyl-6-methoxy-9H-purine. It has the molecular formula C11H15N5O5 and... |
| Active Ingredient | Nelarabine |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Iv (infusion) |
| Strength | 250mg/50ml (5mg/ml) |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Smithkline Beecham |
For the treatment of pediatric and adult patients with acute T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia and T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma whose disease has not responded to or has relapsed following treatment with at least two chemotherapy regimens.
FDA Label
Nelarabine is indicated for the treatment of patients with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (T-ALL) and T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma (T-LBL) whose disease has not responded to or has relapsed following treatment with at least two chemotherapy regimens.
Due to the small patient populations in these disease settings, the information to support these indications is based on limited data.
Nelarabine is a prodrug of the cytotoxic deoxyguanosine analogue 9-ß-D-arabinofuranosylguanine (ara-G). Nelarabine is demethylated by adenosine deaminase (ADA) to ara-G. Ara-G is then transported into cells, where it undergoes three phosphorylation steps, resulting in the formation of ara-G triphosphate (ara-GTP). In the first phosphorylation step, ara-G is converted to ara-G monophosphate (ara-GMP). Ara-GMP is then monophosphorylated by deoxyguanosine kinase and deoxycytidine kinase to ara-G diphosphate, and then subsequently to the active ara-G triphosphate (ara-GTP). Ara-GTP is the one that exerts the pharmacological effect. Pre-clinical studies have demonstrated that targeted T-cells possess marked sensitivity to the agent.
L01BB07
L01BB07
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01B - Antimetabolites
L01BB - Purine analogues
L01BB07 - Nelarabine
Route of Elimination
Excretion: Nelarabine and ara-G are partially eliminated by the kidneys.
Clearance
197 +/- 189 L/h/m2 [Adult patients with refractory leukemia or lymphoma receiving doses of 199 to 2,900 mg/m2]
259 +/- 409 L/h/m2 [Pediatric patients with refractory leukemia or lymphoma receiving doses of 104 to 2,900 mg/m2]
The principal route of metabolism for nelarabine is O-demethylation by adenosine deaminase to form ara-G, which undergoes hydrolysis to form guanine. In addition, some nelarabine is hydrolyzed to form methylguanine, which is O-demethylated to form guanine. Guanine is N-deaminated to form xanthine, which is further oxidized to yield uric acid. Ring opening of uric acid followed by further oxidation results in the formation of allantoin.
Nelarabine and ara-G are rapidly eliminated from plasma with a half-life of approximately 30 minutes and 3 hours.
Once nelarabine is metabolized into ara-GTP, the metabolite accumulates in leukemic blasts and incorporates into DNA to exert its S phase-specific cytotoxic effects, leading to the induction of fragmentation and apoptosis. Ara-GTP competes with endogenous deoxyGTP (dGTP) for incorporation into DNA. Once ara-GTP is incorporated at the 3' end of DNA, further DNA elongation is inhibited, which signals apoptosis and leads to cellular destruction. Additional cytotoxic activities may exist, but these are not fully understood.


