
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
VMF
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
Australia
0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers

1. Aic246
2. Prevymis
1. 917389-32-3
2. Aic246
3. Prevymis
4. Aic-246
5. Aic 246
6. Mk-8228
7. 1h09y5wo1f
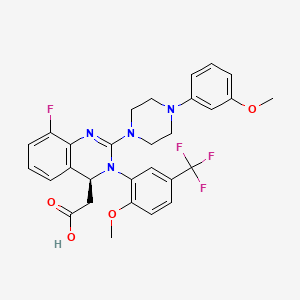
8. 2-[(4s)-8-fluoro-2-[4-(3-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl]-3-[2-methoxy-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4h-quinazolin-4-yl]acetic Acid
9. 2-((4s)-8-fluoro-2-(4-(3-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl)-3-(2-methoxy-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4h-quinazolin-4-yl)acetic Acid
10. 4-quinazolineacetic Acid, 8-fluoro-3,4-dihydro-2-(4-(3-methoxyphenyl)-1-piperazinyl)-3-(2-methoxy-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-, (4s)-
11. Letermovir [inn]
12. Letermovir [usan:inn]
13. Unii-1h09y5wo1f
14. Prevymis (tn)
15. (s)-[8-fluoro-2-[4-(3-methoxyphenyl)piperazine-1-yl]-3-(2-methoxy-5-trifluoromethylphenyl)-3,4-dihydroquinazoline-4-yl]acetic Acid
16. (s)-{8-fluoro-2-[4-(3-methoxyphenyl)piperazine-1-yl]-3-(2-methoxy-5-trifluoromethylphenyl)-3,4-dihydroquinazoline-4-yl}acetic Acid
17. Mk-8828
18. Letermovir(aic246)
19. Letermovir [mi]
20. Letermovir [jan]
21. Letermovir [usan]
22. Letermovir [who-dd]
23. Letermovir (jan/usan/inn)
24. Schembl379403
25. Chembl1241951
26. Letermovir [orange Book]
27. Dtxsid40238683
28. Ex-a1871
29. S8873
30. Zinc100369359
31. Cs-1571
32. Db12070
33. Aic246;aic 246;aic-246
34. Ncgc00378936-01
35. Ncgc00378936-02
36. Ac-35698
37. As-56206
38. Hy-15233
39. J3.556.145e
40. D10801
41. D71052
42. A902281
43. Q15409407
44. (4s)-2-(8-fluoro-2-(4-(3-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl)-3-(2-methoxy-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-4-yl)acetic Acid
45. (4s)-8-fluoro-3,4-dihydro-2-[4-(3-methoxyphenyl)-1-piperazinyl]-3-[2-methoxy-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4-quinazolineacetic Acid
46. (s)-{8-fluoro-2-[4-(3-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl]-3-(2-methoxy-5-trifluoromethylphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-quinazolin-4-yl}acetic Acid
47. (s)-{8-fluoro-2-[4-(3-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl]-3-(2-methoxy-5-trifluoromethylphenyl)-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-4-yl}acetic Acid
48. (s)-2-(8-fluoro-3-(2-methoxy-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2-(4-(3-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-4-yl)acetic Acid
| Molecular Weight | 572.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C29H28F4N4O4 |
| XLogP3 | 4.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 10 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 572.20466804 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 572.20466804 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 77.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 41 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 931 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For use in prophylaxis of cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection and disease in adult CMV-seropositive recipients of an allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT).
FDA Label
Prevymis is indicated for prophylaxis of cytomegalovirus (CMV) reactivation and disease in adult CMV-seropositive recipients [R+] of an allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT).
Consideration should be given to official guidance on the appropriate use of antiviral agents.
Letermovir inhibits the activity of the DNA terminase complex of CMV thereby preventing the cutting of viral DNA into mature length genomes for packaging into viral particles. Letemovir inhibits the DNA terminase complex with an EC50 of 2.1nM.
Antiviral Agents
Agents used in the prophylaxis or therapy of VIRUS DISEASES. Some of the ways they may act include preventing viral replication by inhibiting viral DNA polymerase; binding to specific cell-surface receptors and inhibiting viral penetration or uncoating; inhibiting viral protein synthesis; or blocking late stages of virus assembly. (See all compounds classified as Antiviral Agents.)
Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase Inhibitors
Chemicals and drugs that inhibit the action of POLY(ADP-RIBOSE)POLYMERASES. (See all compounds classified as Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase Inhibitors.)
J05
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J05 - Antivirals for systemic use
J05A - Direct acting antivirals
J05AX - Other antivirals
J05AX18 - Letermovir
Absorption
Letermovir has a bioavailability of 94% in healthy subjects when administered without cyclosporin, 35% in HSCT recipients when administered without cyclosporin, and 85% in HSCT recipients when administered with cyclosporin. Letermovir's Tmax is 45 min to 2.25 h. Time to steady state has been observed to be 9-10 days. Taking Letermovir with food increases Cmax by an average of 129.82% (range of 104.35%-161.50%). No significant effect on AUC has been observed .
Route of Elimination
Letemovir is taken up by the liver through OATP1B1/3 transporters. 93% is excreted in the feces with 70% as the parent drug. <2% is excreted in the urine.
Volume of Distribution
The mean steady state volume of distrubution is 45.5L
Clearance
The mean clearance is 11.25 L/h in healthy subjects
Letermovir undergoes a minor degree of metabolism through UGT1A1/1A3.
The mean terminal half-life was observed to be 12 hours following administration of Letemovir 480 mg IV once daily.
CMV relies on a DNA terminase complex consisting of multiple subunits (pUL51, pUL56, and pUL89) for processing of viral DNA. Viral DNA is produced in a single repeating strand which is then cut by the DNA terminase complex into individual viral genomes which can then be packaged into mature viral particles. Letemovir inhibits the activity of this complex to prevent production of mature viral genomes and the production of viable viral particles. The exact nature of Letemovir's binding to this complex is not currently known. Initially, the observation of resistance-causing mutations in pUL56 suggested this subunit was the location of Letemovir binding. However, resistance mutations have now been observed in pUL51, pUL56, and pUL89. It is possible that changes in amino acid sequence in one subunit could result in conformational changes to interacting subunits affecting Letemovir binding or that Letemovir interacts with multiple subunits of the complex but evidence towards either of these distinctions has not yet been seen. pUL89 is known to contain the endonuclease activity of the complex but because all members of the complex are necessary for targeting as well as protection from proteosomal degradation, it is difficult to discern if Letemovir inhibits pUL89's activity directly.

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
ABOUT THIS PAGE
72
PharmaCompass offers a list of Letermovir API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Letermovir manufacturer or Letermovir supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Letermovir manufacturer or Letermovir supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Letermovir API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Letermovir API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Letermovir Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Letermovir Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Letermovir [INN] manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Letermovir [INN], including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Letermovir [INN] manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Letermovir [INN] API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Letermovir [INN] manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Letermovir [INN] supplier is an individual or a company that provides Letermovir [INN] active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Letermovir [INN] finished formulations upon request. The Letermovir [INN] suppliers may include Letermovir [INN] API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Letermovir [INN] suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Letermovir [INN] DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Letermovir [INN] active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Letermovir [INN] DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Letermovir [INN] USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Letermovir [INN] DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Letermovir [INN] USDMF includes data on Letermovir [INN]'s chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Letermovir [INN] USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Letermovir [INN] suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a Letermovir [INN] Drug Master File in Korea (Letermovir [INN] KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of Letermovir [INN]. The MFDS reviews the Letermovir [INN] KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the Letermovir [INN] KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a Letermovir [INN] KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their Letermovir [INN] API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of Letermovir [INN] suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Letermovir [INN] written confirmation (Letermovir [INN] WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Letermovir [INN] manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Letermovir [INN] active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Letermovir [INN] APIs or Letermovir [INN] finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Letermovir [INN] WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Letermovir [INN] suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Letermovir [INN] as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Letermovir [INN] API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Letermovir [INN] as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Letermovir [INN] and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Letermovir [INN] NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Letermovir [INN] suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Letermovir [INN] Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Letermovir [INN] GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Letermovir [INN] GMP manufacturer or Letermovir [INN] GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Letermovir [INN] CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Letermovir [INN]'s compliance with Letermovir [INN] specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Letermovir [INN] CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Letermovir [INN] CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Letermovir [INN] may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Letermovir [INN] EP), Letermovir [INN] JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Letermovir [INN] USP).

