
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
API Suppliers
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book
0
Europe
0
Canada
0
Australia
0
South Africa
0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
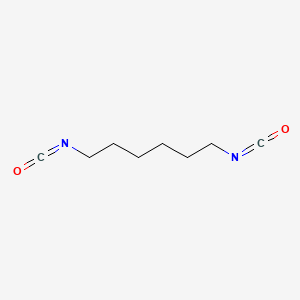

1. 1,6-diisocyanatohexane
2. 1,6-hexamethylene Diisocyanate
3. 1,6-hexane Diisocyanate
4. Hdi Cpd
1. 1,6-diisocyanatohexane
2. 822-06-0
3. 1,6-hexamethylene Diisocyanate
4. Hmdi
5. Hexane, 1,6-diisocyanato-
6. Hexane 1,6-diisocyanate
7. 1,6-hexylene Diisocyanate
8. Hexamethylene-1,6-diisocyanate
9. Hexamethylenediisocyanate
10. 1,6-hexanediol Diisocyanate
11. Isocyanic Acid, Hexamethylene Ester
12. Tl 78
13. Hdi
14. Szesciometylenodwuizocyjanian
15. Metyleno-bis-fenyloizocyjanian
16. Nsc 11687
17. Chebi:53578
18. Hexamethylene Diisocyanate, 1,6-
19. Isocyanic Acid, Diester With 1,6-hexanediol
20. 1,6-diisocyanato-hexane
21. Hexamethylene Di-isocyanate
22. 0i70a3i1uf
23. Hexamethylene 1,6-diisocyanate
24. Nsc-11687
25. Dsstox_cid_4143
26. Hexamethylene-1,6-diisocyanate [diisocyanates]
27. Dsstox_rid_77303
28. Dsstox_gsid_24143
29. 1,6-hexane Diisocyanate
30. 53895-37-7
31. Cas-822-06-0
32. Hexamethylendiisokyanat [czech]
33. Hexamethylendiisokyanat
34. Hsdb 6134
35. Einecs 212-485-8
36. Mfcd00002047
37. Un2281
38. Hexamethylene-1,6-diisocyanate (diisocyanates)
39. Szesciometylenodwuizocyjanian [polish]
40. Metyleno-bis-fenyloizocyjanian [polish]
41. Brn 0956709
42. Unii-0i70a3i1uf
43. Ai3-28285
44. Ccris 8431
45. Desmodur H
46. Hexane,6-diisocyanato-
47. 1,6-diisocyanato Hexane
48. Wln: Ocn6nco
49. Epitope Id:115018
50. Ec 212-485-8
51. Isocyanic Acid,6-hexanediol
52. Schembl15038
53. 1,6-diisocyanatohexamethylene
54. Ocn-(ch2)6-nco
55. 1,6-hexamethylene-diisocyanate
56. 1,6-diisocyanatohexane, 98%
57. Gtpl6291
58. 1,6-hexamethylene Di-isocyanate
59. Chembl1896533
60. Dtxsid4024143
61. Hexane,1,6-diisocyanate
62. Hexane, 1,6-diisocyanato-, Dimer
63. Nsc11687
64. Zinc1718505
65. Tox21_202206
66. Tox21_300161
67. Stl301890
68. Akos000120355
69. Hexamethylene Diisocyanate [hsdb]
70. Ncgc00164175-01
71. Ncgc00164175-02
72. Ncgc00164175-03
73. Ncgc00254122-01
74. Ncgc00259755-01
75. S 90
76. S-90
77. Ft-0627021
78. H0324
79. 1,6-hexamethylene Diisocyanate [inci]
80. Hexamethylene Diisocyanate [un2281] [poison]
81. A840272
82. Q418197
83. Hexamethylene Diisocyanate, Purum, >=98.0% (gc)
84. W-104184
85. Hexamethylene Diisocyanate, Puriss., >=99.0% (gc)
| Molecular Weight | 168.19 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C8H12N2O2 |
| XLogP3 | 3.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 168.089877630 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 168.089877630 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 58.9 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 12 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 169 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Air Pollutants
Any substance in the air which could, if present in high enough concentration, harm humans, animals, vegetation or materials. Substances include GASES; PARTICULATE MATTER; and volatile ORGANIC CHEMICALS. (See all compounds classified as Air Pollutants.)
Cross-Linking Reagents
Reagents with two reactive groups, usually at opposite ends of the molecule, that are capable of reacting with and thereby forming bridges between side chains of amino acids in proteins; the locations of naturally reactive areas within proteins can thereby be identified; may also be used for other macromolecules, like glycoproteins, nucleic acids, or other. (See all compounds classified as Cross-Linking Reagents.)
Air Pollutants, Occupational
Toxic air-borne matter related to work performed They are usually produced by the specific nature of the occupation. (See all compounds classified as Air Pollutants, Occupational.)
Absorption of significant amounts of HDI into the general circulation would not be expected. Any free HDI that may reach the blood may bind to serum proteins and not be available as a free form in the blood.
DHHS/ATSDR; Toxicological Profile for Hexamethylene diisocyanate (PB/99/102543/AS) (August 1998). Available from, as of March 30, 2012: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/index.asp
Six males were administered an oral dose of 0.1 mg/kg HDA on 2 occasions 3 months apart, and urine was collected for several hours after dosing. Peak amounts of free HDA in single urine samples ranged from 0.080 to 0.19 mg 2-5 hours after dosing. Four of the 6 men tested had no detectable levels of HDA in their urine 10 hours after dosing; however, 2 subjects had detectable levels of HDA in the urine 15 hours after dosing. ... 1-6% of the total HDA dose was recovered in the urine. /1,6-Hexamethylene diamine/
DHHS/ATSDR; Toxicological Profile for Hexamethylene diisocyanate (PB/99/102543/AS) (August 1998). Available from, as of March 30, 2012: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/index.asp
5 men (age, 36-50 years; mean age, 42 years) inhaled 95-L 15 ug (0.01-0.02 ppm) of HDI in air (range, 25-29 ug/cu m or approximately 0.004 ppm) for 7.5 hours. Blood and urine samples were taken at 2-hour intervals. Beginning almost immediately after exposure, urinary levels of 1,6-hexamethylene diamine (HDA) began to accumulate in the urine. The urinary elimination rates for all men ranged from 1.1 to 1.7 ug/hr, with the average urinary level of HDA ranging from 0.01-0.03 mmol/mol creatinine for the 5-hour sample and 0.006 mmol/mol creatinine for the 10-hour sample. HDA levels were undetectable by 15 hours after exposure began (or 7.5 hours after exposure ended). The cumulative excretion of HDA over a 28hour period was 8.0-14 ug, which is about 1l-21% of the inhaled dose of HDI.
DHHS/ATSDR; Toxicological Profile for Hexamethylene diisocyanate (PB/99/102543/AS) (August 1998). Available from, as of March 30, 2012: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/index.asp
On the basis of the ability to acetylate an oral dose of HDA, /investigators/ determined the phenotypes of 6 individuals as either rapid or slow acetylators. The rapid acetylators excreted approximately twice as much acetylated HDA over the subsequent 15 hours as did the slow acetylators. The potential importance of this difference in excretory rates with respect to toxicity has not been investigated. However, the author suggests that after measurements of urinary metabolites have been made in conjunction with determinations of acetylation phenotypes, it would be worth considering the possibility of biological monitoring of occupation exposure to HDA and HDI.
DHHS/ATSDR; Toxicological Profile for Hexamethylene diisocyanate (PB/99/102543/AS) (August 1998). Available from, as of March 30, 2012: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/index.asp
Volunteers exposed to HDI in a test chamber (3.6 ppb for 7.5 hours) had the corresponding amine (1,6-hexamethylene diamine, HDA) in hydrolyzed urine. The biological half time was about 1 hour. In a similar study with lower exposures (1.7 to 3.1 ppb for 2 hours), HDA levels in urine were proportional to HDI levels in air, and the half time was 2.5 hours. HDA could not be found in unhydrolyzed urine, which suggests that this metabolite occurs as an adduct. HDA was not detected in plasma in either of these studies. HDA could be identified in hydrolyzed urine from car painters exposed to prepolymerized HDI and production workers making HDI monomers. Of 22 car painters who used HDI-based paint and wore face masks with air filters, 4 had HDA in hydrolyzed urine; none of seven controls had detectable amounts.
Montelius J ed.; Scientific Basis for Swedish Occupational Standards XXII p.65 (2001). Available from, as of March 7, 2012: https://www.inchem.org/documents/kemi/kemi/ah2001_20.pdf
Authors noted two pathways by which HDA could be metabolized: (1) to N-acetyl-1,6-hexamethylene diamine, via N-acetyl transferase, and (2) 6-aminohexanoic acid, via diamine oxidase. Both HDA metabolites may appear in the urine. /1,6-Hexamethylene diamine/
DHHS/ATSDR; Toxicological Profile for Hexamethylene diisocyanate (PB/99/102543/AS) (August 1998). Available from, as of March 30, 2012: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/index.asp
The hydrolysis of hexamethylene diisocyanate in water was tested in a dynamic and stationary system. Without catalysts, the reaction was very slow (< 1% in 10 min at 30 C) while the addition of simple carboxylic acid containing neutral buffers markedly catalyses the formation of 1,6-diaminohexane as the known hydrolysis product. It is suggested that the hydrolysis of inhaled hexamethylene diisocyanate in the lungs may be catalysed by bicarbonate in the blood, giving rise to amines found as urinary metabolites following occupational exposure.
Berode M et al; Toxicol Lett (AMST) 56 (1-2): 173-8 (1991)
Six males were administered an oral dose of 0.1 mg/kg HDA on 2 occasions 3 months apart, and urine was collected for several hours after dosing. ... The elimination half-life was calculated to be approximately 1.5 hours... /1,6-Hexamethylene diamine/
DHHS/ATSDR; Toxicological Profile for Hexamethylene diisocyanate (PB/99/102543/AS) (August 1998). Available from, as of March 30, 2012: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/index.asp
The urinary elimination was rapid, and half-time, for the concentration of 1,6-hexamethylene diamine in urine, showed an average of 1.2 hr (range 1.1-1.4 hr).
PMID:2228259 Brorson T et al; Int Arch Occup Environ Health 62 (5): 385-9 (1990)
Study explored whether the mechanism for the irritation reaction and the toxic respiratory effect of isocyanates is due to their ability to inhibit cholinesterases. Hexamethylene diisocyanate completely inhibited purified human serum cholinesterase when added at molar ratios of 4:1 to 8:1 (isocyanate: enzyme). Enzyme inhibition was also achieved by exposure of purified cholinesterase to an atmosphere containing 1 ppm isocyanates.
PMID:6280343 BROWN WE ET AL; TOXICOL APPL PHARMACOL 63 (1): 45 (1982)
Aliphatic isocyanates are stronger inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase activity than are aromatic isocyanates. Incubation at 21-23 C for several days leads to slow & limited spontaneous reactivation of the inhibited enzyme. This enzyme inhibition may be a contributing factor in the induction of respiratory disease observed in approx 5% of workers exposed to isocyanate vapors.
PMID:6854416 DEWAIR M ET AL; J OCCUP MED 25 (4): 279-82 (1983)
Rates of reaction of hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI) with protein, human serum albumin, were studied. The reaction of HDI with human serum albumin was quantified by combined assays of gas chromatography of the hexamethylenediamine formed after acid hydrolysis of the conjugate, & by amino acid analysis of the protein. HDI isocyanate groups reacting with the lysyl residues & other sites on the protein molecule formed at least 2 reaction products, 1 of which was easily hydrolyzable by acid & the other resistant to hydrolysis. The chemical structures proposed by these observations are similar to those of classical hapten derivatives. Such derivatives may be immunogenic &/or allergenic in some workers exposed to the vapors of these reagents.
PMID:230615 Tse CST, Pesce AJ; Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 51: 39-46 (1979)
ABOUT THIS PAGE
81
PharmaCompass offers a list of Hexamethylene Diisocyanate API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Hexamethylene Diisocyanate manufacturer or Hexamethylene Diisocyanate supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Hexamethylene Diisocyanate manufacturer or Hexamethylene Diisocyanate supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Hexamethylene Diisocyanate API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Hexamethylene Diisocyanate API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Hexamethylene Diisocyanate Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Hexamethylene Diisocyanate Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Hexamethylene Diisocyanate manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Hexamethylene Diisocyanate, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Hexamethylene Diisocyanate manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Hexamethylene Diisocyanate API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A Hexamethylene Diisocyanate supplier is an individual or a company that provides Hexamethylene Diisocyanate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Hexamethylene Diisocyanate finished formulations upon request. The Hexamethylene Diisocyanate suppliers may include Hexamethylene Diisocyanate API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
Hexamethylene Diisocyanate Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Hexamethylene Diisocyanate GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Hexamethylene Diisocyanate GMP manufacturer or Hexamethylene Diisocyanate GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Hexamethylene Diisocyanate CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Hexamethylene Diisocyanate's compliance with Hexamethylene Diisocyanate specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Hexamethylene Diisocyanate CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Hexamethylene Diisocyanate CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Hexamethylene Diisocyanate may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Hexamethylene Diisocyanate EP), Hexamethylene Diisocyanate JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Hexamethylene Diisocyanate USP).

