



API Suppliers
0

US DMFs Filed
0

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
0
Other Suppliers
0
0
0

USA (Orange Book)

Europe
0

Canada
0

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
0
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
0
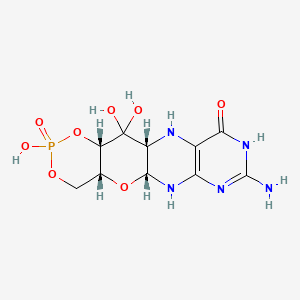

1. Alxn1101
2. Cpmp Cpd
3. Fosdenopterin
4. Nulibry
1. Fosdenopterin
2. Cpmp
3. Precursor Z Hydrate
4. C(pmp)
5. Alxn1101
6. 150829-29-1
7. Precursor Z, Hydrated
8. Fosdenopterin [usan]
9. Chebi:60210
10. 4x7k2681y7
11. Alxn-1101 Anhydrous Free Base
12. Fosdenopterin (usan)
13. (4ar,5ar,11ar,12as)-8-amino-2,12,12-trihydroxy-4a,5a,6,9,11,11a,12,12a-octahydro[1,3,2]dioxaphosphinino[4',5':5,6]pyrano[3,2-g]pteridin-10(4h)-one 2-oxide
14. Unii-4x7k2681y7
15. Fosdenopterin [inn]
16. Fosdenopterin [who-dd]
17. Cyclic Pyranopterin Monophoshate
18. Chembl2338675
19. Schembl16156371
20. Dtxsid90934067
21. Who 11150
22. Zinc34962340
23. Hy-109145
24. Cs-0115961
25. C18239
26. D11779
27. Q5198226
28. (1r,10r,12s,17r)-5-amino-11,11,14-trihydroxy-14-oxo-13,15,18-trioxa-2,4,6,9-tetraza-14lambda5-phosphatetracyclo[8.8.0.03,8.012,17]octadeca-3(8),4-dien-7-one
29. 1,3,2-dioxaphosphorino(4',5':5,6)pyrano(3,2-g)pteridin-10(4h)-one, 8-amino-4a,5a,6,7,11,11a,12,12a-octahydro-2,12,12-trihydroxy-, 2-oxide, (4ar,5ar,11ar,12as)-
| Molecular Weight | 363.22 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H14N5O8P |
| XLogP3 | -4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 11 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 363.05799942 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 363.05799942 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 197 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 722 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Fosdenopterin is indicated to reduce the risk of mortality in patients with molybdenum cofactor deficiency (MoCD) type A.
NULIBRY is indicated for the treatment of patients with molybdenum cofactor deficiency (MoCD) Type A.
Fosdenopterin replaces an intermediate substrate in the synthesis of molybdenum cofactor, a compound necessary for the activation of several molybdenum-dependent enzymes including sulfite oxidase (SOX). Given that SOX is responsible for detoxifying sulfur-containing acids and sulfites such as S-sulfocysteine (SSC), urinary levels of SSC can be used as a surrogate marker of efficacy for fosdenopterin. Long-term therapy with fosdenopterin has been shown to result in a sustained reduction in urinary SSC normalized to creatinine. Animal studies have identified a potential risk of phototoxicity in patients receiving fosdenopterin - these patients should avoid or minimize exposure to sunlight and/or artificial UV light. If sun exposure is necessary, use protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses, in addition to seeking shade whenever practical. Consider the use of a broad-spectrum sunscreen in patients 6 months of age or older.
A16AX19
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A16 - Other alimentary tract and metabolism products
A16A - Other alimentary tract and metabolism products
A16AX - Various alimentary tract and metabolism products
A16AX19 - Fosdenopterin
Absorption
In healthy adult subjects, the observed Cmax and AUC0-inf following the intravenous administration of 0.68 mg/kg (0.76x the maximum recommended dose) were 2800 ng/mL and 5960 ng*h/mL, respectively. Both Cmax and AUC0-inf appear to increase proportionally with increasing doses.
Route of Elimination
Renal clearance of fosdenopterin accounts for approximately 40% of total clearance.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution of fosdenopterin is approximately 300 mL/kg.
Clearance
Total body clearance of fosdenopterin ranges from 167 to 195 mL/h/kg.
Fosdenopterin metabolism occurs mainly via non-enzymatic degradation into Compound Z, which is a pharmacologically inactive product of endogenous cyclic pyranopterin monophosphate.
The mean half-life of fosdenopterin ranges from 1.2 to 1.7 hours.
Molybdenum cofactor deficiency (MoCD) is a rare autosomal-recessive disorder in which patients are deficient in three molybdenum-dependent enzymes: sulfite oxidase (SOX), xanthine dehydrogenase, and aldehyde dehydrogenase. The loss of SOX activity appears to be the main driver of MoCD morbidity and mortality, as the build-up of neurotoxic sulfites typically processed by SOX results in rapid and progressive neurological damage. In MoCD type A, the disorder results from a mutation in the _MOCS1_ gene leading to deficient production of MOCS1A/B, a protein that is responsible for the first step in the synthesis of molybdenum cofactor: the conversion of guanosine triphosphate into cyclic pyranopterin monophosphate (cPMP). Fosdenopterin is an exogenous form of cPMP, replacing endogenous production and allowing for the synthesis of molybdenum cofactor to proceed.


