
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
VMF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
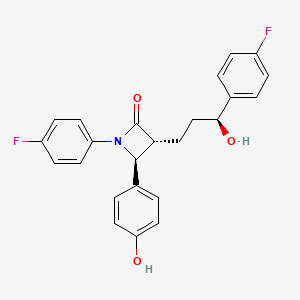

1. (1-(4-fluorophenyl)-(3r)-(3-(4-fluorophenyl)-(3s)-hydroxypropyl)-(4s)-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-azetidinone)
2. 58235, Sch
3. Ezetimib
4. Ezetrol
5. Sch 58235
6. Sch-58235
7. Sch58235
8. Zetia
1. 163222-33-1
2. Zetia
3. Ezetrol
4. Ezedoc
5. Sch 58235
6. Sch58235
7. (3r,4s)-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-[(3s)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-hydroxypropyl]-4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)azetidin-2-one
8. Sch-58235
9. Ezetimibe (zetia)
10. (3r,4s)-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-((s)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-hydroxypropyl)-4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)azetidin-2-one
11. Eor26lqq24
12. Chebi:49040
13. Mk0653
14. Nsc-758923
15. (3r,4s)-1-(p-fluorophenyl)-3-((3s)-3-(p-fluorophenyl)-3-hydroxypropyl)-4-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-2-azetidinone
16. 1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3(r)-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3(s)-hydroxypropyl]-4(s)-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-azetidinone
17. Dsstox_cid_24223
18. Dsstox_rid_80127
19. Dsstox_gsid_44223
20. Zient
21. (-)-sch 58235
22. (3~{r},4~{s})-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-[(3~{s})-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-oxidanyl-propyl]-4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)azetidin-2-one
23. 2-azetidinone, 1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-((3s)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-hydroxypropyl)-4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-, (3r,4s)-
24. 2-azetidinone, 1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-[(3s)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-hydroxypropyl]-4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-, (3r,4s)-
25. Smr000466334
26. Cas-163222-33-1
27. Zetia (tn)
28. Unii-eor26lqq24
29. Ezetimiba
30. Ezetimibum
31. Ezetimibe [usan:inn:ban]
32. Ezetimibe)
33. Mfcd00937872
34. Hsdb 7737
35. Ezetimibe Anhydrate
36. Ezetimibe- Bio-x
37. Ncgc00095134-01
38. Ezetimibe [usan]
39. Mk-0653
40. Ezetimibe [inn]
41. Ezetimibe [jan]
42. Ezetimibe [mi]
43. Ezetimibe [hsdb]
44. Ezetimibe [vandf]
45. Ezetimibe [mart.]
46. Ezetimibe [usp-rs]
47. Ezetimibe [who-dd]
48. Schembl2871
49. Chembl1138
50. Ezetimibe (jan/usp/inn)
51. Mls000759443
52. Mls001424125
53. Mls006011921
54. Gtpl6816
55. Ezetimibe [orange Book]
56. Dtxsid1044223
57. Ezetimibe, >=98% (hplc)
58. Roszet Component Ezetimibe
59. Ex-a795
60. Ezetimibe [usp Monograph]
61. Vytorin Component Ezetimibe
62. Hms2051k16
63. Hms2236a04
64. Hms3715d06
65. Nexlizet Component Ezetimibe
66. (3r,4s)-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-hydroxypropyl]-4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-azetidinone
67. Act03511
68. Zinc3810860
69. Ezetimibe Component Of Roszet
70. Tox21_111443
71. Bdbm50371521
72. S1655
73. Stk640490
74. Ezetimibe Component Of Vytorin
75. Akos005572111
76. Ezetimibe Component Of Nexlizet
77. Tox21_111443_1
78. Ac-1057
79. Am84560
80. Ccg-100884
81. Db00973
82. Ks-1170
83. Nc00134
84. Nsc 758923
85. Ncgc00263575-01
86. Ncgc00263575-07
87. (3r,4s)-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-[(3s)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-hydroxy-propyl]-4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)azetidin-2-one
88. 2-azetidinone, 1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-hydroxypropyl)-4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-, (3r-(3alpha(s*),4beta))-
89. Be164439
90. Hy-17376
91. E1449
92. D01966
93. Ab00639916-06
94. Ab00639916-08
95. Ab00639916_09
96. 222e331
97. Ar-270/43507897
98. Q417997
99. 3-hydroxypropyl)-4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)azetidin-2-one
100. Brd-k42260897-001-09-2
101. Z1550648770
102. (3r,4s)-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-((s)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-
103. Ezetimibe, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
104. Ezetimibe, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
105. (3r,4s)-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-[(3 S)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-hydroxypropyl]-4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)azetidin-2-one
106. (3r,4s)-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-[(3s)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)- 3-hydroxypropyl]-4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)azetidin-2-one
107. (3r,4s)-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-[(s)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-hydroxypropyl]-4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-azetidin-2-one
108. 1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-hydroxypropyl]-4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-azetidinone
109. 2-azetidinone, 1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-hydroxypropyl)-4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-, (3r-(3.alpha.(s*),4.beta.))-
110. H56
| Molecular Weight | 409.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C24H21F2NO3 |
| XLogP3 | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 409.14894986 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 409.14894986 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 60.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 567 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ezetimibe |
| PubMed Health | Ezetimibe (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihyperlipidemic |
| Drug Label | ZETIA (ezetimibe) is in a class of lipid-lowering compounds that selectively inhibits the intestinal absorption of cholesterol and related phytosterols. The chemical name of ezetimibe is 1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3(R)-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3(S)-hydroxypropyl]... |
| Active Ingredient | Ezetimibe |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | oral |
| Strength | 10mg |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Glenmark Generics |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Zetia |
| PubMed Health | Ezetimibe (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihyperlipidemic |
| Drug Label | ZETIA (ezetimibe) is in a class of lipid-lowering compounds that selectively inhibits the intestinal absorption of cholesterol and related phytosterols. The chemical name of ezetimibe is 1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3(R)-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3(S)-hydroxypropyl]... |
| Active Ingredient | Ezetimibe |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 10mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Msd Intl Gmbh |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ezetimibe |
| PubMed Health | Ezetimibe (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihyperlipidemic |
| Drug Label | ZETIA (ezetimibe) is in a class of lipid-lowering compounds that selectively inhibits the intestinal absorption of cholesterol and related phytosterols. The chemical name of ezetimibe is 1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3(R)-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3(S)-hydroxypropyl]... |
| Active Ingredient | Ezetimibe |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | oral |
| Strength | 10mg |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Glenmark Generics |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Zetia |
| PubMed Health | Ezetimibe (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihyperlipidemic |
| Drug Label | ZETIA (ezetimibe) is in a class of lipid-lowering compounds that selectively inhibits the intestinal absorption of cholesterol and related phytosterols. The chemical name of ezetimibe is 1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3(R)-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3(S)-hydroxypropyl]... |
| Active Ingredient | Ezetimibe |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 10mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Msd Intl Gmbh |
Ezetimibe is used alone or in combination with other antilipemic agents (i.e., a hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A [HMG-CoA] reductase inhibitor (statin), fenofibrate) as an adjunct to dietary therapy in the treatment of primary hypercholesterolemia and mixed dyslipidemia, homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia, and/or homozygous familial sitosterolemia. /Included in US product label/
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 1728
Ezetimibe is used alone or in combination with a statin as an adjunct to dietary therapy to decrease elevated serum total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-cholesterol, and apolipoprotein B (apo B) concentrations in the treatment of primary (heterozygous familial and nonfamilial) hypercholesterolemia. Ezetimibe in fixed combination with simvastatin is used as an adjunct to dietary therapy to decrease elevated serum total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, apo B, triglyceride, and non-HDL-cholesterol concentrations, and to increase HDL-cholesterol concentrations in the treatment of primary hypercholesterolemia or mixed dyslipidemia. Ezetimibe also is used in combination with fenofibrate as an adjunct to dietary therapy to decrease elevated serum total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, apo B, and non-HDL-cholesterol concentrations in the treatment of mixed dyslipidemia. /Included in US product label/
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 1728
Ezetimibe is used as an adjunct to dietary therapy to decrease elevated serum sitosterol and campesterol concentrations in patients with homozygous familial sitosterolemia. /Included in US product label/
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 1729
Ezetimibe may be used in combination with atorvastatin or simvastatin to decrease elevated serum total and LDL-cholesterol concentrations in patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia as an adjunct to other lipid-lowering therapies (e.g., plasma LDL apheresis) or when such therapies are not available. /Included in US product label/
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 1729
This is a retrospective review of all pediatric patients who received ezetimibe monotherapy as treatment for hypercholesterolemia and for whom follow-up clinical and lipid results were available. Of 36 identified patients, 26 had lipoprotein profiles suggestive of familial hypercholesterolemia (FH), and 10 had profiles suggestive of familial combined hyperlipidemia (FCHL). After a mean 105 days of treatment with ezetimibe (range, 32-175 days), total cholesterol (TC) levels decreased from 7.3 +/- 1.0 mmol/L to 5.7 +/- 1.0 mmol/L (P < .0001), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels decreased from 5.3 +/- 0.9 mmol/L to 3.9 +/- 0.8 (P < .0001) in patients with FH. In patients with FCHL, TC levels decreased from 6.4 +/- 2.0 mmol/L to 5.6 +/- 0.4 mmol/L (P < or = .002), and LDL-C levels decreased from 4.7 +/- 1.0 mmol/L to 3.8 +/- 0.6 mmol/L (P < or = .005). For all patients, the mean decrease in individual LDL-C values was 1.5 +/- 0.9 mmol/L or 28%. There was no significant change in triglyceride or high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels with ezetimibe. Patients were maintained on ezetimibe with no adverse effects attributable to the medication for as long as 3.5 years. At a mean of 13.6 months (range, 1-44 months) after the initiation of ezetimibe, LDL-C levels remained decreased at 4.0 +/- 0.6 mmol/L. In this small retrospective series of children and adolescents with hypercholesterolemia, ezetimibe was safe and effective in lowering LDL-C levels.
PMID:192308 Clauss S et al; J Pediatr 154 (6): 869-72 (2009).
Ezetimibe, in combination with a hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitor (statin), is contraindicated in patients with active liver disease or unexplained, persistent increases in serum aminotransferase (transaminase) concentrations.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 1730
In the Zetia controlled clinical trials database (placebo-controlled) of 2396 patients with a median treatment duration of 12 weeks (range 0 to 39 weeks), 3.3% of patients on Zetia and 2.9% of patients on placebo discontinued due to adverse reactions. The most common adverse reactions in the group of patients treated with Zetia that led to treatment discontinuation and occurred at a rate greater than placebo were: Arthralgia (0.3%); dizziness (0.2%); and gamma-glutamyltransferase increased (0.2%) The most commonly reported adverse reactions (incidence =2% and greater than placebo) in the Zetia monotherapy controlled clinical trial database of 2396 patients were: upper respiratory tract infection (4.3%), diarrhea (4.1%), arthralgia (3.0%), sinusitis (2.8%), and pain in extremity (2.7%).
Thomson Health Care Inc.; Physicians' Desk Reference 63 ed., Montvale, NJ 2009, p. 2158
In the Zetia + statin controlled clinical trials database of 11,308 patients with a median treatment duration of 8 weeks (range 0 to 112 weeks), 4.0% of patients on Zetia + statin and 3.3% of patients on statin alone discontinued due to adverse reactions. The most common adverse reactions in the group of patients treated with Zetia + statin that led to treatment discontinuation and occurred at a rate greater than statin alone were: Alanine aminotransferase increased (0.6%) Myalgia (0.5%) Fatigue, aspartate aminotransferase increased, headache, and pain in extremity (each at 0.2%) The most commonly reported adverse reactions (incidence =2% and greater than statin alone) in the Zetia + statin controlled clinical trial database of 11,308 patients were: nasopharyngitis (3.7%), myalgia (3.2%), upper respiratory tract infection (2.9%), arthralgia (2.6%) and diarrhea (2.5%).
Thomson Health Care Inc.; Physicians' Desk Reference 63 ed., Montvale, NJ 2009, p. 2158
In post-marketing experience with Zetia, cases of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis have been reported. Most patients who developed rhabdomyolysis were taking a statin prior to initiating Zetia. However, rhabdomyolysis has been reported with Zetia monotherapy and with the addition of Zetia to agents known to be associated with increased risk of rhabdomyolysis, such as fibrates. Zetia and any statin or fibrate that the patient is taking concomitantly should be immediately discontinued if myopathy is diagnosed or suspected. The presence of muscle symptoms and a CPK level >10 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) indicates myopathy.
Thomson Health Care Inc.; Physicians' Desk Reference 63 ed., Montvale, NJ 2009, p. 2158
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Ezetimibe (15 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Ezetimibe is indicated to reduce elevated total-C, LDL-C, Apo B, and non-HDL-C in patients with primary hyperlipidemia, alone or in combination with an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor (statin). It is also indicated to reduce elevated total-C, LDL-C, Apo B, and non-HDL-C in patients with mixed hyperlipidemia in combination with fenofibrate, and to reduce elevated total-C and LDL-C in patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH), in combination with atorvastatin or simvastatin. Ezetimibe may also be used to reduce elevated sitosterol and campesterol in patients with homozygous sitosterolemia (phytosterolemia).
FDA Label
Prevention of coronary heart disease
Treatment of hypercholesterolaemia, Treatment of sitosterolaemia
Ezetimibe was shown to reduce the levels of total cholesterol (total-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), apoprotein B (Apo B), non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C), and triglycerides (TG), and increase high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) in patients with hyperlipidemia. This therapeutic effect was more profound when ezetimibe was co-administered with a statin or fenofibrate compared to either treatment alone. In clinical trials involving patients with homozygous and heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia and in those with sitosterolemia, a recommended therapeutic dose of ezetimibe was effective in reducing the LDL levels by 15-20% while increasing HDL-C by 2.5-5%. The effects of increased exposure to ezetimibe secondary to moderate-severe hepatic impairment have not been assessed - patients meeting these criteria should avoid the use of ezetimibe. Post-marketing reports indicate the potential for myopathy and rhabdomyolysis in patients taking ezetimibe, and this risk appears to be exacerbated in patients concurrently receiving, or having recently received, statin therapy.
Anticholesteremic Agents
Substances used to lower plasma cholesterol levels. (See all compounds classified as Anticholesteremic Agents.)
C10AX09
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
C - Cardiovascular system
C10 - Lipid modifying agents
C10A - Lipid modifying agents, plain
C10AX - Other lipid modifying agents
C10AX09 - Ezetimibe
Absorption
Administration of a single 10-mg dose of ezetimibe in fasted adults resulted in peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) of 3.4-5.5 ng/mL within 4-12 hours (Tmax). The Cmax of the major pharmacologically-active metabolite, ezetimibe-glucuronide, was 45-71 ng/mL and its Tmax was 1-2 hours. Food consumption has minimal effect on ezetimibe absorption, but the Cmax is increased by 38% when administered alongside a high-fat meal. The true bioavailability of ezetimibe cannot be determined, as it is insoluble in aqueous media suitable for intravenous injection.
Route of Elimination
Approximately 78% and 11% of orally administered radiolabelled ezetimibe are recovered in the feces and urine, respectively. Unchanged parent drug is the major component in feces and accounts for approximately 69% of an administered dose, while ezetimibe-glucuronide is the major component in urine and accounts for approximately 9% of an administered dose. High recovery of unchanged parent drug in feces suggests low absorption and/or hydrolysis of ezetimibe-glucuronide secreted in the bile.
Volume of Distribution
The relative volume of distribution of ezetimibe is 107.5L.
Clearance
There are no pharmacokinetic data available on the clearance of ezetimibe.
Ezetimibe is the first member of a new class of selective cholesterol absorption inhibitors. The drug and its active glucuronide metabolite impair the intestinal reabsorption of both dietary and hepatically excreted biliary cholesterol through inhibition of a membrane transporter yet to be identified. Absorption of ezetimibe is rapid and not altered by food content following oral administration. The drug is not metabolized by the cytochrome P450 system but extensive glucuronidation takes place in the intestine. Consequently, plasma concentrations of ezetimibe represent approximately 10% of total ezetimibe in plasma. Enterohepatic recirculation observed for ezetimibe and its glucuronimide significantly increases the residence time of these compounds in the intestine, at their site of action. Elimination of ezetimibe glucuronimide appears impaired in elderly patients and patients with renal insufficiency with plasma concentrations increased 1.5- to 2-fold. So far, no drug interaction study has been associated with major changes in either the pharmokinetics of ezetimibe or coadministered drugs.
PMID:14571304 Simard C, Turgeon J; Can J Clin Pharmacol 10 (Suppl A): 13A-20A (2003).
Ezetimibe lowers plasma cholesterol levels by inhibiting the uptake of cholesterol in the intestine. Due to extensive enterohepatic circulation of ezetimibe, relative low doses are required to be effective. In blood and bile the majority of ezetimibe is present as a glucuronide-conjugate, which is formed in the enterocyte. Presently, it is not clear which mechanisms are responsible for this efficient enterohepatic circulation. Abcc2, Abcc3 and Abcg2 are ABC transporters, which are expressed in both liver and intestine and are capable of transporting glucuronidated compounds. The aim of this study was to investigate the contribution of these transporters in the enterohepatic cycling of ezetimibe-glucuronide (Ez-gluc). Transport studies were performed in plasma membrane vesicles from ABCC2, ABCC3 and ABCG2 expressing Sf21 insect cells. Furthermore, intestinal explants from wild-type and Abcc3-/- mice were used to study vectorial transport in an Ussing chamber setup. Finally, biliary excretion of Ez-gluc was measured in vivo after duodenal delivery of ezetimibe in wild-type, Abcc3-/-, Abcc2-/-, Abcg2-/- and Abcg2-/-/Abcc2-/- mice. ABCC3-, ABCC2- and ABCG2-mediated transport was dose dependently inhibited by Ez-gluc. In the Ussing chamber Ez-gluc recovered from the basolateral side was significantly reduced in duodenal (2.2%), in jejunal (23%) and in ileal (23%) tissue of Abcc3-/- compared to wild-type mice. Biliary excretion of Ez-gluc was significantly reduced in Abcc3-/- (34%), Abcc2-/- (56%) and Abcg2-/-/Abcc2-/- (2.5%) compared to wild-type mice. These data demonstrate that enterohepatic circulation of Ez-gluc strongly depends on the joint function of Abcc3, Abcc2 and Abcg2.
PMID:19443695 de Waart DR et al; Drug Metab Dispos. 2009 May 14. (Epub ahead of print).
It is not known whether ezetimibe is excreted into human breast milk. In rat studies, exposure to total ezetimibe in nursing pups was up to half of that observed in maternal plasma.
Thomson Health Care Inc.; Physicians' Desk Reference 63 ed., Montvale, NJ 2009, p. 2158
After oral administration, ezetimibe is absorbed and extensively conjugated to a pharmacologically active phenolic glucuronide (ezetimibe-glucuronide). After a single 10-mg dose of Zetia to fasted adults, mean ezetimibe peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) of 3.4 to 5.5 ng/mL were attained within 4 to 12 hours (Tmax). Ezetimibe-glucuronide mean Cmax values of 45 to 71 ng/mL were achieved between 1 and 2 hours (Tmax). There was no substantial deviation from dose proportionality between 5 and 20 mg. The absolute bioavailability of ezetimibe cannot be determined, as the compound is virtually insoluble in aqueous media suitable for injection.
Thomson Health Care Inc.; Physicians' Desk Reference 63 ed., Montvale, NJ 2009, p. 2159
In humans, ezetimibe is rapidly and extensively metabolized via a phase II glucuronide conjugation reaction in the small intestine and liver to form its main phenolic metabolite, ezetimibe glucuronide. The main human liver and/or intestinal uridine 5-diphosphate (UDP)-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) enzymes responsible for the glucuronidation of ezetimibe were shown to be UGT1A1, 1A3, and 2B15 _in vitro_. Minimal phase I reaction involving oxidation of ezetimibe also occurs to form SCH 57871, and human jejunum microsomes also produced trace levels of a benzylic glucuronide (SCH 488128). Ezetimibe glucuronide accounts for 80-90% of the total circulating compound in plasma, and retains some pharmacological activity in inhibiting intestinal cholesterol uptake. In humans, ezetimibe and ezetimibe-glucuronide constitutes approximately 93% of the total drug in plasma. Plasma concentration-time profiles exhibit multiple peaks, suggestive of enterohepatic recycling, and about 20% of the drug distributed is reabsorbed due to enterohepatic recirculation.
Ezetimibe is primarily metabolized in the small intestine and liver via glucuronide conjugation (a phase II reaction) with subsequent biliary and renal excretion. Minimal oxidative metabolism (a phase I reaction) has been observed in all species evaluated. In humans, ezetimibe is rapidly metabolized to ezetimibe-glucuronide. Ezetimibe and ezetimibe-glucuronide are the major drug-derived compounds detected in plasma, constituting approximately 10 to 20% and 80 to 90% of the total drug in plasma, respectively. Both ezetimibe and ezetimibe-glucuronide are eliminated from plasma with a half-life of approximately 22 hours for both ezetimibe and ezetimibe-glucuronide. Plasma concentration-time profiles exhibit multiple peaks, suggesting enterohepatic recycling. Following oral administration of (14)C-ezetimibe (20 mg) to human subjects, total ezetimibe (ezetimibe + ezetimibe-glucuronide) accounted for approximately 93% of the total radioactivity in plasma. After 48 hours, there were no detectable levels of radioactivity in the plasma. Approximately 78% and 11% of the administered radioactivity were recovered in the feces and urine, respectively, over a 10-day collection period. Ezetimibe was the major component in feces and accounted for 69% of the administered dose, while ezetimibe-glucuronide was the major component in urine and accounted for 9% of the administered dose.
Thomson Health Care Inc.; Physicians' Desk Reference 63 ed., Montvale, NJ 2009, p. 21259
Ezetimibe has known human metabolites that include Ezetimibe-glucuronide.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
Both ezetimibe and ezetimibe-glucuronide display an approximate half-life of 22 hours.
Both ezetimibe and ezetimibe-glucuronide are eliminated from plasma with a half-life of approximately 22 hours for both ezetimibe and ezetimibe-glucuronide.
Thomson Health Care Inc.; Physicians' Desk Reference 63 ed., Montvale, NJ 2009, p. 2159
Ezetimibe mediates its blood cholesterol-lowering effect via selectively inhibiting the absorption of cholesterol and phytosterol by the small intestine without altering the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and nutrients. The primary target of ezetimibe is the cholesterol transport protein Niemann-Pick C1-Like 1 (NPC1L1) protein. NPC1L1 is expressed on enterocytes/gut lumen (apical) as well as the hepatobiliary (canalicular) interface and plays a role in facilitating internalization of free cholesterol into the enterocyte in conjunction with the adaptor protein 2 (AP2) complex and clathrin. Once cholesterol in the gut lumen or bile is incorporated into the cell membrane of enterocytes, it binds to the sterol-sensing domain of NPC1L1 and forms a NPC1L1/cholesterol complex. The complex is then internalized or endocytosed by joining to AP2 clathrin, forming a vesicle complex that is translocated for storage in the endocytic recycling compartment. Ezetimibe does not require exocrine pancreatic function for its pharmacological activity; rather, it localizes and appears to act at the brush border of the small intestine. Ezetimibe selectively blocks the NPC1L1 protein in the jejunal brush border, reducing the uptake of intestinal lumen micelles into the enterocyte. Overall, ezetimibe causes a decrease in the delivery of intestinal cholesterol to the liver and reduction of hepatic cholesterol stores and an increase in clearance of cholesterol from the blood. While the full mechanism of action of ezetimibe in reducing the entry of cholesterol into both enterocytes and hepatocytes is not fully understood, one study proposed that ezetimibe prevents the NPC1L1/sterol complex from interacting with AP2 in clathrin coated vesicles and induces a conformational change in NPC1L1, rendering it incapable of binding to sterols. Another study suggested that ezetimibe disrupts the function of other protein complexes involved in regulating cholesterol uptake, including the CAV1annexin 2 heterocomplex.
Niemann-Pick C1-like 1 (NPC1L1) is a polytopic transmembrane protein that plays a critical role in cholesterol absorption. Ezetimibe, a hypocholesterolemic drug, has been reported to bind NPC1L1 and block cholesterol absorption. However, the molecular mechanism of NPC1L1-mediated cholesterol uptake and how ezetimibe inhibits this process are poorly defined. Here we find that cholesterol specifically promotes the internalization of NPC1L1 and that this process requires microfilaments and the clathrin/AP2 complex. Blocking NPC1L1 endocytosis dramatically decreases cholesterol internalization, indicating that NPC1L1 mediates cholesterol uptake via its vesicular endocytosis. Ezetimibe prevents NPC1L1 from incorporating into clathrin-coated vesicles and thus inhibits cholesterol uptake. ...
PMID:18522832 Ge L et al; Cell Metab 7 (6): 508-19 (2008).
Niemann-Pick C1-like protein (NPC1L1) mediates the absorption of dietary cholesterol in the proximal region of the intestine, a process that is blocked by cholesterol absorption inhibitors (CAIs), including ezetimibe. Using a proteomic approach, /it is/ demonstrated that NPC1L1 is the protein to which ezetimibe and its analogs bind. Next, ... the site of interaction of ezetimibe analogs /was determined/ with NPC1L1 by exploiting the different binding affinities of mouse and dog NPC1L1 for the radioligand analog of ezetimibe, [(3)H]AS. Chimeric and mutational studies indicate that high-affinity binding of [(3)H]AS to dog NPC1L1 depends on molecular determinants present in a 61-aa region of a large extracellular domain (loop C), where Phe-532 and Met-543 appear to be key contributors. These data suggest that the [(3)H]AS-binding site resides in the intestinal lumen and are consistent with preclinical data demonstrating in vivo efficacy of a minimally bioavailable CAI. Furthermore, these determinants of [(3)H]AS binding lie immediately adjacent to a hotspot of human NPC1L1 polymorphisms correlated with hypoabsorption of cholesterol. These observations, taken together with the recently described binding of cholesterol to the N terminus (loop A) of the close NPC1L1 homologue, NPC1, may provide a molecular basis for understanding ezetimibe inhibition of NPC1L1-mediated cholesterol absorption. Specifically, ezetimibe binding to an extracellular site distinct from where cholesterol binds prevents conformational changes in NPC1L1 that are necessary for the translocation of cholesterol across the membrane.
PMID:18682566 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2516253 Weinglass AB et al; Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105 (32): 11140-5 (2008).
Ezetimibe has a mechanism of action that differs from those of other classes of cholesterol-reducing compounds (statins, bile acid sequestrants [resins], fibric acid derivatives, and plant stanols). The molecular target of ezetimibe has been shown to be the sterol transporter, Niemann-Pick C1-Like 1 (NPC1L1), which is involved in the intestinal uptake of cholesterol and phytosterols. Ezetimibe does not inhibit cholesterol synthesis in the liver, or increase bile acid excretion. Instead, ezetimibe localizes at the brush border of the small intestine and inhibits the absorption of cholesterol, leading to a decrease in the delivery of intestinal cholesterol to the liver. This causes a reduction of hepatic cholesterol stores and an increase in clearance of cholesterol from the blood; this distinct mechanism is complementary to that of statins and of fenofibrate.
Thomson Health Care Inc.; Physicians' Desk Reference 63 ed., Montvale, NJ 2009, p. 2159

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS

Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ANALYTICAL

ABOUT THIS PAGE
36
PharmaCompass offers a list of Ezetimibe API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Ezetimibe manufacturer or Ezetimibe supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Ezetimibe manufacturer or Ezetimibe supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Ezetimibe API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Ezetimibe API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Ezetimibe Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Ezetimibe Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Ezetimibe manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Ezetimibe, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Ezetimibe manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Ezetimibe API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Ezetimibe manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Ezetimibe supplier is an individual or a company that provides Ezetimibe active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Ezetimibe finished formulations upon request. The Ezetimibe suppliers may include Ezetimibe API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Ezetimibe suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Ezetimibe DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Ezetimibe active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Ezetimibe DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Ezetimibe USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Ezetimibe DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Ezetimibe USDMF includes data on Ezetimibe's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Ezetimibe USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Ezetimibe suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) established the Japan Drug Master File (JDMF), also known as the Master File (MF), to permit Japanese and foreign manufacturers of drug substances, intermediates, excipients, raw materials, and packaging materials (‘Products’) to voluntarily register confidential information about the production and management of their products in Japan.
The Ezetimibe Drug Master File in Japan (Ezetimibe JDMF) empowers Ezetimibe API manufacturers to present comprehensive information (e.g., production methods, data, etc.) to the review authority, i.e., PMDA (Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Agency).
PMDA reviews the Ezetimibe JDMF during the approval evaluation for pharmaceutical products. At the time of Ezetimibe JDMF registration, PMDA checks if the format is accurate, if the necessary items have been included (application), and if data has been attached.
click here to find a list of Ezetimibe suppliers with JDMF on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a Ezetimibe Drug Master File in Korea (Ezetimibe KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of Ezetimibe. The MFDS reviews the Ezetimibe KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the Ezetimibe KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a Ezetimibe KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their Ezetimibe API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of Ezetimibe suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Ezetimibe written confirmation (Ezetimibe WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Ezetimibe manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Ezetimibe active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Ezetimibe APIs or Ezetimibe finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Ezetimibe WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Ezetimibe suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Ezetimibe as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Ezetimibe API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Ezetimibe as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Ezetimibe and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Ezetimibe NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Ezetimibe suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Ezetimibe Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Ezetimibe GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Ezetimibe GMP manufacturer or Ezetimibe GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Ezetimibe CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Ezetimibe's compliance with Ezetimibe specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Ezetimibe CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Ezetimibe CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Ezetimibe may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Ezetimibe EP), Ezetimibe JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Ezetimibe USP).

