



API Suppliers

US DMFs Filed
0

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
EU WC
0
Listed Suppliers
0
0

USA (Orange Book)

Europe

Canada
0

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
0
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
0

1. Bextra
2. Sc 65872
3. Sc-65872
1. 181695-72-7
2. Bextra
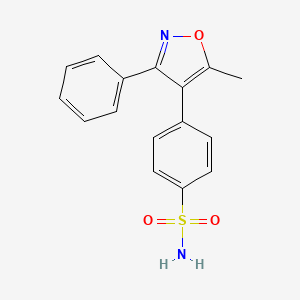
3. 4-(5-methyl-3-phenylisoxazol-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide
4. Valdyn
5. Sc 65872
6. Sc-65872
7. 4-(5-methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazolyl)benzenesulfonamide
8. Kudeq
9. 4-(5-methyl-3-phenyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide
10. Benzenesulfonamide, 4-(5-methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazolyl)-
11. Ym-974
12. P-(5-methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazolyl)benzenesulfonamide
13. Chembl865
14. Nsc-759846
15. 4-(5-methyl-3-phenyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl)benzene-1-sulfonamide
16. Chebi:63634
17. Cox
18. Ncgc00095129-01
19. Valdecoxib [usan]
20. 2919279q3w
21. Dsstox_cid_24226
22. Dsstox_rid_80128
23. Dsstox_gsid_44226
24. Valecoxib
25. Smr000466327
26. Cas-181695-72-7
27. Hsdb 7302
28. Valdecoxib (usan/inn)
29. 4-[5-methyl-3-phenylisoxazol-4-yl]benzenesulfonamide
30. Valdecoxibum
31. 4-(5-methyl-3-phenyl-isoxazol-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide
32. Valdecoxib [usan:inn:ban]
33. Unii-2919279q3w
34. Mfcd00950568
35. 4-(5-methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazolyl) Benzenesulfonamide
36. Nd-0214
37. Spectrum_001747
38. 2aw1
39. Valdecoxib [mi]
40. Valdecoxib [inn]
41. Spectrum2_000508
42. Spectrum3_001001
43. Spectrum4_001129
44. Spectrum5_001476
45. Valdecoxib [hsdb]
46. Valdecoxib [vandf]
47. Schembl3356
48. Valdecoxib [mart.]
49. Valdecoxib [who-dd]
50. Bspbio_002721
51. Kbiogr_001617
52. Kbioss_002227
53. Mls000759433
54. Mls001165699
55. Mls001195631
56. Mls001424105
57. Spectrum1504302
58. Valdecoxib [ema Epar]
59. Spbio_000435
60. 4-(methyl-3-phenyl-isoxazol-4-yl)-benzenesulfonamide
61. Cid_119607
62. Gtpl2894
63. Zinc6694
64. Dtxsid6044226
65. Valdecoxib [orange Book]
66. Valdecoxib, >=98% (hplc)
67. Bdbm13063
68. Kbio2_002227
69. Kbio2_004795
70. Kbio2_007363
71. Kbio3_001941
72. Ex-a241
73. Hms1922j21
74. Hms2051p07
75. Hms2232p23
76. Hms3372d12
77. Hms3393p07
78. Hms3652i04
79. Hms3715l18
80. Hms3885o20
81. Pharmakon1600-01504302
82. Amy31078
83. Bcp02419
84. Tox21_111438
85. Ac-120
86. Ccg-39589
87. Nsc759846
88. S4049
89. Akos000280920
90. Tox21_111438_1
91. Cs-1674
92. Db00580
93. Nc00184
94. Nsc 759846
95. Sb19519
96. Mrf-0000216
97. Ncgc00095129-02
98. Ncgc00095129-03
99. Ncgc00095129-06
100. Valdecoxib, Analytical Reference Material
101. Hy-15762
102. Db-044435
103. Unm-0000305814
104. Ft-0631199
105. Ft-0675755
106. Sw197564-2
107. A13342
108. C21552
109. D02709
110. Ab00639996-08
111. Ab00639996_10
112. 695v727
113. A812629
114. Q347613
115. Sr-01000759421
116. J-011613
117. J-513600
118. Sr-01000759421-4
119. 4-[5-methyl-3-phenylisoxazol-4-yl]benzensulfonamide
120. Brd-k12994359-001-02-8
121. Brd-k12994359-001-14-3
122. 4-(5-methyl-3-phenyl-isoxazol-4-yl)-benzenesulfonamide
123. Benzenesulfonamide, 4-(5-methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazolyl)- (9ci)
124. Vlx
| Molecular Weight | 314.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H14N2O3S |
| XLogP3 | 2.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 314.07251349 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 314.07251349 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 94.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 462 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Valdecoxib is indicated for the relief of the signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis and adult rheumatoid arthritis. /Included in US product labeling/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 2775
Valdecoxib is indicated for treatment of primary dysmenorrhea. /Included in US product labeling/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 2775
Serious, potentially life-threatening skin reactions, including exfoliative dermatitis, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, or toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), have been reported during postmarketing surveillance of valdecoxib. Fatalities due to Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis have been reported. While serious reactions may occur at any time during therapy with valdecoxib, the risk of such reactions appears to be highest within the first 2 weeks of therapy. While patients with a history of sulfonamide hypersensitivity may be at greater risk for skin reactions, patients without such a history also are at risk for serious skin reactions. These reactions are rare but have been reported at a greater frequency with valdecoxib than with other selective COX-2 inhibitors (e.g., celecoxib). Discontinue valdecoxib at the first appearance of a rash or any other manifestation of hypersensitivity.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1938
Risk of potentially fatal GI ulceration, bleeding, and perforation. Most studies indicate less risk of GI ulceration than prototypical /SRP: NSAIDs/; however, the relative risk remains to be established. Use with caution in patients at risk for GI bleeding (e.g., history of GI bleeding or ulceration, treatment with oral corticosteroids or anticoagulants, longer duration of /SRP: NSAID/ therapy, geriatric patients, debilitation, smokers, or alcohol dependence). Consider alternative therapy in those at high risk for GI bleeding. ...
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1938
Severe (rarely fatal) anaphylactoid reactions have occurred in patients receiving /SRP: NSAIDs/, and anaphylactoid reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis, angioedema) have been reported during postmarketing surveillance of valdecoxib. Such reactions occurred in patients with or without a history of allergic-type reactions to sulfonamides. ...Cross-sensitivity between aspirin and other /SRP: NSAIDs/ may occur. Do not use in patients with bronchospastic aspirin sensitivity. Avoid use in patients with aspirin triad. Caution in patients with preexisting asthma, as bronchospasms may occur.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1938
Conditions predisposing to and/or exacerbated by fluid retention (congestive heart disease or edema, pre-existing hypertension), valdecoxib may cause additive fluid retention or edema; also, risk of renal failure is increased in patients with congestive heart disease; valdecoxib should be initiated at the lowest dose in these patients).
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 2776
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for VALDECOXIB (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the treatment of osteoarthritis and dysmenorrhoea
FDA Label
Symptomatic relief in the treatment of osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis .
Treatment of primary dysmenorrhoea.
The decision to prescribe a selective COX-2 inhibitor should be based on an assessment of the individual patient's overall risk (see sections 4. 3, 4. 4).
Symptomatic relief in the treatment of osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis .
Treatment of primary dysmenorrhoea.
Symptomatic relief in the treatment of osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis .
Treatment of primary dysmenorrhoea.
Valdecoxib, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor, is classified as a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). Valdecoxib is used for its anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic activities in the management of osteoarthritis (OA) and for the treatment of dysmenorrhea or acute pain. Unlike celecoxib, valdecoxib lacks a sulfonamide chain and does not require CYP450 enzymes for metabolism.
Cyclooxygenase 2 Inhibitors
A subclass of cyclooxygenase inhibitors with specificity for CYCLOOXYGENASE-2. (See all compounds classified as Cyclooxygenase 2 Inhibitors.)
M01AH03
M01AH03
M01AH03
M - Musculo-skeletal system
M01 - Antiinflammatory and antirheumatic products
M01A - Antiinflammatory and antirheumatic products, non-steroids
M01AH - Coxibs
M01AH03 - Valdecoxib
Absorption
Oral bioavailability is 83%.
Route of Elimination
Valdecoxib is eliminated predominantly via hepatic metabolism with less than 5% of the dose excreted unchanged in the urine and feces. About 70% of the dose is excreted in the urine as metabolites, and about 20% as valdecoxib N-glucuronide.
Volume of Distribution
86 L
Clearance
oral cl=6 L/h
6 7 L/h [In patients undergoing hemodialysis]
6 7 L/h [healthy elderly subjects]
At recommended doses, the mean oral bioavailability is 83%. The peak plasma concentration and area under the plasma concentration-time curve are roughly proportional across the clinical dose range. Valdecoxib may be coadministered with meals. Peak-plasma concentrations and extent of absorption were not affected after valdecoxib was taken with a high fat meal.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 2775
Time to peak concentration: Approximately 3 hours. Note: Time to peak concentration was delayed by 1 to 2 hours when administered with a high fat meal.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 2775
Steady state apparent volume of distribution (Vss/F) of valdecoxib is approximately 86 L after oral administration. Valdecoxib and its active metabolite preferentially partition into erythrocytes with a blood to plasma concentration ratio of about 2.5:1. This ratio remains approximately constant with time and therapeutic blood concentrations.
Physicians Desk Reference. 58th ed. Thomson PDR. Montvale, NJ 2004., p. 2574
Protein binding: Very high (98%).
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 2775
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for VALDECOXIB (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Hepatic (involves CYP3A4 and 2C9)
One active metabolite of valdecoxib has been identified in human plasma at approximately 10% the concentration of valdecoxib. This metabolite, which is a less potent COX-2 specific inhibitor than the parent also undergoes extensive metabolism and constitutes <2% of the valdecoxib dose excreted in the urine and feces. Due to the low concentration in the systemic circulation, it is not likely to contribute significantly to the efficacy profile of valdecoxib.
Physicians Desk Reference. 58th ed. Thomson PDR. Montvale, NJ 2004., p. 2574
In humans, valdecoxib undergoes extensive hepatic metabolism involving both P450 isoenzymes (3A4 and 2C9) and non-P450 dependent pathways (i.e., glucuronidation).
Physicians Desk Reference. 58th ed. Thomson PDR. Montvale, NJ 2004., p. 2574
Valdecoxib has known human metabolites that include 4-[3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-5-methyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl]benzene-1-sulfonamide and 4-[5-(hydroxymethyl)-3-phenyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl]benzene-1-sulfonamide.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
8-11 hours
Elimination: 8 to 11 hours. Terminal: 8.11 hours.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 2775
Both COX-1 and COX-2 catalyze the conversion of arachidonic acid to prostaglandin (PG) H2, the precursor of PGs and thromboxane. Valdecoxib selectively inhibits the cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) enzyme, important for the mediation of inflammation and pain. Unlike non-selective NSAIDs, valdecoxib does not inhibit platelet aggregation.
Valdecoxib is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with antiinflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic therapeutic effects. It has been proposed that valdecoxib inhibits the activity of the enzyme cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), resulting in a decreased formation of precursors of prostaglandins. However, unlike most NSAIDs, valdecoxib does not inhibit cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) isoenzyme in humans at therapeutic concentrations.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 2775


