
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
VMF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
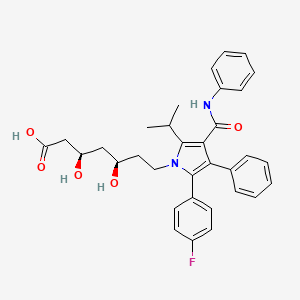

1. (3r,5r)-7-(2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-isopropyl-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-1h-pyrrol-1-yl)-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic Acid
2. Atorvastatin Calcium
3. Atorvastatin Calcium Anhydrous
4. Atorvastatin Calcium Hydrate
5. Atorvastatin Calcium Trihydrate
6. Atorvastatin, Calcium Salt
7. Ci 981
8. Ci-981
9. Ci981
10. Lipitor
11. Liptonorm
1. 134523-00-5
2. Cardyl
3. Lipitor
4. 110862-48-1
5. Torvast
6. Atorvastatin Calcium
7. Rel-atorvastatin
8. (3r,5r)-7-(2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-isopropyl-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-1h-pyrrol-1-yl)-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic Acid
9. Atorvastatin (inn)
10. Ci 981
11. Lipitor (tn)
12. Tozalip
13. Xavator
14. (3r,5r)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-propan-2-ylpyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic Acid
15. A0jwa85v8f
16. Chembl1487
17. (r-(r*,r*))-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-beta,delta-dihydroxy-5-(1-methylethyl)-3-phenyl-4-((phenylamino)carbonyl)-1h-pyrrole-1-heptanoic Acid
18. Chebi:39548
19. (3r,5r)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1h-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic Acid
20. 134523-03-8
21. Atorvastatin [inn]
22. Atorvastatin [inn:ban]
23. 1h-pyrrole-1-heptanoic Acid, 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-beta,delta-dihydroxy-5-(1-methylethyl)-3-phenyl-4-((phenylamino)carbonyl)-, (r-(r*,r*))-
24. 7-[2-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-5-isopropyl-3-phenyl-4-phenylcarbamoyl-pyrrol-1-yl]- 3,5-dihydroxy-heptanoic Acid
25. Atorvastatin Calcium Salt
26. Atorvastatina
27. Atorvastatine
28. Atrovastin
29. Atofast
30. Atorcor
31. Atorlip
32. Lipilou
33. Lipinon
34. Atorin
35. Ator
36. Lipitor(tm)
37. (3r,5r)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-(1-methylethyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-1h-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic Acid
38. (3r,5r)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-isopropyl-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxy-heptanoic Acid
39. (3r,5r)-7-[3-(anilinocarbonyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-isopropyl-4-phenyl-1h-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic Acid
40. Sortis (tn)
41. Ccris 7159
42. Hsdb 7039
43. Ncgc00159458-03
44. Unii-a0jwa85v8f
45. Atorvastatinum
46. (betar,deltar)-2-(p-fluorophenyl)-beta,delta-dihydroxy-5-isopropyl-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)pyrrole-1-heptanoic Acid
47. Atorvastatin & Primycin
48. Atorvastatin [mi]
49. Dsstox_cid_9868
50. Atorvastatin [hsdb]
51. Schembl3831
52. Atorvastatin [vandf]
53. Dsstox_rid_78825
54. Dsstox_gsid_29868
55. Atorvastatin [who-dd]
56. Bidd:gt0336
57. Atorvastatin (relative Stereo)
58. Gtpl2949
59. Dtxsid8029868
60. Bdbm22164
61. Dtxsid60274003
62. Hms3715l05
63. Hms3886c20
64. Lipilou; Tozalip; Torvast; Cardyl
65. (3s,5s)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-propan-2-ylpyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic Acid
66. Act03225
67. Hy-b0589
68. Zinc3920719
69. Tox21_302417
70. Mfcd00899261
71. S5715
72. Akos000281127
73. Ac-9386
74. Ccg-221172
75. Db01076
76. Mrf-0000761
77. Ncgc00159458-02
78. Ncgc00159458-20
79. Ncgc00255181-01
80. (3r,5r)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-isopropyl-3-phenyl-4-phenylcarbamoylpyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic Acid
81. 1h-pyrrole-1-heptanoic Acid, 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-beta,delta-dihydroxy-5-(1-methylethyl)-3-phenyl-4-((phenylamino)carbonyl)-, (betar,deltar)-
82. 7-[2-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-5-isopropyl-3-phenyl-4-phenylcarbamoyl-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxy-heptanoic Acid
83. As-35260
84. Cas-134523-00-5
85. C06834
86. D07474
87. 523a005
88. A802259
89. A806791
90. A806793
91. Q668093
92. Sr-01000872702
93. Sr-01000872702-1
94. Brd-k69726342-001-02-6
95. Atorvastatin Is Known As An Hmg-coa Reductase Inhibitor.
96. (.beta.r,.delta.r)-2-(p-fluorophenyl)-.beta.,.delta.-dihydroxy-5-isopropyl-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)pyrrole-1-heptanoic Acid
97. (3r,5r)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-propan-2-yl-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxy-heptanoic Acid
98. (3r,5r)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-isopropyl-3-phenyl-4-phenylcarbamoyl-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxy-heptanoic Acid
99. (3r,5r)-7-[3-(anilinocarbonyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-phenyl-2-(propan-2-yl)-1h-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic Acid
100. 1h-pyrrole-1-heptanoic Acid, 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-.beta.,.delta.-dihydroxy-5-(1-methylethyl)-3-phenyl-4-((phenylamino)carbonyl)-, (r-(r*,r*))-
101. Sodium 7-[5-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-isopropyl-4-phenyl-3-(phenylcarbamoyl)-2,3-dihydropyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxy-heptanoate
| Molecular Weight | 558.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C33H35FN2O5 |
| XLogP3 | 5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 12 |
| Exact Mass | 558.25300038 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 558.25300038 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 112 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 41 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 822 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lipitor |
| PubMed Health | Atorvastatin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihyperlipidemic |
| Drug Label | LIPITOR (atorvastatin calcium) is a synthetic lipid-lowering agent. Atorvastatin is an inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase. This enzyme catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate, an early and rate-limiting... |
| Active Ingredient | Atorvastatin calcium |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 20mg base; eq 40mg base; eq 80mg base; eq 10mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pfizer |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lipitor |
| PubMed Health | Atorvastatin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihyperlipidemic |
| Drug Label | LIPITOR (atorvastatin calcium) is a synthetic lipid-lowering agent. Atorvastatin is an inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase. This enzyme catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate, an early and rate-limiting... |
| Active Ingredient | Atorvastatin calcium |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 20mg base; eq 40mg base; eq 80mg base; eq 10mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pfizer |
Anticholesteremic Agents; Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA Reductase Inhibitors
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Atorvastatin. Online file (MeSH, 2016). Available from, as of October 28, 2016: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/2016/mesh_browser/MBrowser.html
In adult patients without clinically evident coronary heart disease, but with multiple risk factors for coronary heart disease such as age, smoking, hypertension, low HDL-C, or a family history of early coronary heart disease, Lipitor is indicated to: Reduce the risk of myocardial infarction; Reduce the risk of stroke; Reduce the risk for revascularization procedures and angina. /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Lipitor (Atorvastatin Calcium) Tablet, Film-coated (Updated: November 2015). Available from, as of October 28, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=c6e131fe-e7df-4876-83f7-9156fc4e8228
In patients with type 2 diabetes, and without clinically evident coronary heart disease, but with multiple risk factors for coronary heart disease such as retinopathy, albuminuria, smoking, or hypertension, Lipitor is indicated to: Reduce the risk of myocardial infarction; Reduce the risk of stroke. /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Lipitor (Atorvastatin Calcium) Tablet, Film-coated (Updated: November 2015). Available from, as of October 28, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=c6e131fe-e7df-4876-83f7-9156fc4e8228
In patients with clinically evident coronary heart disease, Lipitor is indicated to: Reduce the risk of non-fatal myocardial infarction; Reduce the risk of fatal and non-fatal stroke; Reduce the risk for revascularization procedures; Reduce the risk of hospitalization for congestive heart failure (CHF); Reduce the risk of angina. /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Lipitor (Atorvastatin Calcium) Tablet, Film-coated (Updated: November 2015). Available from, as of October 28, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=c6e131fe-e7df-4876-83f7-9156fc4e8228
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for ATORVASTATIN (15 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Lipitor is contraindicated in women who are or may become pregnant. Serum cholesterol and triglycerides increase during normal pregnancy. Lipid lowering drugs offer no benefit during pregnancy because cholesterol and cholesterol derivatives are needed for normal fetal development. Atherosclerosis is a chronic process, and discontinuation of lipid-lowering drugs during pregnancy should have little impact on long-term outcomes of primary hypercholesterolemia therapy.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Lipitor (Atorvastatin Calcium) Tablet, Film-coated (Updated: November 2015). Available from, as of October 28, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=c6e131fe-e7df-4876-83f7-9156fc4e8228
Statins may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Lipitor should be administered to women of childbearing potential only when such patients are highly unlikely to conceive and have been informed of the potential hazards. If the woman becomes pregnant while taking Lipitor, it should be discontinued immediately and the patient advised again as to the potential hazards to the fetus and the lack of known clinical benefit with continued use during pregnancy.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Lipitor (Atorvastatin Calcium) Tablet, Film-coated (Updated: November 2015). Available from, as of October 28, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=c6e131fe-e7df-4876-83f7-9156fc4e8228
It is not known whether atorvastatin is excreted in human milk, but a small amount of another drug in this class does pass into breast milk. Nursing rat pups had plasma and liver drug levels of 50% and 40%, respectively, of that in their mother's milk. Animal breast milk drug levels may not accurately reflect human breast milk levels. Because another drug in this class passes into human milk and because statins have a potential to cause serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, women requiring Lipitor treatment should be advised not to nurse their infants.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Lipitor (Atorvastatin Calcium) Tablet, Film-coated (Updated: November 2015). Available from, as of October 28, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=c6e131fe-e7df-4876-83f7-9156fc4e8228
Myopathy (defined as muscle aches or weakness in conjunction with increases in creatine kinase [CK, creatine phosphokinase, CPK] concentrations exceeding 10 times the upper limit of normal [ULN]) has been reported occasionally in patients receiving statins, including atorvastatin. Rhabdomyolysis with acute renal failure secondary to myoglobinuria also has been reported rarely in patients receiving statins, including atorvastatin.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2016; Drug Information 2016. Bethesda, MD. 2016, p. 1844
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for ATORVASTATIN (33 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Atorvastatin is indicated for the treatment of several types of dyslipidemias, including primary hyperlipidemia and mixed dyslipidemia in adults, hypertriglyceridemia, primary dysbetalipoproteinemia, homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia, and heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia in adolescent patients with failed dietary modifications. Dyslipidemia describes an elevation of plasma cholesterol, triglycerides or both as well as to the presence of low levels of high-density lipoprotein. This condition represents an increased risk for the development of atherosclerosis. Atorvastatin is indicated, in combination with dietary modifications, to prevent cardiovascular events in patients with cardiac risk factors and/or abnormal lipid profiles. Atorvastatin can be used as a preventive agent for myocardial infarction, stroke, revascularization, and angina, in patients without coronary heart disease but with multiple risk factors and in patients with type 2 diabetes without coronary heart disease but multiple risk factors. Atorvastatin may be used as a preventive agent for non-fatal myocardial infarction, fatal and non-fatal stroke, revascularization procedures, hospitalization for congestive heart failure and angina in patients with coronary heart disease. Prescribing of statin medications is considered standard practice following any cardiovascular events and for people with a moderate to high risk of development of CVD. Statin-indicated conditions include diabetes mellitus, clinical atherosclerosis (including myocardial infarction, acute coronary syndromes, stable angina, documented coronary artery disease, stroke, trans ischemic attack (TIA), documented carotid disease, peripheral artery disease, and claudication), abdominal aortic aneurysm, chronic kidney disease, and severely elevated LDL-C levels.
FDA Label
Atorvastatin is an oral antilipemic agent that reversibly inhibits HMG-CoA reductase. It lowers total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C), apolipoprotein B (apo B), non-high density lipoprotein-cholesterol (non-HDL-C), and triglyceride (TG) plasma concentrations while increasing HDL-C concentrations. High LDL-C, low HDL-C and high TG concentrations in the plasma are associated with increased risk of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. The total cholesterol to HDL-C ratio is a strong predictor of coronary artery disease, and high ratios are associated with a higher risk of disease. Increased levels of HDL-C are associated with lower cardiovascular risk. By decreasing LDL-C and TG and increasing HDL-C, atorvastatin reduces the risk of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Elevated cholesterol levels (and high low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels in particular) are an important risk factor for the development of CVD. Clinical studies have shown that atorvastatin reduces LDL-C and total cholesterol by 36-53%. In patients with dysbetalipoproteinemia, atorvastatin reduced the levels of intermediate-density lipoprotein cholesterol. It has also been suggested that atorvastatin can limit the extent of angiogenesis, which can be useful in the treatment of chronic subdural hematoma. **Myopathy/Rhabdomyolysis** Atorvastatin, like other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, is associated with a risk of drug-induced myopathy characterized by muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness in conjunction with elevated levels of creatine kinase (CK). Myopathy often manifests as rhabdomyolysis with or without acute renal failure secondary to myoglobinuria. The risk of statin-induced myopathy is dose-related, and the symptoms of myopathy are typically resolved upon drug discontinuation. Results from observational studies suggest that 10-15% of people taking statins may experience muscle aches at some point during treatment. **Liver Dysfunction** Statins, like some other lipid-lowering therapies, have been associated with biochemical abnormalities of liver function. Persistent elevations (> 3 times the upper limit of normal [ULN] occurring on two or more occasions) in serum transaminases occurred in 0.7% of patients who received atorvastatin in clinical trials. This effect appears to be dose-related. **Endocrine Effects** Statins are associated with a risk of increased serum HbA1c and glucose levels. An _in vitro_ study demonstrated a dose-dependent cytotoxic effect on human pancreatic islet cells following treatment with atorvastatin. Moreover, insulin secretion rates decreased relative to control. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors interfere with cholesterol synthesis and may theoretically interfere with the production of adrenal and/or gonadal steroids. Clinical studies with atorvastatin and other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors have suggested that these agents do not affect plasma cortisol concentrations, basal plasma testosterone concentration, or adrenal reserve. However, the effect of statins on male fertility has not been fully investigated. The effects of statins on the pituitary-gonadal axis in premenopausal women are unknown. **Cardiovascular** Significant decreases in circulating ubiquinone levels in patients treated with atorvastatin and other statins have been observed. The clinical significance of a potential long-term statin-induced deficiency of ubiquinone has not been established. It has been reported that a decrease in myocardial ubiquinone levels could lead to impaired cardiac function in patients with borderline congestive heart failure. **Lipoprotein A** In some patients, the beneficial effect of lowered total cholesterol and LDL-C levels may be partly blunted by the concomitant increase in Lp(a) lipoprotein concentrations. Present knowledge suggests the importance of high Lp(a) levels as an emerging risk factor for coronary heart disease. Further studies have demonstrated statins affect Lp(a) levels differently in patients with dyslipidemia depending on their apo(a) phenotype; statins increase Lp(a) levels exclusively in patients with the low molecular weight apo(a) phenotype.
Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA Reductase Inhibitors
Compounds that inhibit HYDROXYMETHYLGLUTARYL COA REDUCTASES. They have been shown to directly lower CHOLESTEROL synthesis. (See all compounds classified as Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA Reductase Inhibitors.)
Anticholesteremic Agents
Substances used to lower plasma cholesterol levels. (See all compounds classified as Anticholesteremic Agents.)
C10AA05
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
C - Cardiovascular system
C10 - Lipid modifying agents
C10A - Lipid modifying agents, plain
C10AA - Hmg coa reductase inhibitors
C10AA05 - Atorvastatin
Absorption
Atorvastatin presents a dose-dependent and non-linear pharmacokinetic profile. It is very rapidly absorbed after oral administration. After the administration of a dose of 40 mg, its peak plasma concentration of 28 ng/ml is reached 1-2 hours after initial administration with an AUC of about 200 ngh/ml. Atorvastatin undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism in the wall of the gut and the liver, resulting in an absolute oral bioavailability of 14%. Plasma atorvastatin concentrations are lower (approximately 30% for Cmax and AUC) following evening drug administration compared with morning. However, LDL-C reduction is the same regardless of the time of day of drug administration. Administration of atorvastatin with food results in prolonged Tmax and a reduction in Cmax and AUC. Breast Cancer Resistance Protein (BCRP) is a membrane-bound protein that plays an important role in the absorption of atorvastatin. Evidence from pharmacogenetic studies of c.421C>A single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the gene for BCRP has demonstrated that individuals with the 421AA genotype have reduced functional activity and 1.72-fold higher AUC for atorvastatin compared to study individuals with the control 421CC genotype. This has important implications for the variation in response to the drug in terms of efficacy and toxicity, particularly as the BCRP c.421C>A polymorphism occurs more frequently in Asian populations than in Caucasians. Other statin drugs impacted by this polymorphism include [fluvastatin], [simvastatin], and [rosuvastatin]. Genetic differences in the OATP1B1 (organic-anion-transporting polypeptide 1B1) hepatic transporter encoded by the SCLCO1B1 gene (Solute Carrier Organic Anion Transporter family member 1B1) have been shown to impact atorvastatin pharmacokinetics. Evidence from pharmacogenetic studies of the c.521T>C single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the gene encoding OATP1B1 (SLCO1B1) demonstrated that atorvastatin AUC was increased 2.45-fold for individuals homozygous for 521CC compared to homozygous 521TT individuals. Other statin drugs impacted by this polymorphism include [simvastatin], [pitavastatin], [rosuvastatin], and [pravastatin].
Route of Elimination
Atorvastatin and its metabolites are mainly eliminated in the bile without enterohepatic recirculation. The renal elimination of atorvastatin is very minimal and represents less than 1% of the eliminated dose.
Volume of Distribution
The reported volume of distribution of atorvastatin is of 380 L.
Clearance
The registered total plasma clearance of atorvastatin is of 625 ml/min.
/MILK/ In a separate experiment, a single dose of 10 mg/kg atorvastatin administered to female Wistar rats on gestation day 19 or lactation day 13 provided evidence of placental transfer and excretion into the milk.
PMID:9520344 Henck JW et al; Toxicol Sci 41 (1): 88-99 (1998)
Lipitor and its metabolites are eliminated primarily in bile following hepatic and/or extra-hepatic metabolism; however, the drug does not appear to undergo enterohepatic recirculation. ... Less than 2% of a dose of Lipitor is recovered in urine following oral administration.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Lipitor (Atorvastatin Calcium) Tablet, Film-coated (Updated: November 2015). Available from, as of October 28, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=c6e131fe-e7df-4876-83f7-9156fc4e8228
/MILK/ It is not known whether atorvastatin is excreted in human milk, but a small amount of another drug in this class does pass into breast milk. Nursing rat pups had plasma and liver drug levels of 50% and 40%, respectively, of that in their mother's milk.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Lipitor (Atorvastatin Calcium) Tablet, Film-coated (Updated: November 2015). Available from, as of October 28, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=c6e131fe-e7df-4876-83f7-9156fc4e8228
Mean volume of distribution of Lipitor is approximately 381 liters. Lipitor is >/= 98% bound to plasma proteins. A blood/plasma ratio of approximately 0.25 indicates poor drug penetration into red blood cells.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Lipitor (Atorvastatin Calcium) Tablet, Film-coated (Updated: November 2015). Available from, as of October 28, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=c6e131fe-e7df-4876-83f7-9156fc4e8228
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for ATORVASTATIN (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Atorvastatin is highly metabolized to ortho- and parahydroxylated derivatives and various beta-oxidation products, primarily by Cytochrome P450 3A4 in the intestine and liver. Atorvastatin's metabolites undergo further lactonization via the formation of acyl glucuronide intermediates by the enzymes UGT1A1 and UGT1A3. These lactones can be hydrolyzed back to their corresponding acid forms and exist in equilibirum. _In vitro_ inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase by ortho- and parahydroxylated metabolites is equivalent to that of atorvastatin. Approximately 70% of circulating inhibitory activity for HMG-CoA reductase is attributed to active metabolites.
Lipitor is extensively metabolized to ortho- and parahydroxylated derivatives and various beta-oxidation products. In vitro inhibition of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase by ortho- and parahydroxylated metabolites is equivalent to that of Lipitor. Approximately 70% of circulating inhibitory activity for HMG-CoA reductase is attributed to active metabolites. In vitro studies suggest the importance of Lipitor metabolism by cytochrome P450 3A4, consistent with increased plasma concentrations of Lipitor in humans following co-administration with erythromycin, a known inhibitor of this isozyme. In animals, the ortho-hydroxy metabolite undergoes further glucuronidation.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Lipitor (Atorvastatin Calcium) Tablet, Film-coated (Updated: November 2015). Available from, as of October 28, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=c6e131fe-e7df-4876-83f7-9156fc4e8228
The active forms of all marketed hydroxymethylglutaryl (HMG)-CoA reductase inhibitors share a common dihydroxy heptanoic or heptenoic acid side chain. In this study, we present evidence for the formation of acyl glucuronide conjugates of the hydroxy acid forms of simvastatin (SVA), atorvastatin (AVA), and cerivastatin (CVA) in rat, dog, and human liver preparations in vitro and for the excretion of the acyl glucuronide of SVA in dog bile and urine. Upon incubation of each statin (SVA, CVA or AVA) with liver microsomal preparations supplemented with UDP-glucuronic acid, two major products were detected. Based on analysis by high-pressure liquid chromatography, UV spectroscopy, and/or liquid chromatography (LC)-mass spectrometry analysis, these metabolites were identified as a glucuronide conjugate of the hydroxy acid form of the statin and the corresponding delta-lactone. By means of an LC-NMR technique, the glucuronide structure was established to be a 1-O-acyl-beta-D-glucuronide conjugate of the statin acid. The formation of statin glucuronide and statin lactone in human liver microsomes exhibited modest intersubject variability (3- to 6-fold; n = 10). Studies with expressed UDP glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) revealed that both UGT1A1 and UGT1A3 were capable of forming the glucuronide conjugates and the corresponding lactones for all three statins. Kinetic studies of statin glucuronidation and lactonization in liver microsomes revealed marked species differences in intrinsic clearance (CL(int)) values for SVA (but not for AVA or CVA), with the highest CL(int) observed in dogs, followed by rats and humans. Of the statins studied, SVA underwent glucuronidation and lactonization in human liver microsomes, with the lowest CL(int) (0.4 uL/min/mg of protein for SVA versus approximately 3 uL/min/mg of protein for AVA and CVA). Consistent with the present in vitro findings, substantial levels of the glucuronide conjugate (approximately 20% of dose) and the lactone form of SVA [simvastatin (SV); approximately 10% of dose] were detected in bile following i.v. administration of [(14)C]SVA to dogs. The acyl glucuronide conjugate of SVA, upon isolation from an in vitro incubation, underwent spontaneous cyclization to SV. Since the rate of this lactonization was high under conditions of physiological pH, the present results suggest that the statin lactones detected previously in bile and/or plasma following administration of SVA to animals or of AVA or CVA to animals and humans, might originate, at least in part, from the corresponding acyl glucuronide conjugates. Thus, acyl glucuronide formation, which seems to be a common metabolic pathway for the hydroxy acid forms of statins, may play an important, albeit previously unrecognized, role in the conversion of active HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors to their latent delta-lactone forms.
PMID:11950779 Prueksaritanont T et al; Drug Metab Dispos 30 (5): 505-12 (2002)
The genetic variation underlying atorvastatin (ATV) pharmacokinetics was evaluated in a Mexican population. Aims of this study were: 1) to reveal the frequency of 87 polymorphisms in 36 genes related to drug metabolism in healthy Mexican volunteers, 2) to evaluate the impact of these polymorphisms on ATV pharmacokinetics, 3) to classify the ATV metabolic phenotypes of healthy volunteers, and 4) to investigate a possible association between genotypes and metabolizer phenotypes. A pharmacokinetic study of ATV (single 80-mg dose) was conducted in 60 healthy male volunteers. ATV plasma concentrations were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. Pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated by the non-compartmental method. The polymorphisms were determined with the PHARMAchip microarray and the TaqMan probes genotyping assay. Three metabolic phenotypes were found in our population: slow, normal, and rapid. Six gene polymorphisms were found to have a significant effect on ATV pharmacokinetics: MTHFR (rs1801133), DRD3 (rs6280), GSTM3 (rs1799735), TNFa (rs1800629), MDR1 (rs1045642), and SLCO1B1 (rs4149056). The combination of MTHFR, DRD3 and MDR1 polymorphisms associated with a slow ATV metabolizer phenotype.
PMID:26857559 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4746878 Leon-Cachon RB et al; BMC Cancer16: 74 (2016)
Atorvastatin has known human metabolites that include 7-[2-(4-Fluorophenyl)-4-[(2-hydroxyphenyl)carbamoyl]-3-phenyl-5-propan-2-ylpyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid and 7-[2-(4-Fluorophenyl)-4-[(4-hydroxyphenyl)carbamoyl]-3-phenyl-5-propan-2-ylpyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
The half-life of atorvastatin is 14 hours while the half-life of its metabolites can reach up to 30 hours.
/MILK/ ...After administration to lactating rats, radioactivity in milk reached the maximum of 17.1 ng eq./mL at 6.0 hr and thereafter declined with a half-life of 7.8 hr.
Nemoto H et al; Yakuri To Chiryo 26 (7): 79-96 (1998)
Mean plasma elimination half-life of Lipitor in humans is approximately 14 hours, but the half-life of inhibitory activity for HMG-CoA reductase is 20 to 30 hours due to the contribution of active metabolites.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Lipitor (Atorvastatin Calcium) Tablet, Film-coated (Updated: November 2015). Available from, as of October 28, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=c6e131fe-e7df-4876-83f7-9156fc4e8228
Atorvastatin is a statin medication and a competitive inhibitor of the enzyme HMG-CoA (3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A) reductase, which catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate, an early rate-limiting step in cholesterol biosynthesis. Atorvastatin acts primarily in the liver, where decreased hepatic cholesterol concentrations stimulate the upregulation of hepatic low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptors, which increases hepatic uptake of LDL. Atorvastatin also reduces Very-Low-Density Lipoprotein-Cholesterol (VLDL-C), serum triglycerides (TG) and Intermediate Density Lipoproteins (IDL), as well as the number of apolipoprotein B (apo B) containing particles, but increases High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (HDL-C). _In vitro_ and _in vivo_ animal studies also demonstrate that atorvastatin exerts vasculoprotective effects independent of its lipid-lowering properties, also known as the pleiotropic effects of statins. These effects include improvement in endothelial function, enhanced stability of atherosclerotic plaques, reduced oxidative stress and inflammation, and inhibition of the thrombogenic response. Statins were also found to bind allosterically to 2 integrin function-associated antigen-1 (LFA-1), which plays an essential role in leukocyte trafficking and T cell activation.
In animal models, Lipitor lowers plasma cholesterol and lipoprotein levels by inhibiting 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase and cholesterol synthesis in the liver and by increasing the number of hepatic low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptors on the cell surface to enhance uptake and catabolism of LDL; Lipitor also reduces LDL production and the number of LDL particles. Lipitor reduces LDL-cholesterol (LDL-C) in some patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (FH), a population that rarely responds to other lipid-lowering medication(s).
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Lipitor (Atorvastatin Calcium) Tablet, Film-coated (Updated: November 2015). Available from, as of October 28, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=c6e131fe-e7df-4876-83f7-9156fc4e8228
Lipitor is a selective, competitive inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase, the rate-limiting enzyme that converts 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A to mevalonate, a precursor of sterols, including cholesterol. Cholesterol and triglycerides circulate in the bloodstream as part of lipoprotein complexes. With ultracentrifugation, these complexes separate into HDL (high-density lipoprotein), IDL (intermediate-density lipoprotein), LDL (low-density lipoprotein), and VLDL (very-low-density lipoprotein) fractions. Triglycerides (TG) and cholesterol in the liver are incorporated into VLDL and released into the plasma for delivery to peripheral tissues. LDL is formed from VLDL and is catabolized primarily through the high-affinity LDL receptor. Clinical and pathologic studies show that elevated plasma levels of total cholesterol (total-C), LDL-cholesterol (LDL-C), and apolipoprotein B (apo B) promote human atherosclerosis and are risk factors for developing cardiovascular disease, while increased levels of HDL-C are associated with a decreased cardiovascular risk.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Lipitor (Atorvastatin Calcium) Tablet, Film-coated (Updated: November 2015). Available from, as of October 28, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=c6e131fe-e7df-4876-83f7-9156fc4e8228
Statins are largely used in clinics in the treatment of patients with cardiovascular diseases for their effect on lowering circulating cholesterol. Lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein (LOX-1), the primary receptor for ox-LDL, plays a central role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disorders. We have recently shown that chronic exposure of cells to lovastatin disrupts LOX-1 receptor cluster distribution in plasma membranes, leading to a marked loss of LOX-1 function. Here we investigated the molecular mechanism of statin-mediated LOX-1 inhibition and we demonstrate that all tested statins /including atorvastatin/ are able to displace the binding of fluorescent ox-LDL to LOX-1 by a direct interaction with LOX-1 receptors in a cell-based binding assay. Molecular docking simulations confirm the interaction and indicate that statins completely fill the hydrophobic tunnel that crosses the C-type lectin-like (CTLD) recognition domain of LOX-1. Classical molecular dynamics simulation technique applied to the LOX-1 CTLD, considered in the entire receptor structure with or without a statin ligand inside the tunnel, indicates that the presence of a ligand largely increases the dimer stability. Electrophoretic separation and western blot confirm that different statins binding stabilize the dimer assembly of LOX-1 receptors in vivo. The simulative and experimental results allow us to propose a CTLD clamp motion, which enables the receptor-substrate coupling. ...
PMID:25950192 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4614984 Biocca S et al; Cell Cycle 14 (10): 1583-95 (2015)
3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors (statins) exert potent vasculoprotective effects. However, the potential contribution to angiogenesis is controversial. In the present study, we demonstrate that atorvastatin dose-dependently affects endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis. In vivo relevant concentrations of 0.01 to 0.1 umol/L atorvastatin or mevastatin promote the migration of mature endothelial cells and tube formation. Moreover, atorvastatin also increases migration and the potency to form vessel structures of circulating endothelial progenitor cells, which may contribute to vasculogenesis. In contrast, higher concentrations (>0.1 umol/L atorvastatin) block angiogenesis and migration by inducing endothelial cell apoptosis. The dose-dependent promigratory and proangiogenic effects of atorvastatin on mature endothelial cells are correlated with the activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt pathway, as determined by the phosphorylation of Akt and endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) at Ser1177. In addition, the stimulation of migration and tube formation was blocked by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors. In contrast, the well-established stabilization of eNOS mRNA was achieved only at higher concentrations, suggesting that posttranscriptional activation rather than an increase in eNOS expression mediates the proangiogenic effect of atorvastatin. Taken together, these data suggest that statins exert a double-edged role in angiogenesis signaling by promoting the migration of mature endothelial cells and endothelial progenitor cells at low concentrations, whereas the antiangiogenic effects were achieved only at high concentrations.
PMID:11934843 Urbich C et al; Circ Res 90 (6): 737-44 (2002)
Here, we found that atorvastatin promoted the expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) both in vitro and in vivo. Atorvastatin-derived MDSCs suppressed T-cell responses by nitric oxide production. Addition of mevalonate, a downstream metabolite of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase, almost completely abrogated the effect of atorvastatin on MDSCs, indicating that the mevalonate pathway was involved. Along with the amelioration of dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) -induced murine acute and chronic colitis, we observed a higher MDSC level both in spleen and intestine tissue compared with that from DSS control mice. More importantly, transfer of atorvastatin-derived MDSCs attenuated DSS acute colitis and T-cell transfer of chronic colitis. Hence, our data suggest that the expansion of MDSCs induced by statins may exert a beneficial effect on autoimmune diseases. In summary, our study provides a novel potential mechanism for statins-based treatment in inflammatory bowel disease and perhaps other autoimmune diseases.
PMID:27548304 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5095490 Lei A et al; Immunology 149 (4): 432-446 (2016)

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS

Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ANALYTICAL

ABOUT THIS PAGE
81
PharmaCompass offers a list of Atorvastatin API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Atorvastatin manufacturer or Atorvastatin supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Atorvastatin manufacturer or Atorvastatin supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Atorvastatin API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Atorvastatin API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Atorvastatin Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Atorvastatin Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Atorvastatin manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Atorvastatin, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Atorvastatin manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Atorvastatin API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Atorvastatin manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Atorvastatin supplier is an individual or a company that provides Atorvastatin active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Atorvastatin finished formulations upon request. The Atorvastatin suppliers may include Atorvastatin API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Atorvastatin suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Atorvastatin DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Atorvastatin active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Atorvastatin DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Atorvastatin USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Atorvastatin DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Atorvastatin USDMF includes data on Atorvastatin's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Atorvastatin USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Atorvastatin suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) established the Japan Drug Master File (JDMF), also known as the Master File (MF), to permit Japanese and foreign manufacturers of drug substances, intermediates, excipients, raw materials, and packaging materials (‘Products’) to voluntarily register confidential information about the production and management of their products in Japan.
The Atorvastatin Drug Master File in Japan (Atorvastatin JDMF) empowers Atorvastatin API manufacturers to present comprehensive information (e.g., production methods, data, etc.) to the review authority, i.e., PMDA (Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Agency).
PMDA reviews the Atorvastatin JDMF during the approval evaluation for pharmaceutical products. At the time of Atorvastatin JDMF registration, PMDA checks if the format is accurate, if the necessary items have been included (application), and if data has been attached.
click here to find a list of Atorvastatin suppliers with JDMF on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a Atorvastatin Drug Master File in Korea (Atorvastatin KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of Atorvastatin. The MFDS reviews the Atorvastatin KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the Atorvastatin KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a Atorvastatin KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their Atorvastatin API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of Atorvastatin suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Atorvastatin CEP of the European Pharmacopoeia monograph is often referred to as a Atorvastatin Certificate of Suitability (COS). The purpose of a Atorvastatin CEP is to show that the European Pharmacopoeia monograph adequately controls the purity of Atorvastatin EP produced by a given manufacturer. Suppliers of raw materials can prove the suitability of Atorvastatin to their clients by showing that a Atorvastatin CEP has been issued for it. The manufacturer submits a Atorvastatin CEP (COS) as part of the market authorization procedure, and it takes on the role of a Atorvastatin CEP holder for the record. Additionally, the data presented in the Atorvastatin CEP (COS) is managed confidentially and offers a centralized system acknowledged by numerous nations, exactly like the Atorvastatin DMF.
A Atorvastatin CEP (COS) is recognised by all 36 nations that make up the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. Atorvastatin CEPs may be accepted in nations that are not members of the Ph. Eur. at the discretion of the authorities there.
click here to find a list of Atorvastatin suppliers with CEP (COS) on PharmaCompass.
A Atorvastatin written confirmation (Atorvastatin WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Atorvastatin manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Atorvastatin active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Atorvastatin APIs or Atorvastatin finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Atorvastatin WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Atorvastatin suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Atorvastatin as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Atorvastatin API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Atorvastatin as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Atorvastatin and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Atorvastatin NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Atorvastatin suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Atorvastatin Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Atorvastatin GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Atorvastatin GMP manufacturer or Atorvastatin GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Atorvastatin CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Atorvastatin's compliance with Atorvastatin specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Atorvastatin CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Atorvastatin CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Atorvastatin may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Atorvastatin EP), Atorvastatin JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Atorvastatin USP).

