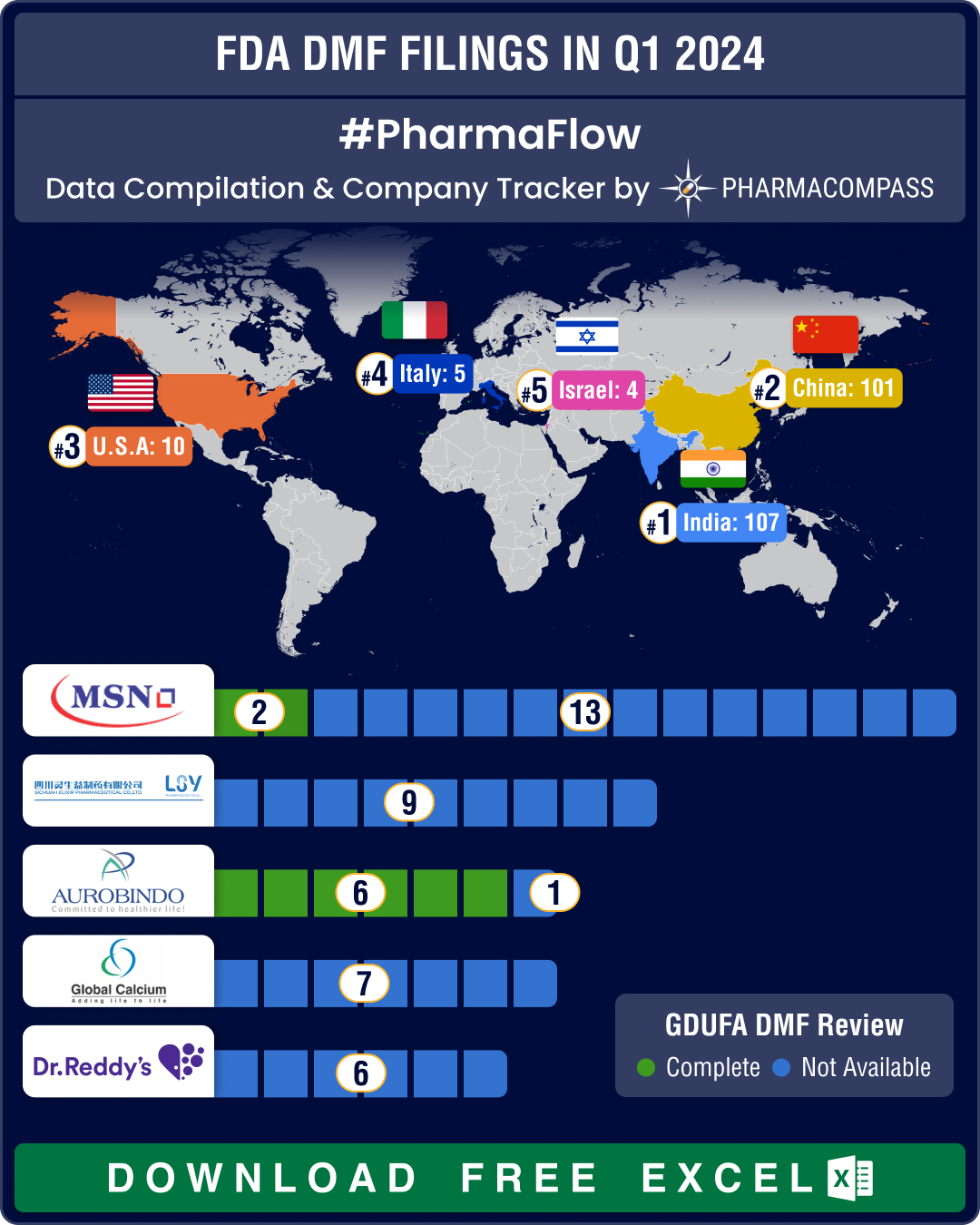
DMF filings rise 4.5% in Q3 2025; China holds lead, India records 20% growth in submissions
The
third quarter (Q3) of 2025 witnessed a steady rise in Drug Master File (DMF) submissions to the
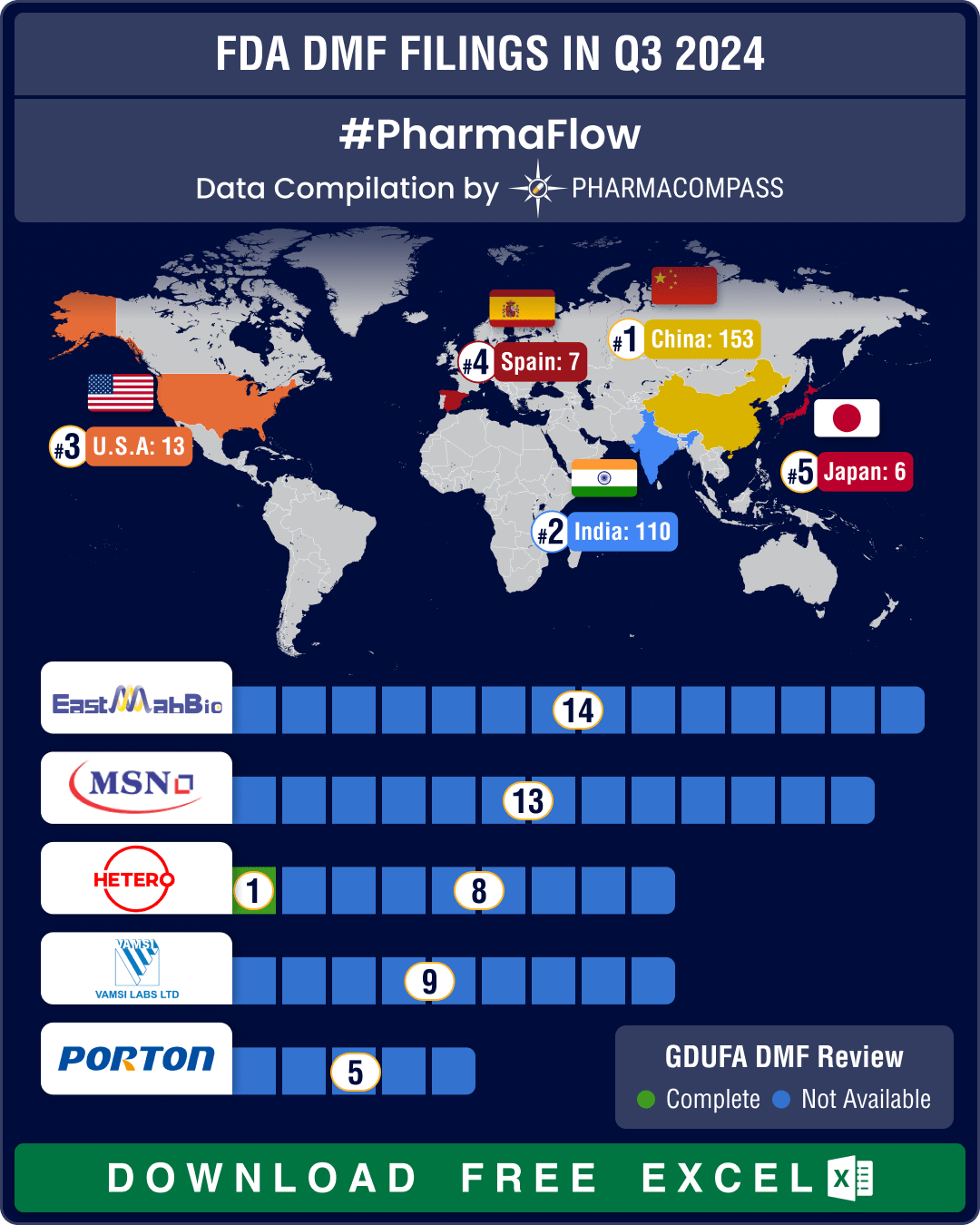
DMF filings hit all-time high in Q3 2024; China tops list with 58% increase in Type II submissions
Drug Master Files, or DMFs, are confidential documents that play a crucial role in the pharmaceutica