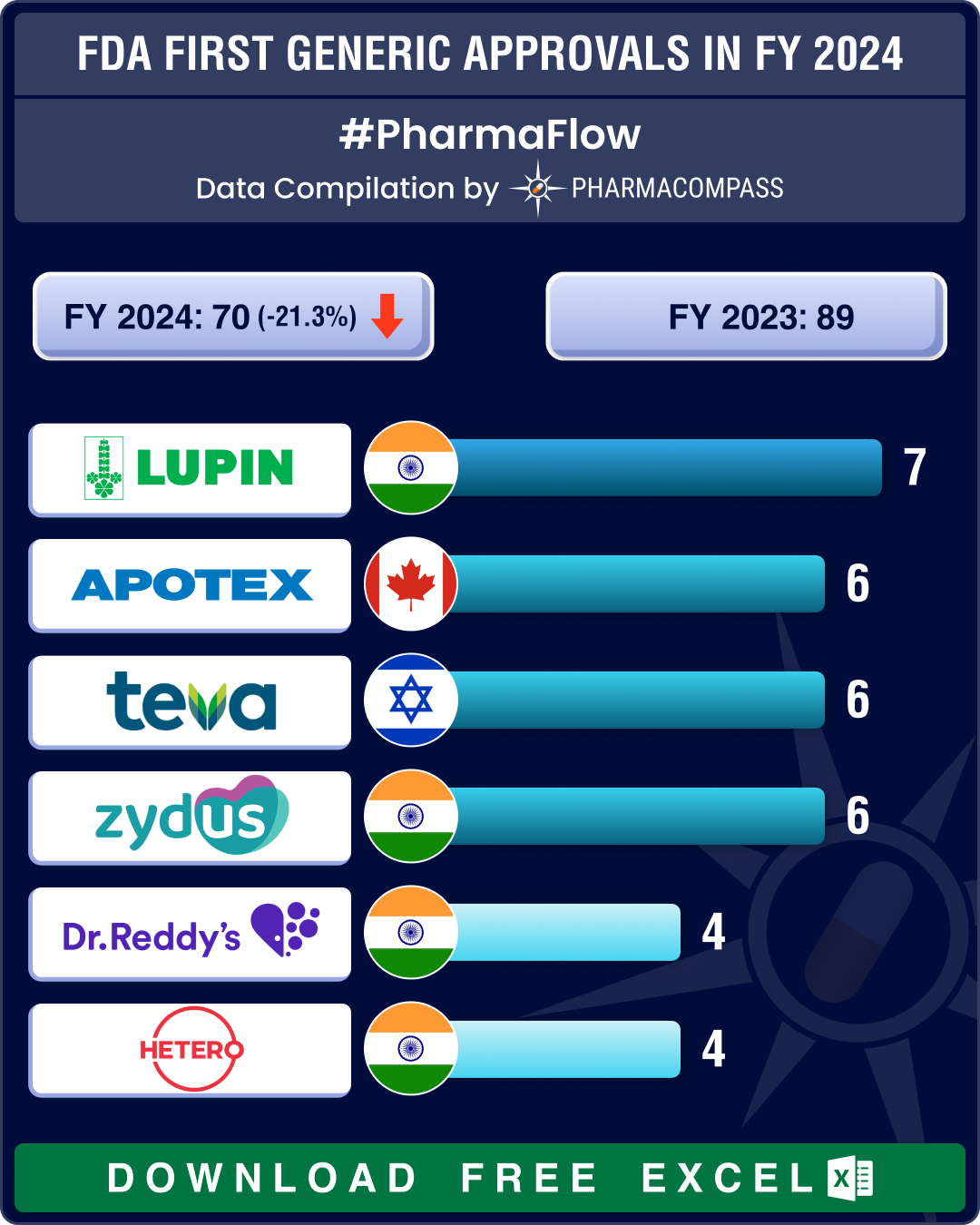
FDA’s first generic approvals slump 21% in 2024; Novartis’ top seller Entresto, cancer blockbuster Tasigna lead 2024 patent cliff
A watershed moment in the journey of a drug is when it transitions from being a patented, high‐
 Market Place
Market Place Sourcing Support
Sourcing Support