

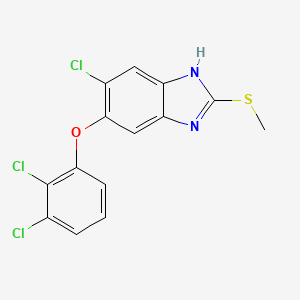

1. 6-chloro-5-(2,3-dichlorophenoxy)-2-methylthiobenzimidazole
2. Egaten
3. Fasicare
4. Fasinex
5. Flukare
6. Tremacide
1. 68786-66-3
2. Fasinex
3. Egaten
4. 6-chloro-5-(2,3-dichlorophenoxy)-2-(methylthio)-1h-benzo[d]imidazole
5. Triclabendazol
6. Triclabendazolum
7. 5-chloro-6-(2,3-dichlorophenoxy)-2-(methylthio)-1h-benzimidazole
8. Nvp-ega230
9. Ega230b
10. 6-chloro-5-(2,3-dichlorophenoxy)-2-methylsulfanyl-1h-benzimidazole
11. Nsc-759250
12. Cpd000466357
13. Mls001424101
14. Chembl1086440
15. 1h-benzimidazole, 6-chloro-5-(2,3-dichlorophenoxy)-2-(methylthio)-
16. Cga89317
17. 4784c8e03o
18. Ncgc00164610-01
19. Smr000466357
20. 5-chloro-6-(2,3-dichlorophenoxy)-2-(methylthio)benzimidazole
21. 6-chloro-5-(2,3-dichlorophenoxy)-2-(methylthio)-1h-benzimidazole
22. 6-[2,3-bis(chloranyl)phenoxy]-5-chloranyl-2-methylsulfanyl-1h-benzimidazole
23. 5-chloro-6-(2,3-dichlorophenoxy)-2-(methylsulfanyl)-1h-1,3-benzodiazole
24. Triclabendazol [inn-spanish]
25. Triclabendazolum [inn-latin]
26. Ccris 8988
27. Cga 89317
28. 5-chloro-6-(2,3-dichlorophenoxy)-2-methylsulfanyl-1h-benzimidazole
29. Unii-4784c8e03o
30. 6-chloro-5-(2,3-dichlorophenoxy)-2-methylthio-benzimidazole
31. Fasinex (tn)
32. Egaten (tn)
33. 1h-benzimidazole, 5-chloro-6-(2,3-dichlorophenoxy)-2-(methylthio)-
34. Dsstox_cid_23952
35. Dsstox_rid_80094
36. Triclabendazole [mi]
37. Dsstox_gsid_43952
38. Oprea1_236106
39. Triclabendazole (usan/inn)
40. Triclabendazole [inn]
41. Cid_50248
42. Mls000759473
43. Mls000876812
44. Schembl165712
45. Triclabendazole [usan]
46. Triclabendazole [mart.]
47. Dtxsid7043952
48. Triclabendazole [who-dd]
49. Bdbm58491
50. Chebi:94759
51. Triclabendazole [usan:inn:ban]
52. Hms2051e16
53. Hms2232d14
54. Hms3370h02
55. Hms3393e16
56. Hms3652m16
57. Hms3715p16
58. Hms3744i09
59. Kuc103451n
60. Pharmakon1600-01505786
61. Hy-b0621
62. Zinc1444556
63. Tox21_112231
64. Cga-89317
65. Mfcd00864519
66. Nsc759250
67. S4114
68. Stk332284
69. Triclabendazole [orange Book]
70. Akos005439340
71. Akos015950804
72. Ac-7627
73. At10531
74. Ccg-100881
75. Ccg-268150
76. Db12245
77. Ks-5329
78. Nc00131
79. Nsc 759250
80. Sb17173
81. Ncgc00164610-02
82. Sbi-0207022.p001
83. Triclabendazole 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
84. Cas-68786-66-3
85. Ft-0602564
86. Sw197511-2
87. T2826
88. Triclabendazole 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
89. D07364
90. Ab00639964-10
91. Ab00639964_12
92. Ab00639964_13
93. 786t663
94. A836250
95. Q419739
96. Sr-01000759363
97. Sr-01000759363-4
98. Triclabendazole, Vetranal(tm), Analytical Standard
99. Brd-k81916719-001-05-5
100. 6-chloro-5-(2,3-dichlorophenoxy)-2-(methylthio)benzimidazole
101. Triclabendazole, Europepharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
102. 5-chloro-6-(2',3'-dichlorophenoxy)-2-(methylthio)benzimidazole
103. 5-chloro-6-(2,3-dichlorophenoxy)-2-(methylthio)-1h-benzo[d]imidazole
104. 6-chloro-5-(2,3-dichlorophenoxy)-2-(methylsulfanyl)-1h-1,3-benzodiazole
105. 6-chloro-5-(2,3-dichlorophenoxy)-2-(methylsulfanyl)-1h-benzimidazole
106. 5-[2,3-bis(chloranyl)phenoxy]-6-chloranyl-2-methylsulfanyl-1h-benzimidazole
107. 6-chloro-5-(2,3-dichlorophenoxy)-2-methylsulfanyl-1h-benzimidazole;triclabendazole
108. Triclabendazole For System Suitability, Europepharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
109. Ja9
| Molecular Weight | 359.7 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H9Cl3N2OS |
| XLogP3 | 5.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 357.950117 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 357.950117 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 63.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 365 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
This drug is indicated for the treatment of fascioliasis in patients aged 6 years old and above.
FDA Label
Triclabendazole and its metabolites are active against both the immature and mature worms of _Fasciola hepatica_ and _Fasciola gigantica_ helminths. **Effect on QT interval** This drug may prolong the cardiac QT interval. Monitor ECG in patients with a history of QT prolongation or who are taking medications known to prolong the QT interval.
Antiplatyhelmintic Agents
Agents used to treat cestode, trematode, or other flatworm infestations in man or animals. (See all compounds classified as Antiplatyhelmintic Agents.)
P - Antiparasitic products, insecticides and repellents
P02 - Anthelmintics
P02B - Antitrematodals
P02BX - Other antitrematodal agents
P02BX04 - Triclabendazole
Absorption
After a single oral dose of 10 mg/kg triclabendazole with a 560-kcal meal to patients diagnosed with fascioliasis, mean peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) for triclabendazole, the sulfoxide, and sulfone metabolites were 1.16, 38.6, and 2.29 mol/L, respectively. The area under the curve (AUC) for triclabendazole, the sulfoxide and sulfone metabolites were 5.72, 386, and 30.5 molh/L, respectively. After the oral administration of a single dose of triclabendazole at 10 mg/kg with a 560 calorie meal to patients with fascioliasis, the median Tmax for the parent compound as well as the active sulfoxide metabolite was 3 to 4 hours. **Effect of Food** Cmax and AUC of triclabendazole and sulfoxide metabolite increased about 2-3 times when triclabendazole was administered as a single dose at 10 mg/kg with a meal containing approximately 560 calories. Additionally, the sulfoxide metabolite Tmax increased from 2 hours in fasting subjects to 4 hours in fed subjects.
Route of Elimination
No data regarding excretion is available in humans. In animals, triclabendazole is primarily excreted by the biliary tract in the feces (90%), together with the sulfoxide and sulfone metabolite. Less than 10% of an oral dose is found excreted in the urine.
Volume of Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution (Vd) of the sulfoxide metabolite in fed patients is about 1 L/kg.
Based on in vitro studies, triclabendazole is mainly metabolized by CYP1A2 enzyme (approximately 64%) into its active _sulfoxide_ metabolite and to a lesser extent by CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP3A, and FMO (flavin containing monooxygenase). This sulfoxide metabolite is further metabolized mainly by CYP2C9 to the active sulfone metabolite, and to a smaller extent by CYP1A1, CYP1A2, CYP1B1, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4, _in vitro_.
The plasma elimination half-life (t1/2) of triclabendazole, the sulfoxide and sulfone metabolites in human is about 8, 14, and 11 hours, respectively.
Triclabendazole is an anthelmintic agent against _Fasciola_ species. The mechanism of action against Fasciola species is not fully understood at this time. In vitro studies and animal studies suggest that triclabendazole and its active metabolites (_sulfoxide_ and _sulfone_) are absorbed by the outer body covering of the immature and mature worms, causing a reduction in the resting membrane potential, the inhibition of tubulin function as well as protein and enzyme synthesis necessary for survival. These metabolic disturbances lead to an inhibition of motility, disruption of the worm outer surface, in addition to the inhibition of spermatogenesis and egg/embryonic cells. **A note on resistance** In vitro studies, in vivo studies, as well as case reports suggest a possibility for the development of resistance to triclabendazole. The mechanism of resistance may be multifactorial and include changes in drug uptake/efflux mechanisms, target molecules, and changes in drug metabolism. The clinical significance of triclabendazole resistance in humans is not yet elucidated.
