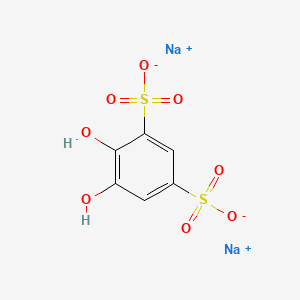

1. 1,2-dihydroxybenzene-3,5-disulfonic Acid Disodium Salt
1. 149-45-1
2. Tiferron
3. Disodium 4,5-dihydroxybenzene-1,3-disulfonate
4. Sodium Catechol Sulfate
5. 1,2-dihydroxybenzene-3,5-disulfonic Acid Disodium Salt
6. 1,3-benzenedisulfonic Acid, 4,5-dihydroxy-, Disodium Salt
7. Sodium 4,5-dihydroxybenzene-1,3-disulfonate
8. Disodium Pyrocatechol-3,5-disulfonate
9. 3,5-disulfocatechol Disodium Salt
10. Sodium Pyrocatechol-3,5-disulfonate
11. Sodium 1,2-dihydroxybenzenedisulfonate
12. Dihydroxy Benzene Disulfonate Disodium Salt
13. Disodium 4,5-dihydroxy-m-benzenedisulfonate
14. Sodium 1,2-dihydroxy-3,5-benzenedisulfonate
15. Chebi:9607
16. Catechol-3,5-disulfonic Acid Disodium Salt
17. Disodium 1,2-dihydroxybenzene-3,5-disulfonate
18. Disodium 4,5-dihydroxybenzene-1,3-disulphonate
19. Disodium 4,5-dihydroxy-1,3-benzenedisulfonate
20. 4,5-dihydroxy-m-benzenedisulfonic Acid Disodium Salt
21. 4x87r5t106
22. M-benzenedisulfonic Acid, 4,5-dihydroxy-, Disodium Salt
23. 4,5-dihydroxy-1,3-benzenedisulfonic Acid Disodium Salt
24. Sdd
25. Nsc-12861
26. Einecs 205-741-5
27. Nsc 12861
28. Pyrocatechol-3,5-disulfonic Acid Disodium Salt
29. Unii-4x87r5t106
30. Tiron, P.a. 99%
31. Tiron [mi]
32. Dsstox_cid_23950
33. Dsstox_rid_80093
34. Dsstox_gsid_43950
35. Schembl22220
36. Chembl110526
37. Dtxsid7043950
38. Amy37894
39. Tox21_302148
40. Mfcd00007473
41. Akos002248727
42. Akos015913779
43. Catechol-3,5-disulfonicaciddisodiumsalt
44. Ncgc00255944-01
45. Cas-149-45-1
46. Sodium Pyrocatechol-2,4-disulfonate
47. Cs-0010164
48. D0567
49. Disodium-1,2-dihydroxybenzene-3,5-disulfonate
50. Q2436330
51. W-108084
52. 4,5-dihydroxy-1,3-benzenedisulfonic Acid, Disodium Salt
53. 1,3-benzenedisulfonic Acid, 4,5-dihydroxy-, Sodium Salt (1:2)
| Molecular Weight | 314.2 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C6H4Na2O8S2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 313.91429799 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 313.91429799 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 172 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 18 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 413 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 3 |
Chymopapain is indicated for the development of chemonucleolysis which is used for the digestion of the nucleus pulposus in patients with disc herniation confirmed by myelography. A disc herniation occurs when the outer portion of the spinal disc breaks down and the inner portion (nucleus pulposus) leaks out pressing surrounding nerves and leading to irradiating pain. The chemonucleolysis is a non-surgical treatment that involves the injection of an enzyme to dissolve the nucleus pulposus.
The first studies showed that after intradiscal injection of chymopapain the effect involved the removal of the nucleus pulposus leaving the annulus intact. The clinical reports indicated a spontaneous remission of symptoms after the administration of chymopapain. It is also highly documented an increased urinary excretion of glycosaminoglycans.
Indicators and Reagents
Substances used for the detection, identification, analysis, etc. of chemical, biological, or pathologic processes or conditions. Indicators are substances that change in physical appearance, e.g., color, at or approaching the endpoint of a chemical titration, e.g., on the passage between acidity and alkalinity. Reagents are substances used for the detection or determination of another substance by chemical or microscopical means, especially analysis. Types of reagents are precipitants, solvents, oxidizers, reducers, fluxes, and colorimetric reagents. (From Grant and Hackh's Chemical Dictionary, 5th ed, p301, p499) (See all compounds classified as Indicators and Reagents.)
M - Musculo-skeletal system
M09 - Other drugs for disorders of the musculo-skeletal system
M09A - Other drugs for disorders of the musculo-skeletal system
M09AB - Enzymes
M09AB01 - Chymopapain
Following intra-discal injection, the level of chymopapain decreases gradually and presents a half-life of 2-3 days. The half-life for urinary excretion is reported to be of about 3 days.
Chymopapain is thought to degrade proteoglycan content of the intervertebral disc causing loss of glycosaminoglycan and water. This effect will cause the shrinkage of the disc and a reduction of the pressure on the nerve root.
