

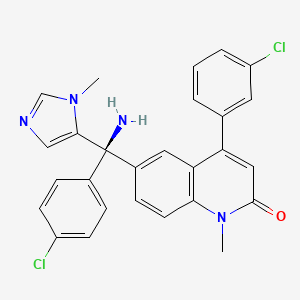

1. (r)-6-(amino(4-chlorophenyl)(1-methyl-1h-imidazol-5-yl)methyl)-4-(3-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-2(1h)-quinolinone
2. 2 (1h))-quinolinone,6-(amino(4-chlorophenyl)(1-methyl-1h-imidazol-5-yl)methyl)-4-(3-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-,(+)-
3. R 115777
4. R-115777
5. R115777
6. Zarnestra
1. 192185-72-1
2. Zarnestra
3. R115777
4. R-115777
5. Tipifarnib (zarnestra)
6. (r)-6-(amino(4-chlorophenyl)(1-methyl-1h-imidazol-5-yl)methyl)-4-(3-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-2(1h)-quinolinone
7. Ind 58359
8. 6-[(r)-amino(4-chlorophenyl)(1-methyl-1h-imidazol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(3-chlorophenyl)-1-methylquinolin-2(1h)-one
9. R-11577
10. Nsc-702818
11. (r)-6-(amino(4-chlorophenyl)(1-methyl-1h-imidazol-5-yl)methyl)-4-(3-chlorophenyl)-1-methylquinolin-2(1h)-one
12. Mat637500a
13. 6-[(r)-amino-(4-chlorophenyl)-(3-methylimidazol-4-yl)methyl]-4-(3-chlorophenyl)-1-methylquinolin-2-one
14. 6-[(s)-amino(4-chlorophenyl)(1-methyl-1h-imidazol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(3-chlorophenyl)-1-methylquinolin-2(1h)-one
15. Tipifarnib [usan]
16. R115777;ind 58359
17. Jan
18. Tipifarnib (usan/inn)
19. Tipifarnib [usan:inn]
20. Tipifarnibum
21. Tipifarneb
22. Unii-mat637500a
23. Ccris 9329
24. Tipifarnib - Zarnestra
25. Tipifarnib [mi]
26. (r)-tipifarnib
27. Tipifarnib [inn]
28. D03720
29. Schembl8097
30. Tipifarnib [mart.]
31. Tipifarnib (r115777)
32. Tipifarnib [who-dd]
33. Mls006011105
34. Gtpl8025
35. Dtxsid5041140
36. Schembl21544535
37. Tipifarnib, >=98% (hplc)
38. R115777; Tipifarnib
39. 1x81
40. Chebi:141969
41. Bcpp000044
42. Hms3654b10
43. Hms3748e21
44. 6-[(r)-amino(4-chlorophenyl)(1-methyl-1h-imidazol-5-yl)methyl}-4-(3-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-2(1h)-quinolinone
45. Amy20627
46. Bcp02262
47. Ex-a2346
48. Bdbm50370385
49. Nsc760444
50. S1453
51. Zinc24809155
52. Akos027326864
53. Ccg-264893
54. Cs-0475
55. Db04960
56. Nsc-760444
57. Sb16693
58. Ncgc00250406-01
59. Ncgc00250406-02
60. 2 (1h))-quinolinone,6-(amino(4-chlorophenyl)(1-methyl-1h-imidazol-5-yl)methyl)-4-(3-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-, (+)-
61. 2 (1h))-quinolinone,6-(amino(4-chlorophenyl)(1-methyl-1h-imidazol-5-yl)methyl)-4-(3-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-,(+)-
62. 2(1h)-quinolinone,6-[(r)-amino(4-chlorophenyl)(1-methyl-1h-imidazol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(3-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-
63. Ac-33171
64. Bs-15758
65. Hy-10502
66. Smr002530065
67. Tipifarnib; Ind 58359; R115777
68. Sw219749-1
69. D70631
70. (r)-(+)-r115777
71. 185t721
72. Q-102509
73. Brd-k62965247-001-01-5
74. Ind 58359;r115777;ind-58359;ind58359;r-115777;r 115777
75. (+)-(r)-6-[amino(4-chlorophenyl)(1-methyl-1h-imidazol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(3-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-2(1h)-quinolinone
76. 2 (1h))-quinolinone,6-(amino(4-chlorophenyl)(1-methyl-1h-imidazol-5-yl)methyl)-4-(3-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-
77. 2(1h)-quinolinone, 6-[(r)-amino(4-chlorophenyl)(1-methyl-1h-imidazol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(3-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-
| Molecular Weight | 489.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C27H22Cl2N4O |
| XLogP3 | 4.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 488.1170667 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 488.1170667 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 64.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 34 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 785 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Investigated for use/treatment in colorectal cancer, leukemia (myeloid), pancreatic cancer, and solid tumors.
Treatment of head and neck epithelial malignant neoplasms
R115777, a nonpeptidomimetic farnesyl transferase inhibitor, suppresses the growth of human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell lines. This growth inhibition is associated with modulation in the phosphorylation levels of signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 (STAT3) and extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK).
Antineoplastic Agents
Substances that inhibit or prevent the proliferation of NEOPLASMS. (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents.)
The farnesyltransferase inhibitors (FTIs) are a class of experimental cancer drugs that target protein farnesyltransferase with the downstream effect of preventing the proper functioning of the Ras protein, which is commonly abnormally active in cancer. After translation, RAS goes through four steps of modification: isoprenylation, proteolysis, methylation and palmitoylation. Isoprenylation involves the enzyme farnesyltransferase (FTase) transferring a farnesyl group from farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) to the pre-RAS protein. Also, a related enzyme geranylgeranyltransferase I (GGTase I) has the ability to transfer a geranylgeranyl group to K and N-RAS. Farnesyl is necessary to attach RAS to the cell membrane. Without attachment to the cell membrane, RAS is not able to transfer signals from membrane receptors (Reuter et al., 2000).
