

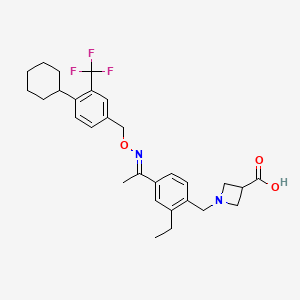

1. 1-(4-(1-((e)-4-cyclohexyl-3-trifluoromethylbenzyloxyimino)-ethyl)-2-ethylbenzyl)-azetidine-3-carboxylic Acid
2. Baf-312
3. Baf312
4. Mayzent
1. 1230487-00-9
2. Baf312 (siponimod)
3. Mayzent
4. Baf-312
5. Siponimod [inn]
6. Nvp-baf312-nx
7. Siponimod [who-dd]
8. Baf312
9. Siponimod [usan]
10. Baf-312(siponimod)
11. 1230487-85-0
12. Rr6p8l282i
13. Chembl2336071
14. 1-((4-((1e)-1-(((4-cyclohexyl- 3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)methoxy)imino)ethyl)- 2-ethylphenyl)methyl)azetidine-3-carboxylic Acid
15. 3-azetidinecarboxylic Acid, 1-((4-((1e)-1-(((4-cyclohexyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)methoxy)imino)ethyl)-2-ethylphenyl)methyl)-
16. 1-[[4-[(e)-n-[[4-cyclohexyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methoxy]-c-methylcarbonimidoyl]-2-ethylphenyl]methyl]azetidine-3-carboxylic Acid
17. Unii-rr6p8l282i
18. 3-azetidinecarboxylic Acid, 1-[[4-[(1e)-1-[[[4-cyclohexyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methoxy]imino]ethyl]-2-ethylphenyl]methyl]-
19. J8c
20. Siponimod [mi]
21. Siponimod (usan/inn)
22. Siponimod [usan:inn]
23. Schembl641699
24. Amy595
25. Baf 312
26. Dtxsid40153847
27. C29h35f3n2o3
28. (e)-1-(4-(1-(((4-cyclohexyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzyl)oxy)imino)ethyl)-2-ethylbenzyl)azetidine-3-carboxylic Acid
29. 1-[[4-[(~{e})-~{n}-[[4-cyclohexyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methoxy]-~{c}-methyl-carbonimidoyl]-2-ethyl-phenyl]methyl]azetidine-3-carboxylic Acid
30. 1-{4-[1-((e)-4-cyclohexyl-3-trifluoromethyl-benzyloxyimino)-ethyl]-2-ethyl-benzyl}-azetidine-3-carboxylic Acid
31. Who 9491
32. Bdbm50428142
33. Mfcd26142651
34. Akos037645089
35. Ccg-269825
36. Cs-3876
37. Db12371
38. 1-(4-(1-((e)-4-cyclohexyl-3-trifluoromethylbenzyloxyimino)-ethyl)-2-ethylbenzyl)-azetidine-3-carboxylic Acid
39. Ac-32779
40. As-56983
41. Hy-12355
42. B3225
43. S7179
44. D11460
45. J-690082
46. (z)-4-cyano-5-((3,5-dichloropyridin-4-yl)thio)-n-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)thiophene-2-carbimidic Acid
47. 2(1h)-isoquinolinebutanoic Acid, Beta-(((4,5-dihydro-5-(2-(1h-imidazol-2-ylamino)ethyl)-3-isoxazolyl)carbonyl)amino)-3,4-dihydro-gamma-oxo-
| Molecular Weight | 516.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C29H35F3N2O3 |
| XLogP3 | 4.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Exact Mass | 516.25997747 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 516.25997747 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 62.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 37 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 777 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
This drug is indicated for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS), to include clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease in adults.
FDA Label
Mayzent is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with secondary progressive multiple sclerosis (SPMS) with active disease evidenced by relapses or imaging features of inflammatory activity.
**Immune system effects** Siponimod causes a dose-dependent decrease of the peripheral blood lymphocyte count within 6 hours of the first dose, caused by the reversible accumulation of lymphocytes in lymphoid tissues, due to lack of lymphocyte release. This results in a decrease in the inflammation that is involved in multiple sclerosis. Lymphocyte counts return to normal in 90% of patients within 10 days after the cessation of therapy. **Effects on heart rate and rhythm** Siponimod causes a temporary decrease in heart rate and atrioventricular conduction upon beginning treatment. The maximum fall in heart rate is observed in the first 6 hours post ingestion. Autonomic heart responses, including diurnal variation of heart rate and response to exercise activities, are not altered by siponimod treatment. **Effects on pulmonary function** Dose-dependent decreases in absolute forced expiratory volume over a time frame of 1 second were noted in siponimod-treated patients and were higher than in patients taking placebo.
Sphingosine 1 Phosphate Receptor Modulators
Agents that affect the function of G-protein coupled SPHINGOSINE 1-PHOSPHATE RECEPTORS. Their binding to the receptors blocks lymphocyte migration and are often used as IMMUNOSUPPRESSANTS. (See all compounds classified as Sphingosine 1 Phosphate Receptor Modulators.)
L04
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L04 - Immunosuppressants
L04A - Immunosuppressants
L04AA - Selective immunosuppressants
L04AA42 - Siponimod
Absorption
The time (Tmax) to attain maximum plasma concentrations (Cmax) after oral administration of immediate-release oral doses of siponimod was found to be approximately 4 hours ( with a range 3 - 8 hours). Siponimod is heavily absorbed (at a rate greater than or equal to 70%). The absolute oral bioavailability of siponimod is about 84%. Steady-state concentrations were attained after approximately 6 days of daily administration of a single dose of siponimod. **Effects of food on absorption** Food ingestion leads to delayed siponimod absorption (the median Tmax increased by approximately 2-3 hours). Food intake has no effect on the systemic exposure of siponimod (Cmax and AUC). Therefore, siponimod may be taken without regard to food.
Route of Elimination
Siponimod is eliminated from the systemic circulation mainly due to metabolism, and subsequent biliary/fecal excretion. Unchanged siponimod was not detected in urine.
Volume of Distribution
Siponimod distributes to body tissues with an average volume of distribution of 124 L. Siponimod fraction mesaured in plasma is 68% in humans. Animal studies demonstrate that siponimod readily crosses the blood-brain-barrier.
Clearance
Apparent systemic clearance of 3.11 L/h has been estimated in MS patients.
Siponimod is extensively metabolized, mainly by CYP2C9 enzyme (79.3%), and subsequently by CYP3A4 enzyme (18.5%). The pharmacological activity of the main metabolites M3 and M17 is not expected to be responsible for the clinical effect and the safety of siponimod in humans.
The apparent elimination half-life is approximately 30 hours.
Inflammation of the white and gray matter tissues in the central nervous system caused by localized immune cell infiltration and their cytokines are the initial cause of damage in MS. B lymphocytes and their cytokines are other factors in the pathogenesis of MS. Lymphotoxin [or transforming growth factor beta (TGF-)] and TNF- produced by these cells encourage inflammation. The S1P receptor is an important receptor related to the function of lymphocytes and can be found in the central nervous system. S1P receptor (S1PR) signaling is associated with a wide variety of physiological processes for lymphocytes, including their egress and recirculation. Siponimod is classified as a sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptor modulator. Siponimod binds with high affinity to both S1P receptors 1 and 5. This drug blocks the ability of lymphocytes to release from the lymph nodes, decreasing the number of lymphocytes found in the peripheral blood. The mechanism by which siponimod exerts therapeutic effects in multiple sclerosis is not known at this time, but may involve the abovementioned decrease of lymphocytes into the central nervous system, decreasing the inflammatory effects of MS.
