







1. R 25061
2. R-25061
3. R25061
4. Tn 762
5. Tn-762
6. Tn762
1. 40828-46-4
2. Profenal
3. Sutoprofen
4. Suprol
5. P-2-thenoylhydratropic Acid
6. Maldocil
7. Masterfen
8. Sulproltin
9. Suprofenum
10. Srendam
11. Suprofene
12. Topalgic
13. Suprocil
14. Suprofene [inn-french]
15. Suprofenum [inn-latin]
16. 4-(2-thenoyl)hydratropsaeure
17. Tn-762
18. 2-[4-(thiophene-2-carbonyl)phenyl]propanoic Acid
19. 2-(4-(2-thenoyl)phenyl)propionsaeure
20. Racemic Suprofen
21. P-(2-thenoyl)hydratropic Acid
22. Tn 762
23. R-25,061
24. Alpha-methyl-4-(2-thienylcarbonyl)benzeneacetic Acid
25. (+-)-2-(p-(2-thenoyl)phenyl)propionic Acid
26. Suprofen (profenal)
27. R 25061
28. R-25061
29. 2-(4-(thiophene-2-carbonyl)phenyl)propanoic Acid
30. Nsc 303611
31. Chebi:9362
32. Hydratropic Acid, P-(2-thenoyl)-
33. Benzeneacetic Acid, .alpha.-methyl-4-(2-thienylcarbonyl)-
34. Chembl956
35. Nsc-303611
36. 988gu2f9pe
37. 2-[4-(thiophen-2-ylcarbonyl)phenyl]propanoic Acid
38. Nsc303611
39. Dsstox_cid_25469
40. Dsstox_rid_80900
41. Dsstox_gsid_45469
42. 2-[4-(thiophene-2-carbonyl)-phenyl]-propionic Acid
43. .alpha.-methyl-4-(2-thienylcarbonyl)benzeneacetic Acid
44. Dolasteron
45. Profenol
46. Profenal (tn)
47. (+/-)-suprofen
48. Sr-05000001776
49. Einecs 255-096-9
50. Suprofen (jan/usp/inn)
51. Unii-988gu2f9pe
52. Tyn-762p
53. Ncgc00016846-01
54. Prestwick_131
55. Cas-40828-46-4
56. Suprofen [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
57. Benzeneacetic Acid, Alpha-methyl-4-(2-thienylcarbonyl)-
58. Spectrum_001157
59. Suprofen [usan]
60. Suprofen [inn]
61. Suprofen [jan]
62. Suprofen [mi]
63. Suprofen [vandf]
64. (.+/-.)-suprofen
65. Prestwick0_000816
66. Prestwick1_000816
67. Prestwick2_000816
68. Prestwick3_000816
69. Spectrum2_001430
70. Spectrum3_000928
71. Spectrum4_001027
72. Spectrum5_001103
73. Suprofen [mart.]
74. Epitope Id:131797
75. Suprofen [usp-rs]
76. Suprofen [who-dd]
77. 2-(4-(2-thienylcarbonyl)phenyl)propanoic Acid
78. Schembl23792
79. Bspbio_000711
80. Kbiogr_001553
81. Kbioss_001637
82. Mls002154015
83. Divk1c_000476
84. Spectrum1501161
85. Spbio_001540
86. Spbio_002632
87. Suprofen [orange Book]
88. 4-(2-thenoyl)hydratropic Acid
89. Bpbio1_000783
90. Gtpl7298
91. Suprofen [usp Impurity]
92. Suprofen, >=98% (hplc)
93. Dtxsid5045469
94. Hms501h18
95. Kbio1_000476
96. Kbio2_001637
97. Kbio2_004205
98. Kbio2_006773
99. Kbio3_001936
100. Ninds_000476
101. Hms1570d13
102. Hms1921l19
103. Hms2092j07
104. Hms2097d13
105. Hms2232o08
106. Hms3372b18
107. Hms3651o17
108. Hms3714d13
109. Hms3884o08
110. Para-(2-thenoyl) Hydratropic Acid
111. Pharmakon1600-01501161
112. A-(p-thenoylphenyl) Propionic Acid
113. Hy-b0270
114. (+)-p-(2-thenoyl)hydratropic Acid
115. (-)-p-(2-thenoyl)hydratropic Acid
116. Tox21_110643
117. Bdbm50090676
118. Ccg-38977
119. Mfcd00079572
120. Nsc757876
121. S1761
122. Akos004909426
123. Tox21_110643_1
124. Ac-4551
125. Db00870
126. Nsc-757876
127. Idi1_000476
128. Ncgc00094916-01
129. Ncgc00094916-02
130. Ncgc00094916-03
131. Ncgc00094916-06
132. Ncgc00094916-09
133. As-15879
134. Smr001233343
135. Db-049665
136. Ab00052231
137. Ft-0630615
138. Sw196442-3
139. U0138
140. C07320
141. D00452
142. (+/-)-2-(p-(2-thenoyl)phenyl)propionic Acid
143. Ab00052231_08
144. (.+/-.)-2-(p-(2-thenoyl)phenyl)propionic Acid
145. 2-[4-(2-thienylcarbonyl)phenyl]propanoic Acid #
146. 828s464
147. Q3978097
148. Sr-05000001776-1
149. Sr-05000001776-3
150. 2-{4-[(thiophen-2-yl)carbonyl]phenyl}propanoic Acid
151. Brd-a34006693-001-04-8
152. Brd-a34006693-001-07-1
153. Suprofen, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
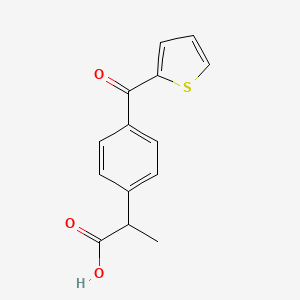
| Molecular Weight | 260.31 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H12O3S |
| XLogP3 | 3.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 260.05071541 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 260.05071541 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 82.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 18 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 321 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Used as eye drops to inhibit the miosis (pupil constriction) that may occur during ocular surgery.
Suprofen is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory analgesic and antipyretic. Ophthalmic anti-inflammatory medicines are used in the eye to lessen problems that can occur during or after some kinds of eye surgery. Sometimes, the pupil of the eye gets smaller during an operation (pupil constriction), making it more difficult for the surgeon to reach some areas of the eye. Suprofen is used to help prevent this.
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal
Anti-inflammatory agents that are non-steroidal in nature. In addition to anti-inflammatory actions, they have analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions. They act by blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, which converts arachidonic acid to cyclic endoperoxides, precursors of prostaglandins. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis accounts for their analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions; other mechanisms may contribute to their anti-inflammatory effects. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal.)
Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors
Compounds or agents that combine with cyclooxygenase (PROSTAGLANDIN-ENDOPEROXIDE SYNTHASES) and thereby prevent its substrate-enzyme combination with arachidonic acid and the formation of eicosanoids, prostaglandins, and thromboxanes. (See all compounds classified as Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors.)
M - Musculo-skeletal system
M01 - Antiinflammatory and antirheumatic products
M01A - Antiinflammatory and antirheumatic products, non-steroids
M01AE - Propionic acid derivatives
M01AE07 - Suprofen
Primarily hepatic (mainly via cytochrome P450 isozyme 2C9).
Suprofen has known human metabolites that include (2S,3S,4S,5R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-[2-[4-(thiophene-2-carbonyl)phenyl]propanoyloxy]oxane-2-carboxylic acid, Suprofen -sulfoxide, and Thiophene-4,5-epoxide.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
Suprofen binds to the cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) isoenzymes, preventing the synthesis of prostaglandins and reducing the inflammatory response. Cyclooxygenase catalyses the formation of prostaglandins and thromboxane from arachidonic acid (itself derived from the cellular phospholipid bilayer by phospholipase A2). Prostaglandins act (among other things) as messenger molecules in the process of inflammation. The overall result is a reduction in pain and inflammation in the eyes and the prevention of pupil constriction during surgery. Normally trauma to the anterior segment of the eye (especially the iris) increases endogenous prostaglandin synthesis which leads to constriction of the iris sphincter.
