




1. Acetate, Chlorhexidine
2. Chlorhexidine Acetate
3. Chlorhexidine Hydrochloride
4. Hydrochloride, Chlorhexidine
5. Mk 412a
6. Mk-412a
7. Mk412a
8. Novalsan
9. Sebidin A
10. Tubulicid
1. 55-56-1
2. Rotersept
3. Fimeil
4. Hexadol
5. Soretol
6. Chlorhexidin
7. Chlorhexidinum
8. Cloresidina [dcit]
9. Chlorhexidin [czech]
10. Chlorhexidinum [inn-latin]
11. Clorhexidina [inn-spanish]
12. Nolvasan
13. Merfen-incolore
14. Hibistat
15. Chlorhexadine
16. Dentisept
17. 1,6-bis(p-chlorophenyldiguanido)hexane
18. 1,6-di(4'-chlorophenyldiguanido)hexane
19. 1,6-bis(5-(p-chlorophenyl)biguandino)hexane
20. Chlorohexidine
21. Tubulicid
22. Chlorhexidine (inn)
23. 1,1'-hexamethylenebis(5-(p-chlorophenyl)biguanide)
24. 1,1'-hexamethylene Bis(5-(p-chlorophenyl)biguanide)
25. 2,4,11,13-tetraazatetradecanediimidamide, N,n''-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3,12-diimino-
26. Sterilon
27. Chembl790
28. R4ko0dy52l
29. Mls001332388
30. Chebi:3614
31. Cloresidina
32. Clorhexidina
33. 56-95-1
34. Chlorhexidine Dihydrochloride
35. Biguanide, 1,1'-hexamethylenebis(5-(p-chlorophenyl)-
36. Cas-55-56-1
37. Ncgc00016246-03
38. Smr000857146
39. Sterido
40. Savlon Babycare
41. Chlorhexidine [inn]
42. N',n'''''-hexane-1,6-diylbis[n-(4-chlorophenyl)(imidodicarbonimidic Diamide)]
43. Dsstox_cid_13314
44. Dsstox_rid_79062
45. N,n'-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3,12-diimino-2,4,11,13-tetraazatetradecanediimidamide
46. Dsstox_gsid_33314
47. Chlorhexidine [inn:ban]
48. Mls001304094
49. 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-[n-[6-[[n-[n-(4-chlorophenyl)carbamimidoyl]carbamimidoyl]amino]hexyl]carbamimidoyl]guanidine
50. N-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-3-(6-{n-[3-(4-chlorophenyl)carbamimidamidomethanimidoyl]amino}hexyl)carbamimidamidomethanimidamide
51. Ccris 9230
52. Hsdb 7196
53. Merfen-incolore (tn)
54. Sr-01000799135
55. Nolvasan (*diacetate*)
56. 1,1'-hexamethylenebis[5-(p-chlorophenyl)biguanide]
57. 3697-42-5
58. Smr000718621
59. Einecs 200-238-7
60. Unii-r4ko0dy52l
61. Lisium (*dihydrochloride*)
62. Brn 2826432
63. 1,6-di(n-p-chlorophenyldiguanido)hexane
64. Dentisept [veterinary] (tn)
65. Prestwick_53
66. (1e)-2-[6-[[amino-[(e)-[amino-(4-chloroanilino)methylidene]amino]methylidene]amino]hexyl]-1-[amino-(4-chloroanilino)methylidene]guanidine
67. Chlorhexidine (1)
68. Mfcd00009673
69. Hibidil (salt/mix)
70. Hibisol (salt/mix)
71. Hibitane (salt/mix)
72. Hibiscrub (salt/mix)
73. Hibispray (salt/mix)
74. Nsc526936
75. Spectrum_000237
76. Savloclens (salt/mix)
77. Prestwick0_000143
78. Prestwick1_000143
79. Prestwick2_000143
80. Prestwick3_000143
81. Spectrum2_000135
82. Spectrum3_000339
83. Spectrum4_000277
84. Spectrum5_001322
85. Chlorhexidine [mi]
86. Hexamethylenebis(5-(4-chlorophenyl)biguanide)
87. Ec 200-238-7
88. Schembl3984
89. Chlorhexidine [hsdb]
90. Chlorhexidine [inci]
91. Chlorhexidine, >=99.5%
92. Bspbio_000246
93. Bspbio_001977
94. Chlorhexidine [vandf]
95. Kbiogr_000774
96. Kbioss_000717
97. 4-12-00-01201 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
98. Mls001332387
99. Mls002154209
100. Chlorhexidine [mart.]
101. Divk1c_000761
102. Spbio_000210
103. Spbio_002185
104. Chlorhexidine [usp-rs]
105. Chlorhexidine [who-dd]
106. Bpbio1_000272
107. Dtxsid2033314
108. Bdbm51937
109. Bdbm64773
110. Cid_9552079
111. Kbio1_000761
112. Kbio2_000717
113. Kbio2_003285
114. Kbio2_005853
115. Kbio3_001197
116. Cid_12303047
117. Ninds_000761
118. Regid_for_cid_9552079
119. Bdbm152706
120. Hms1568m08
121. Hms2095m08
122. Hms2233b16
123. Hms3712m08
124. Hy-b1248
125. Tox21_110325
126. Tox21_201404
127. Tox21_303445
128. Bdbm50170723
129. S5397
130. Stk089248
131. Akos005394319
132. Tox21_110325_1
133. Ccg-220143
134. Cs-4958
135. Db00878
136. 2,4,11,13-tetraazatetradecanediimidamide, N,n'-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3,12-diimino-
137. Idi1_000761
138. N,n''''-hexane-1,6-diylbis[n'-(4-chlorophenyl)(imidodicarbonimidic Diamide)]
139. N,n'-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3,12-diimino-2,4,11,13-tetraazatetradeca- Nediimidamide
140. Qtl1_000020
141. Ncgc00016246-01
142. Ncgc00016246-02
143. Ncgc00016246-04
144. Ncgc00016246-05
145. Ncgc00016246-06
146. Ncgc00016246-07
147. Ncgc00016246-09
148. Ncgc00016246-13
149. Ncgc00016246-21
150. Ncgc00091025-01
151. Ncgc00091025-02
152. Ncgc00091025-04
153. Ncgc00247766-01
154. Ncgc00257242-01
155. Ncgc00258955-01
156. (1e)-2-[6-[[amino-[(e)-[amino-(4-chloroanilino)methylene]amino]methylene]amino]hexyl]-1-[amino-(4-chloroanilino)methylene]guanidine
157. As-12648
158. 1,6-di(n-p-chlorophenylbiguanidino)hexane
159. Chlorhexidine, Purum, >=99.0% (hplc)
160. Sbi-0051301.p003
161. Ab00053427
162. C06902
163. D07668
164. Ab00053427-24
165. Ab00053427-28
166. Ab00053427_29
167. 009c673
168. A830704
169. Q-200828
170. Sr-01000799135-5
171. 1,1''-hexamethylene Bis(5-(p-chlorophenyl)biguanide)
172. Brd-k52256627-300-03-3
173. Brd-k52256627-300-05-8
174. Sr-01000799135-10
175. Sr-01000799135-11
176. Chlorhexidine, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
177. Chlorhexidine, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
178. 2,4,11,13-tetraazatetradecanediimidamide, N1,n14-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3,12-diimino-
179. Chlorhexidine, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
180. N'',n''''''''''-hexane-1,6-diylbis[n-(4-chlorophenyl)(imidodicarbonimidic Diamide)]
181. N,n''-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3,12-diimino-2,4,11,13-tetraazatetradecanediimidamide
182. (1e)-2-[6-[[amino-[(e)-[amino-(4-chloroanilino)methylene]amino]methylene]amino]hexyl]-1-[amino-(4-chloroanilino)methylene]guanidine;hydrochloride
183. (1e)-2-[6-[[azanyl-[(e)-[azanyl-[(4-chlorophenyl)amino]methylidene]amino]methylidene]amino]hexyl]-1-[azanyl-[(4-chlorophenyl)amino]methylidene]guanidine
184. (1e)-2-[6-[[azanyl-[(e)-[azanyl-[(4-chlorophenyl)amino]methylidene]amino]methylidene]amino]hexyl]-1-[azanyl-[(4-chlorophenyl)amino]methylidene]guanidine;hydrochloride
185. 2-[amino-[6-[[amino-[(e)-[amino-(4-chloroanilino)methylidene]amino]methylidene]amino]hexylimino]methyl]-1-(4-chlorophenyl)guanidine
186. 2-[amino-[6-[[amino-[(e)-[amino-(4-chloroanilino)methylidene]amino]methylidene]amino]hexylimino]methyl]-1-(4-chlorophenyl)guanidine;hydrochloride
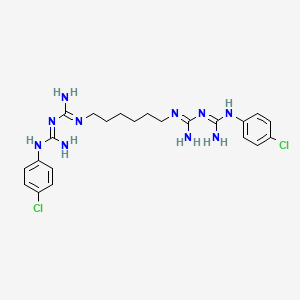
| Molecular Weight | 505.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H30Cl2N10 |
| XLogP3 | 0.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 13 |
| Exact Mass | 504.2031964 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 504.2031964 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 178 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 34 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 649 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Avagard |
| Active Ingredient | Alcohol; chlorhexidine gluconate |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 1%; 61% |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | 3m |
| 2 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Chlorhexidine gluconate |
| PubMed Health | Chlorhexidine |
| Drug Classes | Antibacterial, Antibacterial Cleansing Agent, Wound Care Agent |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorhexidine gluconate |
| Dosage Form | Cloth; Solution; Sponge |
| Route | Dental; Topical |
| Strength | 0.12%; 2%; 4% |
| Market Status | Over the Counter; Prescription |
| Company | Lyne; Wockhardt; Sage Prods; Hi Tech Pharma; Teva; Xttrium; Becton Dickinson |
| 3 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cida-stat |
| PubMed Health | Chlorhexidine |
| Drug Classes | Antibacterial, Antibacterial Cleansing Agent, Wound Care Agent |
| Drug Label | PetcoAntiseptic Spray with Chew DeterrentPETCO Antiseptic Spray with Chew Deterrent is specially formulated to help heal minor wounds caused by small cuts, flea bites and skin irritations. The chew deterrent contains bitter extracts that keep the dog... |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorhexidine gluconate |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 2% |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Ecolab |
| 4 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Dyna-hex |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorhexidine gluconate |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 0.75% |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Bajaj Medical |
| 5 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Exidine |
| PubMed Health | Chlorhexidine |
| Drug Classes | Antibacterial, Antibacterial Cleansing Agent, Wound Care Agent |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorhexidine gluconate |
| Dosage Form | Aerosol, metered; Solution |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 2%; 4% |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Xttrium |
| 6 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Hibiclens |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorhexidine gluconate |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 4% |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Molnlycke Hlth |
| 7 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Hibistat |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorhexidine gluconate |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 0.5% |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Molnlycke Hlth |
| 8 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Peridex |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorhexidine gluconate |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Dental |
| Strength | 0.12% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | 3m |
| 9 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Periochip |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorhexidine gluconate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Dental |
| Strength | 2.5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Dexcel Pharma |
| 10 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Periogard |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorhexidine gluconate |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Dental |
| Strength | 0.12% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Colgate |
| 11 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Avagard |
| Active Ingredient | Alcohol; chlorhexidine gluconate |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 1%; 61% |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | 3m |
| 12 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Chlorhexidine gluconate |
| PubMed Health | Chlorhexidine |
| Drug Classes | Antibacterial, Antibacterial Cleansing Agent, Wound Care Agent |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorhexidine gluconate |
| Dosage Form | Cloth; Solution; Sponge |
| Route | Dental; Topical |
| Strength | 0.12%; 2%; 4% |
| Market Status | Over the Counter; Prescription |
| Company | Lyne; Wockhardt; Sage Prods; Hi Tech Pharma; Teva; Xttrium; Becton Dickinson |
| 13 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cida-stat |
| PubMed Health | Chlorhexidine |
| Drug Classes | Antibacterial, Antibacterial Cleansing Agent, Wound Care Agent |
| Drug Label | PetcoAntiseptic Spray with Chew DeterrentPETCO Antiseptic Spray with Chew Deterrent is specially formulated to help heal minor wounds caused by small cuts, flea bites and skin irritations. The chew deterrent contains bitter extracts that keep the dog... |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorhexidine gluconate |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 2% |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Ecolab |
| 14 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Dyna-hex |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorhexidine gluconate |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 0.75% |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Bajaj Medical |
| 15 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Exidine |
| PubMed Health | Chlorhexidine |
| Drug Classes | Antibacterial, Antibacterial Cleansing Agent, Wound Care Agent |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorhexidine gluconate |
| Dosage Form | Aerosol, metered; Solution |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 2%; 4% |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Xttrium |
| 16 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Hibiclens |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorhexidine gluconate |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 4% |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Molnlycke Hlth |
| 17 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Hibistat |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorhexidine gluconate |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 0.5% |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Molnlycke Hlth |
| 18 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Peridex |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorhexidine gluconate |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Dental |
| Strength | 0.12% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | 3m |
| 19 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Periochip |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorhexidine gluconate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Dental |
| Strength | 2.5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Dexcel Pharma |
| 20 of 20 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Periogard |
| Active Ingredient | Chlorhexidine gluconate |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Dental |
| Strength | 0.12% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Colgate |
Antiseptic; disinfectant. (Vet): antiseptic; disinfectant.
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. Cambridge, UK: Royal Society of Chemistry, 2013., p. 371
Cleanser: As a surgical hand scrub, skin wound and general skin cleanser, health care personnel hand wash, and for preoperative skin preparation. Chlorhedine gluconate significantly reduces the number of microorganisms on the hands and forearms prior to surgery or patient care. /Chlorhexidine gluconate-topical/
Drug Facts and Comparisons 2013. Wolters Kluwer Health St. Louis, MO 2013, p. 3180
EXPL THER To determine if chlorhexidine can be used as an intervention to prolong the time to relapse of oral candidiasis. SUBJECTS AND METHODS: A double-blinded randomized clinical trial was performed in 75 HIV/AIDS subjects with oral candidiasis. Clotrimazole troche was prescribed, and the subjects were re-examined every 2 weeks until the lesions were completely eradicated. The subjects were then randomly divided into two groups; 0.12% chlorhexidine (n = 37, aged 22-52 years, mean 34 years) and 0.9% normal saline (n = 38, aged 22-55 years, mean 38 years). They were re-examined every 2 weeks until the next episode was observed. RESULTS: The time to recurrence of oral candidiasis between the chlorhexidine and the saline group was not statistically significant (P > 0.05). The following variables were significantly associated with the time of recurrence; frequency of antifungal therapy (P = 0.011), total lymphocyte (P = 0.017), alcohol consumption (P = 0.043), and candidiasis on gingiva (P = 0.048). The subjects with lower lymphocyte showed shorter oral candidiasis-free periods (P = 0.034). CONCLUSIONS: Chlorhexidine showed a small but not statistically significant effect in maintenance of oral candidiasis-free period. This lack of significance may be due to the small sample size. Further study should be performed to better assess the size of the effect, or to confirm our findings.
PMID:18627504 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3253386 Nittayananta W et al; Oral Dis. (7): 665-70 (2008)
/EXPTL Therapy:/ Rats were injected with 10 mg/kg azoxymethane sc weekly for 12 weeks to induce colorectal cancers. At 20 weeks, subtotal colectomies were performed on rats with colorectal tumors and without peritoneal implants or liver metastases. At the time of surgery, a cut portion of the tumor was placed in the abdomen for 30 minutes; the rats then randomly received peritoneal irrigation with chlorhexidine, or sterile water (control). Eight weeks postoperatively a necropsy was performed. At that time, obvious and suspected recurrences and the anastomotic area were sampled for histologic evaluation. Significant differences were seen with chlorhexidine vs. water for gross tumor (P=0.05) and microscopic tumor (P<0.05).
Stuntz M et al; Dis Colon Rectum 40 (9): 1058-8 (1997)
For external use only: For external use only. Keep out of eyes, ears, and mouth. Chlorhexidine gluconate should not be used as a preoperative skin preparation of the face or head. Misuse of products containing chlorhexidine gluconate has been reported to cause serious and permanent eye injury when it has been permitted to enter and remain in the eye during surgical procedures. If chlohexidine gluconate should contact these areas, rinse out promptly and thoroughly with cold water. Avoid contact with neninges. Do not use in genital area. /Chlorhexidine gluconate-topical/
Drug Facts and Comparisons 2013. Wolters Kluwer Health St. Louis, MO 2013, p. 3180
Sensitivity: Chlorhexidine gluconate should not be used by persons who have a sensitivity to it or its components.
Drug Facts and Comparisons 2013. Wolters Kluwer Health St. Louis, MO 2013, p. 3180
Hypersensitivity reactions: Irritation, sensitization, and generalized allergic reactions have been reported with chlorhexidine-containing products, especially in the genital areas. If adverse reactions occur and last more than 72 hr, discontinue use immediately and, if severe, contact a health care provider.
Drug Facts and Comparisons 2013. Wolters Kluwer Health St. Louis, MO 2013, p. 3180
Deafness: Chlorhexidine gluconate has been reported to cause deafness when instilled in the middle ear through perforate ear drums. /Chlorhexidine gluconate-topical/
Drug Facts and Comparisons 2013. Wolters Kluwer Health St. Louis, MO 2013, p. 3180
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for CHLORHEXIDINE (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Chlorhexidine is available over-the-counter in various formulations (e.g. solution, sponge, cloth, swab) as a topical antiseptic to sanitize prior to surgeries and/or medical procedures. Dental formulations, available by prescription only, include an oral rinse indicated for the treatment of gingivitis and a slow-release "chip" which is inserted into periodontal pockets and is indicated for the reduction of pocket depth in adult patients with periodontitis as an adjunct therapy to dental scaling and root planing procedures.
FDA Label
Chlorhexidine is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial with demonstrated activity against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, yeasts, and viruses. Antimicrobial activity is dose-dependent - chlorhexidine is bacteriostatic at lower concentrations (0.02%-0.06%) and bactericidal at higher concentrations (>0.12%). Pharmacokinetic studies of oral chlorhexidine rinses indicate that approximately 30% of the active ingredient is retained in the mouth following rinsing, which is subsequently slowly released into oral fluids. This ability to adsorb to dentine, shared with tetracycline antibiotics such as [doxycycline], is known as "substantivity" and is the result of chlorhexidine's positive charge - it is likely that this substantivity plays at least some role in chlorhexidine's antimicrobial activity, as its persistence on surfaces such as dentine prevent microbial colonization. Dental chlorhexidine rinses may result in staining of oral surfaces, such as teeth. This effect is not ubiquitous and appears to be more significant with extended therapy (i.e. up to 6 months) - nevertheless, patients for whom oral staining is unacceptable should use chlorhexidine rinse with caution and for the shortest effective interval. Allergic reactions to chlorhexidine have been associated with the development of anaphylaxis.
Anti-Infective Agents, Local
Substances used on humans and other animals that destroy harmful microorganisms or inhibit their activity. They are distinguished from DISINFECTANTS, which are used on inanimate objects. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Infective Agents, Local.)
Disinfectants
Substances used on inanimate objects that destroy harmful microorganisms or inhibit their activity. Disinfectants are classed as complete, destroying SPORES as well as vegetative forms of microorganisms, or incomplete, destroying only vegetative forms of the organisms. They are distinguished from ANTISEPTICS, which are local anti-infective agents used on humans and other animals. (From Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, 11th ed) (See all compounds classified as Disinfectants.)
Mouthwashes
Solutions for rinsing the mouth, possessing cleansing, germicidal, or palliative properties. (From Boucher's Clinical Dental Terminology, 4th ed) (See all compounds classified as Mouthwashes.)
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A01 - Stomatological preparations
A01A - Stomatological preparations
A01AB - Antiinfectives and antiseptics for local oral treatment
A01AB03 - Chlorhexidine
B - Blood and blood forming organs
B05 - Blood substitutes and perfusion solutions
B05C - Irrigating solutions
B05CA - Antiinfectives
B05CA02 - Chlorhexidine
D - Dermatologicals
D08 - Antiseptics and disinfectants
D08A - Antiseptics and disinfectants
D08AC - Biguanides and amidines
D08AC02 - Chlorhexidine
D - Dermatologicals
D09 - Medicated dressings
D09A - Medicated dressings
D09AA - Medicated dressings with antiinfectives
D09AA12 - Chlorhexidine
R - Respiratory system
R02 - Throat preparations
R02A - Throat preparations
R02AA - Antiseptics
R02AA05 - Chlorhexidine
S - Sensory organs
S01 - Ophthalmologicals
S01A - Antiinfectives
S01AX - Other antiinfectives
S01AX09 - Chlorhexidine
S - Sensory organs
S02 - Otologicals
S02A - Antiinfectives
S02AA - Antiinfectives
S02AA09 - Chlorhexidine
S - Sensory organs
S03 - Ophthalmological and otological preparations
S03A - Antiinfectives
S03AA - Antiinfectives
S03AA04 - Chlorhexidine
Absorption
Topically, chlorhexidine is unlikely to undergo any degree of systemic absorption. Orally administered chlorhexidine, such as that found in oral rinses for dental purposes, is very poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract - the Cmax in human subjects following an oral dose of 300mg was 0.206 g/g and occurred approximately 30 minutes after ingestion (Tmax). Following the insertion of 4 PerioChips in 18 adult patients, no detectable plasma or urine chlorhexidine levels were observed.
Route of Elimination
Excretion of chlorhexidine gluconate occurs almost exclusively via the feces, with less than 1% of an ingested dose excreted in the urine.
34 newborn infants who had been bathed in a standard manner with Hibiscrub were studied to find out whether it was absorbed percutaneously. Low levels of chlorhexidine were found in the blood of all 10 babies sampled by heel prick, and 5 of 24 from whom venous blood was taken. /Chlorhexidine gluconate/
PMID:475414 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1545570 Cowen J et al; Arch Dis Child 54 (5): 379-83 (1979)
Percutaneous absorption of the antimicrobial agent chlorhexidine (labelled with carbon-14) was studied in rats. Less than 5% of the topically applied chlorhexidine was absorbed during a 5-day period. Excretion of absorbed radioactivity occurred mainly in the feces.
Chow CP, et al; Toxicol Lett 1(4): 213-16 (1978)
The percutaneous absorption of chlorhexidine gluconate (chlorhexidine digluconate; Hibitane) through hairless rat skin with or without stratum corneum was studied. For tests carried out on whole skin, storage in cutaneous structures after 48 hr was more important than diffusion; the reverse was observed for stripped skin. When the skin was stripped, the amount absorbed was multiplied by approximately 100, and the amount stored in skin by approximately 10. The difference in chlorhexidine diffusion observed between whole and stripped skin was related to the physicochemical characteristics of chlorhexidine. /Chlorhexidine gluconate/
Lafforque C et al; Int J Pharm 147: 243-6 (1997)
To evaluate the elimination kinetics of chlorhexidine in milk when used as an intramammary infusion to stop lactation in cows. ... The study was performed in 2 phases. Three cows were studied in each phase. All cows were treated with chlorhexidine suspension by infusion into a mastitic mammary gland quarter after 2 milkings 24 hours apart. Foremilk samples (100 mL) were collected from treated and untreated (controls) mammary gland quarters of each cow. Chlorhexidine was extracted from raw milk, and residue concentrations were quantified by use of high-performance liquid chromatography. Foremilk samples from days 2, 5, and 8 were analyzed in phase I, and samples from time 0 and days 3, 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, and 42 were analyzed in phase II. In phases I and II, there was no quantifiable transference of chlorhexidine to milk in untreated mammary gland quarters. Measurable chlorhexidine residues were found in milk from treated mammary gland quarters of 2 cows throughout the 42-day sample period in phase II. Estimated mean elimination half-life for chlorhexidine in milk was 11.5 days.
PMID:12830870 Middleton JR et al; J Am Vet Med Assoc 222 (12): 1746-9 (2003)
As chlorhexidine is very poorly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, it is unlikely to undergo metabolic conversion to any significant extent.
To evaluate the elimination kinetics of chlorhexidine in milk when used as an intramammary infusion to stop lactation in cows. ... The study was performed in 2 phases. Three cows were studied in each phase. All cows were treated with chlorhexidine suspension by infusion into a mastitic mammary gland quarter after 2 milkings 24 hours apart. Foremilk samples (100 mL) were collected from treated and untreated (controls) mammary gland quarters of each cow. Chlorhexidine was extracted from raw milk, and residue concentrations were quantified by use of high-performance liquid chromatography. Foremilk samples from days 2, 5, and 8 were analyzed in phase I, and samples from time 0 and days 3, 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, and 42 were analyzed in phase II. In phases I and II, there was no quantifiable transference of chlorhexidine to milk in untreated mammary gland quarters. Measurable chlorhexidine residues were found in milk from treated mammary gland quarters of 2 cows throughout the 42-day sample period in phase II. Estimated mean elimination half-life for chlorhexidine in milk was 11.5 days.
PMID:12830870 Middleton JR et al; J Am Vet Med Assoc 222 (12): 1746-9 (2003)
Chlorhexidines broad-spectrum antimicrobial effects are due to its ability to disrupt microbial cell membranes. The positively charged chlorhexidine molecule reacts with negatively charged phosphate groups on microbial cell surfaces - this reaction both destroys the integrity of the cell, allowing leakage of intracellular material, and allows chlorhexidine to enter the cell, causing precipitation of cytoplasmic components and ultimately cell death. The specific means of cell death is dependent on the concentration of chlorhexidine - lower concentrations are bacteriostatic and result in leakage of intracellular substances such as potassium and phosphorous, whereas higher concentrations are bactericidal and cause cytoplasmic precipitation.