




1. Axid
2. Ly 139037
3. Ly-139037
4. Ly139037
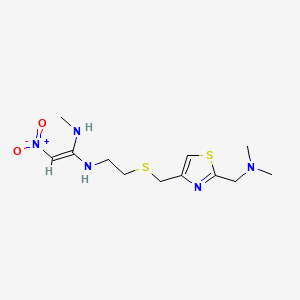
5. N-(2-(((2-((dimethylamino)methyl)-4-thiazolyl)methyl)thio)ethyl)-n'-methyl-2-nitro-1,1-ethenediamine
1. 76963-41-2
2. Axid
3. Zanizal
4. Nizax
5. Ly-139037
6. Niaztidine
7. Nizatidinum
8. Nizatidina
9. Ze-101
10. Zl-101
11. (e)-n-(2-(((2-((dimethylamino)methyl)thiazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)ethyl)-n'-methyl-2-nitroethene-1,1-diamine
12. (e)-n-(2-(((2-((dimethylamino)methyl)thiazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)ethyl)-n-methyl-2-nitroethene-1,1-diamine
13. Dimethyl[(4-{[(2-{[(e)-1-(methylamino)-2-nitroethenyl]amino}ethyl)sulfanyl]methyl}-1,3-thiazol-2-yl)methyl]amine
14. N-(4-(6-methylamino-7-nitro-2-thia-5-aza-6-hepten-1-yl)-2-thiazolylmethyl)-n,n-dimethylamine
15. Smr000466384
16. Acinon (tn)
17. Axid (tn)
18. Chebi:7601
19. Mfcd00865660
20. Ncgc00016934-01
21. Cas-76963-41-2
22. Prestwick2_000921
23. Schembl769
24. Schembl770
25. Chembl653
26. Ly-139037, Nizatidine
27. Mls000759518
28. Mls001076680
29. Mls001424001
30. Bidd:gt0761
31. Nizatidine, Analytical Standard
32. Gtpl7248
33. Nizatidine (jp17/usp/inn)
34. Nizatidine For System Suitability
35. Hms2051k04
36. Hms2094a15
37. Hms2235n05
38. Pharmakon1600-01505985
39. Hy-b0310
40. Zinc1530736
41. Nsc759289
42. Akos015900643
43. Ac-5272
44. Ccg-100836
45. Db00585
46. Hs-0083
47. Nc00086
48. Ncgc00016934-02
49. (e)-n-{2-[({2-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-1,3-thiazol-4-yl}methyl)thio]ethyl}-n'-methyl-2-nitroethene-1,1-diamine
50. Bn166185
51. Sbi-0206937.p001
52. C07270
53. D00440
54. Ab00698253-07
55. Ab00698253_09
56. Benzenesulfonylchloride,4-hydroxy-3-nitro-(9ci)
57. 963n412
58. A838919
59. L000761
60. Sr-01000765410
61. Q1188290
62. Sr-01000765410-4
63. Brd-k73589491-001-05-4
64. Brd-k92193792-001-01-7
65. (e)-1-n'-[2-[[2-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]methylsulfanyl]ethyl]-1-n-methyl-2-nitroethene-1,1-diamine
66. (e)-n-(2-((2-((dimethylamino)methyl)thiazol-4-yl)methylthio)ethyl)-n-methyl-2-nitroethene-1,1-diamine
67. (e)-n1'-[2-[[2-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]methylsulfanyl]ethyl]-n1-methyl-2-nitro-ethene-1,1-diamine
68. (e)-n1'-[2-[[2-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-4-thiazolyl]methylthio]ethyl]-n1-methyl-2-nitroethene-1,1-diamine
69. 1,1-ethenediamine, N'-[2-[[[2-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-4-thiazolyl]methyl]thio]ethyl]-n-methyl-2-nitro-
70. N-(2-(((2-((dimethylamino)methyl)thiazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)ethyl)-n-methyl-2-nitroethene-1,1-diamine
71. N-{2-[({2-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-1,3-thiazol-4-yl}methyl)sulfanyl]ethyl}-n'-methyl-2-nitroethene-1,1-diamine
| Molecular Weight | 331.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H21N5O2S2 |
| XLogP3 | 1.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Exact Mass | 331.11366728 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 331.11366728 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 140 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 349 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Axid |
| PubMed Health | Nizatidine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiulcer, Gastric Acid Secretion Inhibitor |
| Drug Label | Nizatidine (USP) is a histamine H2-receptor antagonist. Chemically, it is N-[2-[[[2-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-4-thiazolyl]methyl]thio]ethyl]-N'-methyl-2-nitro-1,1-ethenediamine. The structural formula is as follows: Nizatidine has the empirical formula |
| Active Ingredient | Nizatidine |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 15mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Braintree |
| 2 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Axid ar |
| Active Ingredient | Nizatidine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 75mg |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Pfizer |
| 3 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Nizatidine |
| PubMed Health | Nizatidine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiulcer, Gastric Acid Secretion Inhibitor |
| Drug Label | Nizatidine USP is a histamine H2-receptor antagonist. Chemically, it is N-[2-[[[2-[(Dimethylamino)methyl]-4-thiazolyl]methyl]thio]ethyl]-N'-methyl-2-nitro-1,1-ethenediamine. The structural formula is represented below:C12H21N5O2S2... |
| Active Ingredient | Nizatidine |
| Dosage Form | Capsule; Solution |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 150mg; 300mg; 15mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Amneal Pharms; Mylan Pharms; Ani Pharms; Sandoz; Watson Labs; Glenmark Generics; Dr Reddys Labs |
| 4 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Axid |
| PubMed Health | Nizatidine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiulcer, Gastric Acid Secretion Inhibitor |
| Drug Label | Nizatidine (USP) is a histamine H2-receptor antagonist. Chemically, it is N-[2-[[[2-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-4-thiazolyl]methyl]thio]ethyl]-N'-methyl-2-nitro-1,1-ethenediamine. The structural formula is as follows: Nizatidine has the empirical formula |
| Active Ingredient | Nizatidine |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 15mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Braintree |
| 5 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Axid ar |
| Active Ingredient | Nizatidine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 75mg |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Pfizer |
| 6 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Nizatidine |
| PubMed Health | Nizatidine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiulcer, Gastric Acid Secretion Inhibitor |
| Drug Label | Nizatidine USP is a histamine H2-receptor antagonist. Chemically, it is N-[2-[[[2-[(Dimethylamino)methyl]-4-thiazolyl]methyl]thio]ethyl]-N'-methyl-2-nitro-1,1-ethenediamine. The structural formula is represented below:C12H21N5O2S2... |
| Active Ingredient | Nizatidine |
| Dosage Form | Capsule; Solution |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 150mg; 300mg; 15mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Amneal Pharms; Mylan Pharms; Ani Pharms; Sandoz; Watson Labs; Glenmark Generics; Dr Reddys Labs |
Anti-Ulcer Agents; Histamine H2 Antagonists
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
In the Zollinger-Ellison syndrome and other acid peptic disorders, the efficacy of nizatidine would be expected to be similar to that of ranitidine, but confirmation in clinical studies is required. Nizatidine relieves symptoms and heals lesions in patients with mild to moderate reflux esophagitis.
American Medical Association, Council on Drugs. AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1994. Chicago, IL: American Medical Association, 1994., p. 903
Histamine H2-receptor antagonists are indicated in the short-term treatment of active duodenal ulcer. They are also indicated (at reduced dosage) in the prevention of duodenal ulcer recurrence in selected patients. /Histamine H2-receptor antagonists; Included in US product labeling/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 16th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: U.S. Pharmaceutical Convention, Inc. 1996 (Plus updates)., p. 1611
Nizatidine ... /is/ indicated in the short-term treatment of active benign gastric ulcer. /Included in US product labeling/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 16th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: U.S. Pharmaceutical Convention, Inc. 1996 (Plus updates)., p. 1611
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for NIZATIDINE (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Nizatidine should be used with caution and the dose and/or frequency of administration reduced in patients with renal impairment (ie., creatinine clearance less than 50 ml/min), since the drug is excreted principally by the kidneys.
McEvoy G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 96. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1996 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2174
Symptomatic response to nizatidine should not be interpreted as precluding the presence of gastric malignancy.
McEvoy G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 96. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1996 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2174
Rhinitis, pharyngitis, sinusitis, or increased cough has occurred in about 2-10% of patients receiving nizatidine. Diaphoresis occurred more often with nizatidine therapy than with placebo but was not considered drug related because of its association with other concurrent adverse events (e.g., fever, anxiety). Pain, including back or chest pain, has been reported in approximately 2-4% of patients receiving nizatidine. Other adverse events reported in patients receiving nizatidine include myalgia, fever, infection, amblyopia, hyperuricemia, and impotence. In most studies, the incidence of these adverse effects, and of surgical procedures or accidental injuries, was similar in patients receiving nizatidine or placebo. Asymptomatic ventricular tachycardia, decreased libido, and gynecomastia have been reported rarely.
McEvoy G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 96. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1996 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2174
Urticaria occurred more often with nizatidine therapy (0.5% of patients) than with placebo (0.1% of patients) in placebo-controlled clinical studies. Rash, pruritus, or exfoliative dermatitis has occurred in up to 2% of patients receiving nizatidine. Serum sickness-like reactions, anaphylaxis, bronchospasm, laryngeal edema, eosinophilia, vasculitis, and erythema multiforme also have been reported rarely.
McEvoy G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 96. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1996 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2174
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for NIZATIDINE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the treatment of acid-reflux disorders (GERD), peptic ulcer disease, active benign gastric ulcer, and active duodenal ulcer.
FDA Label
Nizatidine is a competitive, reversible inhibitor of histamine at the histamine H2-receptors, particularly those in the gastric parietal cells. By inhibiting the action of histamine on stomach cells, nizatidine reduces stomach acid production. Nizatidine had no demonstrable antiandrogenic action. Full-dose therapy for the problems treated by nizatidine lasts no longer than 8 weeks. It has been demonstrated that treatment with a reduced dose of nizatidine is effective as maintenance therapy following healing of active duodenal ulcers.
Histamine H2 Antagonists
Drugs that selectively bind to but do not activate histamine H2 receptors, thereby blocking the actions of histamine. Their clinically most important action is the inhibition of acid secretion in the treatment of gastrointestinal ulcers. Smooth muscle may also be affected. Some drugs in this class have strong effects in the central nervous system, but these actions are not well understood. (See all compounds classified as Histamine H2 Antagonists.)
Anti-Ulcer Agents
Various agents with different action mechanisms used to treat or ameliorate PEPTIC ULCER or irritation of the gastrointestinal tract. This has included ANTIBIOTICS to treat HELICOBACTER INFECTIONS; HISTAMINE H2 ANTAGONISTS to reduce GASTRIC ACID secretion; and ANTACIDS for symptomatic relief. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Ulcer Agents.)
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A02 - Drugs for acid related disorders
A02B - Drugs for peptic ulcer and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (gord)
A02BA - H2-receptor antagonists
A02BA04 - Nizatidine
Absorption
Rapid (bioavailability of nizatidine exceeds 70%)
Volume of Distribution
0.8 to 1.5 L/kg
Clearance
40-60 L/h
7 14 L/h [functionally anephric patients]
Nizatidine has a duration of action of up to 10 hours. It is eliminated primarily by the kidneys; 90% of the administered dose (65% as unchanged drug) is recovered in the urine within 16 hours.
American Medical Association, Council on Drugs. AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1994. Chicago, IL: American Medical Association, 1994., p. 904
Distribution of nizatidine into human body tissues and fluids has not been fully characterized. The apparent volume of distribution of the drug is reported to be 0.8-1.5 l/kg in adults and does not appear to be altered substantially in patients with renal dysfunction.
McEvoy G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 96. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1996 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2172
In one study, the oral bioavailability of nizatidine exceeded 70% and was not affected by food or the anticholinergic drug, propantheline. Its apparent volume of distribution is 1.2 l/kg. Systemic clearance (10 ml/min/kg) is decreased in uremic patients and in the elderly.
American Medical Association, Council on Drugs. AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1994. Chicago, IL: American Medical Association, 1994., p. 904
The safety and disposition of single oral doses of nizatidine were investigated in 8 young volunteers (aged 25-48 yr) who received 100-350 mg nizatidine and in 12 elderly volunteers (aged 66-79 yr) who received 100-300 mg. The nizatidine AUC was directly proportional to dose for both groups of volunteers. Calculated pharmacokinetic variables in the elderly versus the young were Tl/2 (1.9 versus 1.6 hr), apparent plasma clearance (32 versus 40 l/h) and apparent volume of distribution (1.2 versus 1.3 l/kg). The impaired renal function of some elderly volunteers prolonged nizatidine elimination and lowered its clearance. Renal impairment rather than advanced age per se was the predominant factor in decreasing the nizatidine elimination rate. No serious adverse effects occurred.
PMID:2888796 Callaghan JT et al; J Clin Pharmacol 27 (Aug): 618-24 (1987)
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for NIZATIDINE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Hepatic. Less than 7% of an oral dose is metabolized as N2-monodes-methylnizatidine, an H2-receptor antagonist, which is the principal metabolite excreted in the urine. Other likely metabolites are the N2-oxide (less than 5% of the dose) and the S-oxide (less than 6% of the dose).
Nizatidine is metabolized in the liver to N-desmethylnizatidine, nizatidine N-oxide, and nizatidine sulfoxide. Of these metabolites, only N-desmethylnizatidine has histamine H2-receptor blocking activity; studies in animals indicate that this metabolite is approximately 60% as active as nizatidine in blocking gastric acid secretion. Orally administered nizatidine undergoes minimal metabolism on first pass through the liver.
McEvoy G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 96. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1996 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2172
1-2 hours
Half life is 10 hours.
American Medical Association, Council on Drugs. AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1994. Chicago, IL: American Medical Association, 1994., p. 904
Nizatidine competes with histamine for binding at the H2-receptors on the gastric basolateral membrane of parietal cells. Competitive inhibition results in reduction of basal and nocturnal gastric acid secretions. The drug also decreases the gastric acid response to stimuli such as food, caffeine, insulin, betazole, or pentagastrin.