

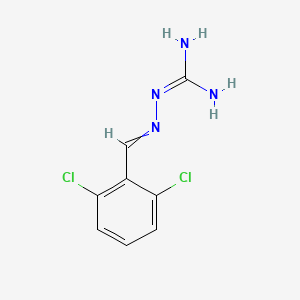

1. 2,6 Dichlorobenzylideneaminoguanidine
2. 2,6-dichlorobenzylideneaminoguanidine
3. Acetate Wyeth-ayerst, Guanabenz
4. Acetate, Guanabenz
5. Br 750
6. Br-750
7. Br750
8. Guanabenz
9. Guanabenz Acetate
10. Guanabenz Acetate Wyeth-ayerst
11. Guanabenz Monoacetate
12. Monoacetate, Guanabenz
13. Wy 8678
14. Wy-8678
15. Wy8678
16. Wyeth Ayerst Of Guanabenz Acetate
17. Wyeth-ayerst Of Guanabenz Acetate
18. Wytensin
1. Guanabenz
2. 5051-62-7
3. Hydrazinecarboximidamide, 2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)methylene]-, (e)-
4. Dsstox_cid_25666
5. Dsstox_rid_81042
6. Dsstox_gsid_45666
7. Cas-5051-62-7
8. Ncgc00024846-03
9. Spectrum_000843
10. Prestwick0_000096
11. Prestwick1_000096
12. Spectrum2_001114
13. Spectrum3_000445
14. Spectrum4_000567
15. Kbiogr_000974
16. Kbioss_001323
17. Divk1c_000010
18. Spbio_001248
19. Spbio_001991
20. Chembl1313657
21. Dtxsid6045666
22. Kbio1_000010
23. Kbio2_001323
24. Kbio2_003891
25. Kbio2_006459
26. Kbio3_001310
27. Ninds_000010
28. Hms2233d12
29. Hms3370a17
30. Bcp30851
31. Tox21_110932
32. Akos017264577
33. Tox21_110932_1
34. Zinc242701441
35. Db00629
36. 2,6-dichlorobenzaldehyde Guanylhydrazone
37. Mrf-0000008
38. Ncgc00024846-08
39. Db-051784
40. Ft-0635524
41. Guanabenzum;wy-8678; Wy 8678; Wy8678
42. N-(2,6-dichlorobenzylidene)-n'-amidino Hydrazine
43. Sr-01000721838
44. Sr-01000721838-5
45. Q27164730
| Molecular Weight | 231.08 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C8H8Cl2N4 |
| XLogP3 | 1.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 230.0126017 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 230.0126017 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 76.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 14 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 228 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For management of High blood pressure
FDA Label
Guanabenz, a centrally acting α-2 adrenergic agonist, is indicated for treatment of hypertension.
Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Agonists
Compounds that bind to and activate ADRENERGIC ALPHA-2 RECEPTORS. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Agonists.)
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
Absorption
Approximately 75% absorbed from gastrointestinal tract
Hepatic
6 hours.
Guanabenz's antihypertensive effect is thought to be due to central alpha-adrenergic stimulation, which results in a decreased sympathetic outflow to the heart, kidneys, and peripheral vasculature in addition to a decreased systolic and diastolic blood pressure and a slight slowing of pulse rate. Chronic administration of guanabenz also causes a decrease in peripheral vascular resistance.
