



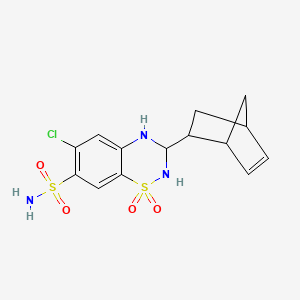

1. 2259-96-3
2. Anhydron
3. Aquirel
4. Fluidil
5. Renazide
6. Valmiran
7. Doburil
8. Ciclotiazide [dcit]
9. Ciclotiazida
10. Cyclothiazidum
11. Ciclotiazida [inn-spanish]
12. Cyclothiazidum [inn-latin]
13. Mdi 193
14. 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-3-(5-norbornen-2-yl)-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
15. 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-3-(2-norbornen-5-yl)-2h-1,2-4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
16. 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-3-(2-norbornen-5-yl)-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
17. 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-3-(2-norbornen-5-yl)-7-sulfamoyl-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide
18. 6-chloro-3-(2-norbornen-5-yl)-7-sulfamyl-3,4-dihydro-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide
19. Nsc-758431
20. Chembl61593
21. P71u09g5bw
22. 2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 3-bicyclo(2.2.1)hept-5-en-2-yl-6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-, 1,1-dioxide
23. 2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 3-bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-en-2-yl-6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-, 1,1-dioxide
24. 2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-3-(5-norbornen-2-yl)-, 1,1-dioxide
25. Ciclotiazide
26. Chebi:31448
27. 3-bicyclo(2.2.1)hept-5-en-2-yl-6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
28. Ncgc00015288-06
29. Dsstox_cid_2871
30. Lilly 35483; Mdi 193; Renazide; Valmiran
31. Dsstox_rid_76767
32. Dsstox_gsid_22871
33. 2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide,3-bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-en-2-yl-6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-, 1,1-dioxide
34. Lilly 35,483
35. Anhydron (tn)
36. 3-(bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-en-2-yl)-6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-2h-benzo[e][1,2,4]thiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
37. 3-{bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-en-2-yl}-6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-2h-1$l^{6},2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
38. 3-bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-en-2-yl-6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
39. 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-3-(5-norbornen-2-yl)-2h-1,2,4-benzothiazidiazine-7-sulfonamide-1,1-dioxide
40. Cas-2259-96-3
41. Hsdb 3310
42. Sr-01000075796
43. Einecs 218-859-7
44. Brn 0722843
45. Unii-p71u09g5bw
46. 3-(bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-en-2-yl)-6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
47. Cyclothiazide (jan/usan/inn)
48. 3-(5-bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-enyl)-6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-2h-1?^{6},2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
49. Cyclothiazide [usan:usp:inn:ban]
50. Disodiumhexafluorozirconate
51. Spectrum4_000050
52. Spectrum5_001639
53. Lilly 35483
54. Cyclothiazide [mi]
55. Biomol-nt_000224
56. C 9847
57. Cyclothiazide [inn]
58. Cyclothiazide [jan]
59. 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-3-(norbornen-2-yl)-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
60. Cyclothiazide [hsdb]
61. Cyclothiazide [usan]
62. Lopac0_000321
63. Cyclothiazide [vandf]
64. Kbiogr_000519
65. 2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 3,4-dihydro-6-chloro-3-(5-norbornen-2-yl)-, 1,1-dioxide
66. 2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 3,4-dihydro-6-chloro-3-(5-norbornen-2-yl)-,1,1-dioxide
67. Mls001077326
68. Cyclothiazide [mart.]
69. Divk1c_000904
70. Schembl121096
71. Cyclothiazide [usp-rs]
72. Cyclothiazide [who-dd]
73. Bpbio1_001320
74. Gtpl4167
75. Dtxsid3022871
76. Hms502n06
77. Kbio1_000904
78. Ninds_000904
79. Cyclothiazide (mixture Of Isomers)
80. Hms2093a19
81. Hms2236k04
82. Hms3261a03
83. Hms3266l17
84. Hms3373e04
85. Hms3411d03
86. Hms3675d03
87. Pharmakon1600-01503263
88. Cyclothiazide [orange Book]
89. Tox21_110124
90. Tox21_500321
91. Bdbm50192229
92. Nsc758431
93. S6611
94. Akos024458615
95. Tox21_110124_1
96. Ccg-204416
97. Db00606
98. Lp00321
99. Nsc 758431
100. Sdccgsbi-0050309.p004
101. Idi1_000904
102. Ncgc00015288-04
103. Ncgc00015288-05
104. Ncgc00015288-07
105. Ncgc00015288-09
106. Ncgc00015288-14
107. Ncgc00022985-02
108. Ncgc00024745-02
109. Ncgc00024745-03
110. Ncgc00024745-04
111. Ncgc00261006-01
112. 3-(2-bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-enyl)-6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-2h-1lambda6,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
113. As-76539
114. Smr000653479
115. Sbi-0050309.p003
116. Hy-101165
117. Cs-0020935
118. Eu-0100321
119. Ft-0665417
120. D01256
121. D81850
122. Ab00053281_04
123. J-014778
124. Q5199066
125. Sr-01000075796-1
126. Sr-01000075796-3
127. Sr-01000075796-4
128. Brd-a38675539-001-01-0
129. Brd-a38675539-001-05-1
130. 3-bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-en-2-yl-6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1lambda*6*-benzo[1,2,4]thiadiazine-7-sulfonic Acid Amide
131. 3-bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-en-2-yl-6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1lambda*6*-benzo[1,2,4]thiadiazine-7-sulfonic Acid Amide(clothiazide)
132. 3-bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-en-2-yl-6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide #
133. 3-bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-en-2-yl-7-chloro-1,1-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1lambda*6*-benzo[1,2,4]thiadiazine-6-sulfonic Acid Amide
134. 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-3-(2-norbornen-5-yl)-2h-1,2-4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide1,1-dioxide
135. 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-3-(5-norbornen-2-yl)-2h-1,2,4-benzothiazidiazine-7-sulfonamide-1 ,1-dioxide
| Molecular Weight | 389.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H16ClN3O4S2 |
| XLogP3 | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 389.0270760 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 389.0270760 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 135 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 758 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Antihypertensive Agents; Diuretics, Thiazide
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
LESS COMMON USAGES INCL TREATMENT OF DIABETES INSIPIDUS & MGMNT OF HYPERCALCIURIA IN PT WITH RECURRENT URINARY CALCULI COMPOSED OF CALCIUM. /THIAZIDES/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 902
THIAZIDE DIURETICS ARE EFFECTIVE AS ADJUNCTIVE THERAPY IN EDEMA ASSOC WITH CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE, HEPATIC CIRRHOSIS, & CORTICOSTEROID & ESTROGEN THERAPY, AS WELL AS EDEMA DUE TO VARIOUS FORMS OF RENAL DYSFUNCTION...& SEVERE EDEMA DUE TO PREGNANCY. /THIAZIDES/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 868
CYCLOTHIAZIDE IS ORALLY EFFECTIVE DIURETIC & ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENT. DIURESIS OCCURS WITHIN 2 HR & LASTS 18 TO 24 HR. ...IT MAY BE USED AS ADJUNCT TO OTHER ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENTS, SUCH AS RESERPINE & GANGLIONIC BLOCKING AGENTS.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 869
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for CYCLOTHIAZIDE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
PLASMA POTASSIUM CONCN SHOULD BE DETERMINED PERIODICALLY IN PATIENTS WHO RECEIVE THIAZIDE DIURECTICS FOR EXTENDED PERIODS. /BENZOTHIADIAZIDES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 832
THIAZIDE DIURETICS ARE CONTRAINDICATED IN ANURIA, PATIENTS HYPERSENSITIVE TO THESE & OTHER SULFONAMIDE DRUGS, & IN OTHERWISE HEALTHY PREGNANT WOMEN WITH OR WITHOUT MILD EDEMA. ...SHOULD BE USED WITH CAUTION IN PATIENTS WITH RENAL DISEASE, SINCE THEY MAY PPT AZOTEMIA. /THIAZIDES/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 868
PERIODIC SERUM ELECTROLYTE DETERMINATION SHOULD BE DONE ON ALL PATIENTS IN ORDER TO DETECT ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCE SUCH AS HYPONATREMIA, HYPOCHLOREMIC ALKALOSIS, & HYPOKALEMIA. /THIAZIDES/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 868
DOMINANT ACTION OF THIAZIDES IS TO INCR RENAL EXCRETION OF SODIUM & CHLORIDE & ACCOMPANYING VOL OF WATER. ... THIAZIDES INHIBIT REABSORPTION OF SODIUM & ITS ATTENDANT ANION, CHLORIDE, IN DISTAL SEGMENT. /THIAZIDES/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 899
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for CYCLOTHIAZIDE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
3. 3= MODERATELY TOXIC: PROBABLE ORAL LETHAL DOSE (HUMAN) 0.5-5 G/KG, BETWEEN 1 OZ & 1 PINT (OR 1 LB) FOR 70 KG PERSON (150 LB). /BENZOTHIADIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gosselin, R.E., H.C. Hodge, R.P. Smith, and M.N. Gleason. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 4th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1976., p. II-239
Cyclothiazide is indicated as adjunctive therapy in edema associated with congestive heart failure, hepatic cirrhosis, and corticosteroid and estrogen therapy. It is also indicated in the management of hypertension either as the sole therapeutic agent or to enhance the effectiveness of other antihypertensive drugs in the more severe forms of hypertension.
Like other thiazides, cyclothiazide promotes water loss from the body (diuretics). It inhibits Na+/Cl- reabsorption from the distal convoluted tubules in the kidneys. Thiazides also cause loss of potassium and an increase in serum uric acid. Thiazides are often used to treat hypertension, but their hypotensive effects are not necessarily due to their diuretic activity. Thiazides have been shown to prevent hypertension-related morbidity and mortality although the mechanism is not fully understood. Thiazides cause vasodilation by activating calcium-activated potassium channels (large conductance) in vascular smooth muscles and inhibiting various carbonic anhydrases in vascular tissue. Cyclothiazide affects the distal renal tubular mechanism of electrolyte reabsorption. At maximal therapeutic dosages, all thiazides are approximately equal in their diuretic efficacy. Cyclothiazide increases excretion of sodium and chloride in approximately equivalent amounts. Natriuresis may be accompanied by some loss of potassium and bicarbonate.
Diuretics
Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. (See all compounds classified as Diuretics.)
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
C - Cardiovascular system
C03 - Diuretics
C03A - Low-ceiling diuretics, thiazides
C03AA - Thiazides, plain
C03AA09 - Cyclothiazide
THIAZIDES ARE RAPIDLY ABSORBED FROM GI TRACT...MOST...SHOW DEMONSTRABLE DIURETIC EFFECT WITHIN HR AFTER ORAL ADMIN. ...THIAZIDES WITH RELATIVELY LONG DURATIONS...SHOW...BOTH BINDING TO PLASMA PROTEINS & REABSORPTION BY RENAL TUBULES. /THIAZIDES/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 902
...THIAZIDES PROBABLY UNDERGO ACTIVE SECRETION IN PROXIMAL TUBULE. RENAL CLEARANCES OF DRUGS ARE HIGH & MAY BE EITHER ABOVE OR BELOW RATE OF FILTRATION. MOST COMPD ARE RAPIDLY EXCRETED WITHIN 3 TO 6 HR. /THIAZIDES/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 902
Hydrochlorothiazide, a thiazide diuretic, inhibits water reabsorption in the nephron by inhibiting the sodium-chloride symporter (SLC12A3) in the distal convoluted tubule, which is responsible for 5% of total sodium reabsorption. Normally, the sodium-chloride symporter transports sodium and chloride from the lumen into the epithelial cell lining the distal convoluted tubule. The energy for this is provided by a sodium gradient established by sodium-potassium ATPases on the basolateral membrane. Once sodium has entered the cell, it is transported out into the basolateral interstitium via the sodium-potassium ATPase, causing an increase in the osmolarity of the interstitium, thereby establishing an osmotic gradient for water reabsorption. By blocking the sodium-chloride symporter, hydrochlorothiazide effectively reduces the osmotic gradient and water reabsorption throughout the nephron.Hydrochlorothiazide, a thiazide diuretic, inhibits water reabsorption in the nephron by inhibiting the sodium-chloride symporter (SLC12A3) in the distal convoluted tubule, which is responsible for 5% of total sodium reabsorption. Normally, the sodium-chloride symporter transports sodium and chloride from the lumen into the epithelial cell lining the distal convoluted tubule. The energy for this is provided by a sodium gradient established by sodium-potassium ATPases on the basolateral membrane. Once sodium has entered the cell, it is transported out into the basolateral interstitium via the sodium-potassium ATPase, causing an increase in the osmolarity of the interstitium, thereby establishing an osmotic gradient for water reabsorption. By blocking the sodium-chloride symporter, hydrochlorothiazide effectively reduces the osmotic gradient and water reabsorption throughout the nephron.
...BENZOTHIADIAZIDES HAVE DIRECT EFFECT ON RENAL TUBULAR TRANSPORT OF SODIUM & CHLORIDE THAT IS INDEPENDENT OF ANY EFFECT ON CARBONIC ANHYDRASE. ... /THEY/... HAVE PARALLEL DOSE-RESPONSE CURVES & COMPARABLE MAX CHLORURETIC EFFECTS. /BENZOTHIADIAZIDES/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 899
RENAL ACTIONS OF THIAZIDE DIURETICS DECR EXTRACELLULAR FLUID & PLASMA VOL, CARDIAC OUTPUT, & TOTAL EXCHANGEABLE SODIUM IN INDIVIDUALS WITHOUT ANY EVIDENCE OF CARDIAC FAILURE. ...SODIUM & WATER DEPLETION...BASIS FOR ANTIHYPERTENSIVE EFFECT. ...DIURETIC THIAZIDES RELAX PERIPHERAL ARTERIOLAR SMOOTH MUSCLE. /BENZOTHIADIAZIDES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 712
...AS ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENTS...EFFECTS APPEAR TO RESULT FROM ALTERED SODIUM BALANCE. ...DRUG-INDUCED SODIUM EXCRETION AS DETERMINANT OF REDUCTION OF BLOOD PRESSURE IS SUGGESTED...PERIPHERAL VASCULAR RESISTANCE IS DECR...DIRECT ACTION...ON ARTERIOLAR SMOOTH MUSCLE HAS BEEN SUGGESTED. /BENZOTHIADIAZIDES/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 803
Thiazide diuretics increase urinary excretion of sodium and water by inhibiting sodium reabsorption in the early distal tubules. They increase the rate of delivery of tubular fluid and electrolytes to the distal sites of hydrogen and potassium ion secretion, while plasma volume contraction increases aldosterone production. The increased delivery and increase in aldosterone levels promote sodium reabsorption at the distal tubules, thus increasing the loss of potassium and hydrogen ions. /Thiazide diuretics/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 17th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: Convention, Inc., 1997. (Plus Updates)., p. 1258
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for CYCLOTHIAZIDE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.