

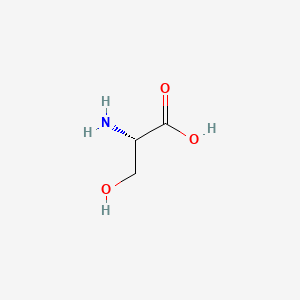

1. L Serine
2. L-serine
1. L-serine
2. 56-45-1
3. (s)-2-amino-3-hydroxypropanoic Acid
4. (s)-serine
5. H-ser-oh
6. Beta-hydroxyalanine
7. L-ser
8. L-(-)-serine
9. (2s)-2-amino-3-hydroxypropanoic Acid
10. L-serin
11. Serine, L-
12. Serinum [latin]
13. Serina [spanish]
14. Serine (van)
15. L-3-hydroxy-alanine
16. (-)-serine
17. Beta-hydroxy-l-alanine
18. L-2-amino-3-hydroxypropionic Acid
19. Serine [usan:inn]
20. Ser (iupac Abbrev)
21. Alpha-amino-beta-hydroxypropionic Acid
22. 2-amino-3-hydroxypropionic Acid
23. L-3-hydroxy-2-aminopropionic Acid
24. (s)-2-amino-3-hydroxypropionic Acid
25. Hsdb 680
26. (s)-(-)-serine
27. 2-amino-3-hydroxypropanoic Acid, (s)-
28. Propanoic Acid, 2-amino-3-hydroxy-, (s)-
29. Mfcd00064224
30. Brn 1721404
31. Ser
32. Chebi:17115
33. (s)-alpha-amino-beta-hydroxypropionic Acid
34. (2s)-2-amino-3-hydroxy-propanoic Acid
35. 6898-95-9
36. Serine (l-serine)
37. 452vly9402
38. Nsc-118365
39. (s)-2-amino-3-hydroxy-propanoic Acid
40. (s)-(+)-2-amino-3-hydroxypropionic Acid
41. Serinum
42. Serene
43. Serina
44. .beta.-hydroxyalanine
45. B-hydroxy-l-alanine
46. Einecs 200-274-3
47. Nsc 118365
48. Rac-serine
49. Racemic Serine
50. 2-amino-3-hydroxypropanoate
51. Unii-452vly9402
52. 3h-l-serine
53. L-serine;
54. H-ser
55. (s)-a-amino-b-hydroxypropionic Acid
56. Serine (usp)
57. 3-hydroxy-l-alanine
58. L-serine,(s)
59. Tocris-0226
60. Tocris-0227
61. L-serine (jp17)
62. Serine [vandf]
63. Serine [hsdb]
64. Serine [inci]
65. Serine [usan]
66. L-alanine, 3-hydroxy-
67. Serine [inn]
68. Serine [who-dd]
69. Lopac-s-4250
70. Serine [ii]
71. Serine [mi]
72. L-serine [fcc]
73. L-serine [jan]
74. Serine [mart.]
75. (l)-serine
76. Bmse000048
77. Bmse000809
78. Bmse000867
79. Bmse000885
80. Epitope Id:150900
81. Ec 200-274-3
82. Schembl1775
83. L-serine [usp-rs]
84. Gtpl726
85. 4-04-00-03118 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
86. Chembl11298
87. Serine [ep Monograph]
88. L-3-hydroxy-2-aminopropionate
89. Serine [usp Monograph]
90. (s)-a-amino-b-hydroxypropionate
91. (s)-b-amino-3-hydroxypropionate
92. Dtxsid60883230
93. (s)-2-amino-3-hydroxypropanoate
94. Dtxsid301031857
95. Pharmakon1600-01301010
96. Zinc895034
97. L-serine - Cas 56-45-1
98. (s)-2-amino-3-hydroxy-propanoate
99. Act08366
100. Hy-n0650
101. L-2-amino-3-hydroxypropanoic Acid
102. L-serine, Vetec(tm), 98.5%
103. Str02557
104. (s)-beta-amino-3-hydroxypropionate
105. Fmoc-(2-aminomethylphenyl)aceticacid
106. L-2-amino-3-hydroxy-propanoic Acid
107. L-serine, >=99.0% (nt)
108. Bdbm50357212
109. Nsc760115
110. (s)-b-amino-3-hydroxypropionic Acid
111. Akos015854115
112. (s)-alpha-amino-beta-hydroxypropionate
113. Ac-1190
114. Ccg-266038
115. Cs-w020136
116. Db00133
117. Nsc-760115
118. (s)-beta-amino-3-hydroxypropionic Acid
119. L-serine, Tested According To Ph.eur.
120. (2s)-2-amino-3-hydroxypropanoic Acid.
121. Ncgc00015952-01
122. Ncgc00024507-01
123. Ncgc00024507-02
124. Bp-13282
125. L-serine, Bioultra, >=99.5% (nt)
126. Sy002847
127. 2-amino-3-hydroxypropanoic Acid-, (s)-
128. Db-029983
129. Propanoic Acid, 2-amino-3-hydroxy-, (s)
130. Am20100375
131. S0035
132. S9353
133. L-serine, Reagentplus(r), >=99% (hplc)
134. L-serine, Vetec(tm) Reagent Grade, >=99%
135. A20660
136. C00065
137. D00016
138. L-serine, Cell Culture Reagent (h-l-ser-oh)
139. 064s224
140. Q183290
141. Sr-01000597708
142. .alpha.-amino-.beta.-hydroxypropionic Acid-, (s)-
143. Sr-01000597708-1
144. L-serine, Certified Reference Material, Tracecert(r)
145. F1905-7047
146. Serine, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
147. Z1270387256
148. 3ab40d3a-043a-488f-8361-d1bf309f842c
149. L-serine, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
150. (s)-2-amino-3-hydroxypropanoicacid;2-amion-3-hydroxypropionicacid
151. L-serine, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
152. L-serine, From Non-animal Source, Meets Ep, Usp Testing Specifications, Suitable For Cell Culture, 98.5-101.0%
153. L-serine, Pharmagrade, Ajinomoto, Ep, Usp, Jp, Manufactured Under Appropriate Controls For Use In Pharma Or Biopharmaceutical Production, Suitable For Cell Culture
154. L-serine, Pharmagrade, Ajinomoto, Ep, Usp, Manufactured Under Appropriate Gmp Controls For Pharma Or Biopharmaceutical Production, Suitable For Cell Culture
| Molecular Weight | 105.09 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C3H7NO3 |
| XLogP3 | -3.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 105.042593085 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 105.042593085 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 83.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 7 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 72.6 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Used as a natural moisturizing agent in some cosmetics and skin care products.
Serine is classified as a nutritionally non-essential amino acid. Serine is critical for the production of the body's proteins, enzymes and muscle tissue. Serine is needed for the proper metabolism of fats and fatty acids. It also helps in the production of antibodies. Serine is used as a natural moisturizing agent in some cosmetics and skin care products. The main source of essential amino acids is from the diet, non-essential amino acids are normally synthesize by humans and other mammals from common intermediates.
IN PT AGE 2-9 YR, SERINE PRESENT IN ACID MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDES. EXCESSIVE ACCUMULATION & EXCRETION IN URINE OF MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDES MAY BE RELATED TO ABNORMAL BONDING BETWEEN MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDES & PROTEIN.
RENNERT OM, DEKABAN AS; AMINO ACID METAB IN PT WITH HURLER'S SYNDROME; METAB, CLIN EXP; 15(5) 429 (1966)
IN PT AGE 2-9 YR, URINARY SERINE EXCRETION INCR FROM 0.059-0.162 UMOL/24 HR & PLASMA SERINE LEVELS INCR FROM 0.102-0.158 UMOL/ML.
RENNERT OM, DEKABAN AS; AMINO ACID METAB IN PT WITH HURLER'S SYNDROME; METAB, CLIN EXP; 15(5) 429 (1966)
IN PT AGE 2-9 YR, SERINE IS PROBABLY NOT ESTERIFIED THROUGH ITS BETA-HYDROXYL GROUP TO ACID MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDES BUT IS LINKED BY CARBOXYL GROUP.
RENNERT OM, DEKABAN AS; AMINO ACID METAB IN PT WITH HURLER'S SYNDROME; METAB, CLIN EXP; 15(5) 429 (1966)
DETERMINATION OF SERINE LEVELS IN 13 REGIONS OF THE RAT CEREBRAL CORTEX FAILED TO SHOW ANY MARKED DIFFERENCES IN THE AMINO ACID CONTENTS OF CORTEX AREAS OF DIVERSE FUNCTIONS.
ELEKES I ET AL; DRUGS, BIOCHEM METAB, SCI MATER PAP COLLOQ 37 (1981)
L-Serine plays a role in cell growth and development (cellular proliferation). The conversion of L-serine to glycine by serine hydroxymethyltransferase results in the formation of the one-carbon units necessary for the synthesis of the purine bases, adenine and guanine. These bases when linked to the phosphate ester of pentose sugars are essential components of DNA and RNA and the end products of energy producing metabolic pathways, ATP and GTP. In addition, L-serine conversion to glycine via this same enzyme provides the one-carbon units necessary for production of the pyrimidine nucleotide, deoxythymidine monophosphate, also an essential component of DNA.
