





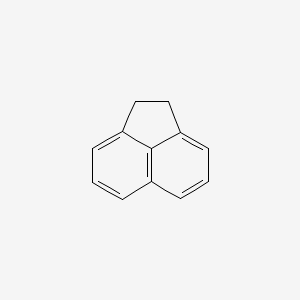

1. 83-32-9
2. 1,2-dihydroacenaphthylene
3. 1,8-ethylenenaphthalene
4. Peri-ethylenenaphthalene
5. Naphthyleneethylene
6. Acenaphthylene, 1,2-dihydro-
7. Ethylenenaphthalene
8. 1,8-dihydroacenaphthalene
9. V8ut1gac5y
10. Chebi:22154
11. Nsc-7657
12. Mfcd00003807
13. Dsstox_cid_1774
14. Dsstox_rid_76319
15. Dsstox_gsid_21774
16. Cas-83-32-9
17. Ccris 5951
18. Hsdb 2659
19. Nsc 7657
20. Einecs 201-469-6
21. Unii-v8ut1gac5y
22. 1,2-dihydro Acenaphthylene
23. Ai3-00128
24. Acenaphthene, 97%
25. Acenaphthene, 99%
26. Acenaphthene,
27. Acenaphthene [mi]
28. Acenaphthene [hsdb]
29. Acenaphthene [iarc]
30. Ec 201-469-6
31. Naphthalene, 1,8-ethylene-
32. Bidd:gt0787
33. Chembl1797271
34. Dtxsid3021774
35. Acenaphthene, Analytical Standard
36. Nsc7657
37. Zinc1235986
38. Tox21_202400
39. Tox21_300013
40. Stl483068
41. Akos000119983
42. Fs-4341
43. Acenaphthene 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
44. Ncgc00163966-01
45. Ncgc00163966-02
46. Ncgc00163966-03
47. Ncgc00163966-04
48. Ncgc00254079-01
49. Ncgc00259949-01
50. Ac-19767
51. Acenaphthene 10 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
52. Acenaphthene 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
53. Db-056708
54. A0003
55. A0135
56. Acenaphthene 1000 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
57. Ft-0621716
58. C19312
59. D97698
60. Acenaphthene Zone Refined (number Of Passes:30)
61. Q415103
62. W-104147
63. Z56926550
64. 73bcd470-1e93-4e76-bf03-e06fb8fe00ea
65. Acenaphthene, Certified Reference Material, Tracecert(r)
66. F1908-0103
67. Acenaphthene Solution, 100 Mug/ml In Cyclohexane, Analytical Standard
68. Acenaphthene Solution, Certified Reference Material, 200 Mug/ml In Methanol
| Molecular Weight | 154.21 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H10 |
| XLogP3 | 3.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 0 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 154.078250319 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 154.078250319 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 0 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 12 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 155 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
The waxy surface of some plant leaves and fruits can concentrate polyaromatic hydrocarbons through surface adsorption. /Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons/
USEPA; Ambient Water Quality Criteria Doc: Polynuclear Aromatic Hydrocarbons p.C-11 (1980)
The filamentous fungus Cunninghamella elegans ATCC 36112 metabolized within 72 hr of incubation approximately 64% of the [1,8-(14)C]acenaphthene added. The radioactive metabolites were extracted with ethyl acetate and separated by thin-layer chromatography and reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Seven metabolites were identified by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance, UV, and mass spectral techniques as 6-hydroxyacenaphthenone (24.8%), 1,2-acenaphthenedione (19.9%), trans-1,2-dihydroxyacenaphthene (10.3%), 1,5-dihydroxyacenaphthene (2.7%), 1-acenaphthenol (2.4%), 1-acenaphthenone (2.1%), and cis-1,2-dihydroxyacenaphthene (1.8%). Parallel experiments with rat liver microsomes indicated that the major metabolite formed from acenaphthene by rat liver microsomes was 1-acenaphthenone. The fungal metabolism of acenaphthene was similar to bacterial and mammalian metabolism, since the primary site of enzymatic attack was on the two carbons of the five-member ring.
PMID:1482186 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC183157 Pothuluri JV et al; Appl Environ Microbiol 58 (11): 3654-9 (1992)
Metabolized to naphthalene-1,8-dicarboxylic acid in rats. /From table/
Goodwin, B.L. Handbook of Intermediary Metabolism of Aromatic Compounds. New York: Wiley, 1976., p. A-1
... Possibility of limited metabolism of acenaphthene to naphthalic acid and naphthalic anhydride.
Acenaphthene; pp 46-7 in Priority Toxic Pollutants; Sittig M, ED (1980)
A Beijerinckia species and a mutant strain, Beijerinckia species strain B8/36, were shown to oxidize the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons acenaphthene and acenaphthylene. Both organisms oxidized acenaphthene to the same spectrum of metabolites, which included 1-acenaphthenol, 1-acenaphtheneone, 1,2-acenaphthenediol, acenaphthenequinone, and a compound that was tentatively identified as 1,2-dihydroxyacenaphthylene. In contrast, acenaphthylene was oxidized to acenaphthenequinone and the compound tentatively identified as 1,2-dihydroxyacenaphthylene was also formed when the organism was incubated with synthetic cis-1,2-acenaphthenediol. A metabolite identified as cis-1,2-acenaphthenediol was formed from acenaphthylene by the mutant Beijerinckia species strain B8/36. Cell extracts prepared from the wild-type Beijerinckia strain contain a constitutive pyridine nucleotide-dependent dehydrogenase which can oxidize 1-acenaphthenol and 9-fluorenol. The results indicate that although acenaphthene and acenaphthylene are both oxidized to acenaphthenequinone, the pathways leading to the formation of this end product are different.
PMID:6089663 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC240288 Schocken MJ, Gibson DT; Appl Environ Microbiol 48 (1): 10-16 (1984)
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for ACENAPHTHENE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
The half-life of acenaphthene in /the bluegill fish/ is less than 1 day.
USEPA; Ambient Water Quality Criteria Doc: Acenaphthene (Draft) p.B-2 (1980)
